




How to Convert Newtons to Dynes with Examples
The relation between newton and dyne is fundamental in understanding the units of force in different measurement systems, particularly the SI and CGS systems. This topic is essential for clear concept building in classical mechanics and for solving JEE Main physics problems involving unit conversions and force calculations.
Defining Force in Different Measurement Systems
Force is a physical quantity that causes a change in the state of motion of a body. In physics, force is mathematically defined as the product of mass and acceleration, expressed as $F = m \times a$.
The SI (International System of Units) uses newton (N) as the unit of force, while the CGS (centimetre-gram-second) system uses dyne as the unit of force. Both units represent the same physical quantity but in different magnitudes and base units.

In SI units, mass is measured in kilograms and acceleration in metres per second squared. In CGS units, mass is measured in grams and acceleration in centimetres per second squared. The relation between these units is important for converting results between the two systems.
Definition of Newton and Dyne
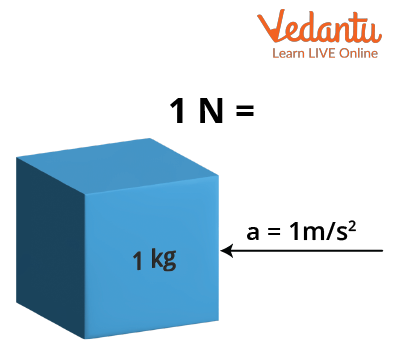
A newton is defined as the force needed to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one metre per second squared. Symbolically, $1~\text{N} = 1~\text{kg} \cdot 1\,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text{s}^2}$.
A dyne is the force required to accelerate a mass of one gram by one centimetre per second squared. It is written as $1~\text{dyne} = 1~\text{g} \cdot 1\,\dfrac{\text{cm}}{\text{s}^2}$.
Both newton and dyne are derived units of force, and their use depends on the measurement system chosen for a particular problem or analysis.
Derivation of the Relation Between Newton and Dyne
To establish the relation between newton and dyne, express one newton in terms of base CGS units. In the SI system, $1~\text{N} = 1~\text{kg} \cdot 1\,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text{s}^2}$.
Convert kilograms to grams and metres to centimetres as follows: $1~\text{kg} = 1000~\text{g}$ and $1~\text{m} = 100~\text{cm}$.
Thus, $1~\text{N} = 1000~\text{g} \times 100~\dfrac{\text{cm}}{\text{s}^2} = 100,000~\dfrac{\text{g} \cdot \text{cm}}{\text{s}^2}$.
Since $1~\text{dyne} = 1~\dfrac{\text{g} \cdot \text{cm}}{\text{s}^2}$, it follows that $1~\text{N} = 10^5~\text{dyne}$.
| SI Unit | CGS Unit |
|---|---|
| 1 newton (N) | $10^5$ dyne |
| 1 dyne | $10^{-5}$ newton (N) |
Therefore, one newton equals one hundred thousand dyne, which allows conversion of force values between SI and CGS units. For more details on the SI unit of force, refer to Unit of Force 404.
Dimensional Analysis and Its Importance
The dimensional formula for force in any system is $[\text{M}^1 \text{L}^1 \text{T}^{-2}]$. This agrees for both newton and dyne, confirming that they represent the same physical dimension, only differing by magnitude and system of units.
Dimensional analysis helps in converting one unit to another and checking the correctness of physical equations. The relation established above clearly demonstrates the application of dimensional consistency.
In competitive exams like JEE Main, understanding unit conversions and dimensional analysis is important for solving various numerical questions accurately. Revision of related topics, such as Acceleration Formula, is recommended for a complete understanding.
Solved Example: Converting Newton to Dyne
Example: Calculate the force in dyne if a constant force of $7~\text{N}$ is acting on a body.
Given, $1~\text{N} = 10^5~\text{dyne}$.
Therefore, $7~\text{N} = 7 \times 10^5~\text{dyne} = 700,000~\text{dyne}$.
Key Differences Between Newton and Dyne
Newton and dyne differ in their system of use, base units, and magnitude. Newton is used in SI, based on kilograms and metres, while dyne is used in CGS, based on grams and centimetres.
- 1 newton is used in scientific and engineering contexts
- 1 dyne appears mainly in older scientific literature
- Newton is a much larger unit than dyne
Physical situations demanding higher precision at small force values may use dyne, but most modern scientific applications employ newton.
The relation between newton and dyne can help convert results when different data sources use separate unit systems. For example, topics like Kinematics may involve units of force in both systems.
Applications and Significance in Physics
Understanding the relation between newton and dyne is critical for correct unit handling in physics problems. This knowledge is widely applicable in Electric Field Intensity, gravitational calculations, and pressure measurement.
Accurate unit conversion ensures consistency in calculations and proper interpretation of physical results, especially when working with formulas expressed in different metric systems.
Summary Table: Relation Between Newton and Dyne
| Unit | Definition |
|---|---|
| Newton (N) | $1~\text{N} = 1~\text{kg} \cdot 1\,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text{s}^2}$ |
| Dyne | $1~\text{dyne} = 1~\text{g} \cdot 1\,\dfrac{\text{cm}}{\text{s}^2}$ |
| Relation | $1~\text{N} = 10^5~\text{dyne}$ |
A clear understanding of the relation between newton and dyne allows for accurate and efficient calculations in both SI and CGS systems, which is essential for students preparing for examinations such as the JEE Main and advanced studies in physics. For further reading on comparing physical quantities, see Distance vs Displacement.
FAQs on Understanding the Relationship Between Newton and Dyne
1. What is the relation between newton and dyne?
Newton and dyne are both units of force, with the relation being 1 newton = 105 dyne.
The conversion can be summarized as:
- 1 newton (N) = 100,000 dyne
- 1 dyne = 0.00001 newton
2. How do you convert newton to dyne?
To convert newton (N) to dyne, multiply by 100,000.
Steps to convert:
- Multiply the value in newton by 105 (or 100,000).
- For example, 3 N = 3 × 100,000 = 300,000 dyne.
3. What is the SI unit of force?
The SI unit of force is the newton (N).
Key points to remember:
- Newton is the standard scientific unit for measuring force.
- Defined as the force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass by 1 m/s2.
4. Define 1 newton and 1 dyne.
1 newton is the force needed to accelerate a mass of 1 kilogram by 1 meter per second squared.
1 dyne is the force required to accelerate a mass of 1 gram by 1 centimeter per second squared.
Summary:
- 1 N = 1 kg × 1 m/s2
- 1 dyne = 1 g × 1 cm/s2
5. Why do we need to convert between newton and dyne?
Converting between newton and dyne allows us to solve physics problems in both SI and CGS systems.
Reasons for conversion:
- Different textbooks and problems use different units (SI or CGS).
- It helps in standardizing answers and understanding scientific concepts better.
- It is frequently required in CBSE numerical questions and board exams.
6. Is newton bigger than dyne?
Yes, newton is a much larger unit than dyne.
Quick facts:
- 1 newton = 100,000 dyne
- This means newton is 105 times bigger than dyne.
7. What is the formula to convert dyne into newton?
To convert dyne to newton, divide the number of dyne by 100,000.
Formula:
- Value in newton = Value in dyne ÷ 100,000
- Example: 250,000 dyne = 250,000 ÷ 100,000 = 2.5 newton
8. Which system uses newton and which uses dyne?
Newton is used in the SI (International System of Units) while dyne is used in the CGS (Centimeter-Gram-Second) system.
Comparison:
- Newton: SI system (standard used worldwide)
- Dyne: CGS system (older scientific works, some exams)
9. How are newton and dyne derived from their basic units?
Newton and dyne are derived from the basic units of mass, length, and time in their respective systems.
Derivations:
- 1 newton (N) = 1 kilogram × 1 meter/second2
- 1 dyne = 1 gram × 1 centimeter/second2
10. List the differences between newton and dyne with examples.
Newton and dyne differ in magnitude, system, and usage.
Main differences:
- Unit system: Newton (SI), Dyne (CGS)
- 1 N = 105 dyne
- Used in: Newton (global, modern texts), Dyne (older CGS-based texts)
- Example:
- 1 N = 1 kg × 1 m/s2
- 1 dyne = 1 g × 1 cm/s2

































