
Find the moment of inertia through the face diagonal of a cube. Edge length of a cube is $a$ units.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Moment of inertia of a body is defined as the tendency of the body to resist change in angular acceleration.
It is calculated for individual axis of rotations and depends on shape of the body because shape affects distribution of mass.
General formula: $I = \sum {} {m_i}{({r_i})^2}$
Where $I = $ Moment of inertia around a particular axis
${m_{i}}$ = mass of ${i_{th}}$ particle
${r_{i}}$ = distance of ${i_{th}}$ particle from axis of rotation
Moment of inertia of triangle= ${I_{tri}} = \dfrac{1}{6}M{r^2}$ --equation( $1$ )
Complete step by step solution:
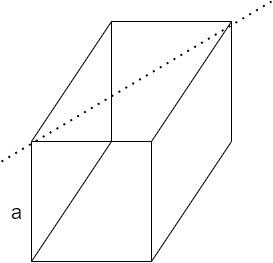
An overhead view of the cube is given below. When calculated using Pythagoras Theorem , the diagonal of a cube of edge length $a$ turns out to be $\sqrt 2 a$ . The distance between axis of rotation and a corner of the cube will be designated as $r = \sqrt 2 \dfrac{a}{2} = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ --equation( $2$)
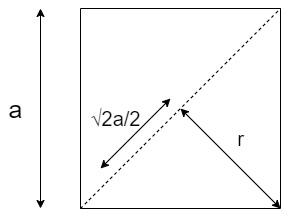
As per the figure given below, the moment of inertia of a face of the square plate face will be twice that of the triangle.
$\therefore I = 2 \times ({\text{moment of inertia of triangle)}}$--equation( $3$)
From equation $1$ , moment of inertia of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{6}M{r^2}$
$\therefore $ moment of inertia of square plate = $\dfrac{1}{6}\dfrac{M}{2}{r^2}$ = $\dfrac{1}{6}\dfrac{M}{2}{\left( {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2}$ = $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{24}}$--equation($4$)
Notice that $M$ has been replaced by $\dfrac{M}{2}$ . This is because the mass of the triangle is half that of square.
Put equation $(4)$ in $(3)$ .
$\therefore I = 2 \times \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{24}} = \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$ --equation (5)
Equation $(5)$ represents moment of inertia of square plate along the diagonal, to calculate the moment of inertia of the cube, integrate it keeping in mind that the cube is made up of square plates each of mass dm from height $0$ to $a$ .
$\therefore $ moment of inertia of cube for the diagonal passing through face is
$\Rightarrow \int\limits_0^I {dI = \int_0^M {\dfrac{{{a^2}dm}}{{12}}} } $
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$
Moment of inertia of a cube for a diagonal going through a face is $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$.
Note: Moment of inertia is different for each axis of rotation.
If the moment of inertia for one of the axes was given, we could have used the theorem of perpendicular axis or the theorem of parallel axis too.
In this case it was convenient to take the mass of the triangular portion as half that of square because of uniform density only.
It is calculated for individual axis of rotations and depends on shape of the body because shape affects distribution of mass.
General formula: $I = \sum {} {m_i}{({r_i})^2}$
Where $I = $ Moment of inertia around a particular axis
${m_{i}}$ = mass of ${i_{th}}$ particle
${r_{i}}$ = distance of ${i_{th}}$ particle from axis of rotation
Moment of inertia of triangle= ${I_{tri}} = \dfrac{1}{6}M{r^2}$ --equation( $1$ )
Complete step by step solution:
An overhead view of the cube is given below. When calculated using Pythagoras Theorem , the diagonal of a cube of edge length $a$ turns out to be $\sqrt 2 a$ . The distance between axis of rotation and a corner of the cube will be designated as $r = \sqrt 2 \dfrac{a}{2} = \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }}$ --equation( $2$)
As per the figure given below, the moment of inertia of a face of the square plate face will be twice that of the triangle.

$\therefore I = 2 \times ({\text{moment of inertia of triangle)}}$--equation( $3$)
From equation $1$ , moment of inertia of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{6}M{r^2}$
$\therefore $ moment of inertia of square plate = $\dfrac{1}{6}\dfrac{M}{2}{r^2}$ = $\dfrac{1}{6}\dfrac{M}{2}{\left( {\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)^2}$ = $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{24}}$--equation($4$)
Notice that $M$ has been replaced by $\dfrac{M}{2}$ . This is because the mass of the triangle is half that of square.
Put equation $(4)$ in $(3)$ .
$\therefore I = 2 \times \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{24}} = \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$ --equation (5)
Equation $(5)$ represents moment of inertia of square plate along the diagonal, to calculate the moment of inertia of the cube, integrate it keeping in mind that the cube is made up of square plates each of mass dm from height $0$ to $a$ .
$\therefore $ moment of inertia of cube for the diagonal passing through face is
$\Rightarrow \int\limits_0^I {dI = \int_0^M {\dfrac{{{a^2}dm}}{{12}}} } $
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$
Moment of inertia of a cube for a diagonal going through a face is $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$.
Note: Moment of inertia is different for each axis of rotation.
If the moment of inertia for one of the axes was given, we could have used the theorem of perpendicular axis or the theorem of parallel axis too.
In this case it was convenient to take the mass of the triangular portion as half that of square because of uniform density only.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




