
Explain the construction and working of a Geiger-Muller counter.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint A Geiger-Muller counter is a device used for the detection and measurement of ionizing radiation. It is mainly used for applications like the nuclear industry, radiological protection, radiation dosimetry, and experimental physics. It is one of the best devices for the detection of radiation, in the world.
Step by step solution
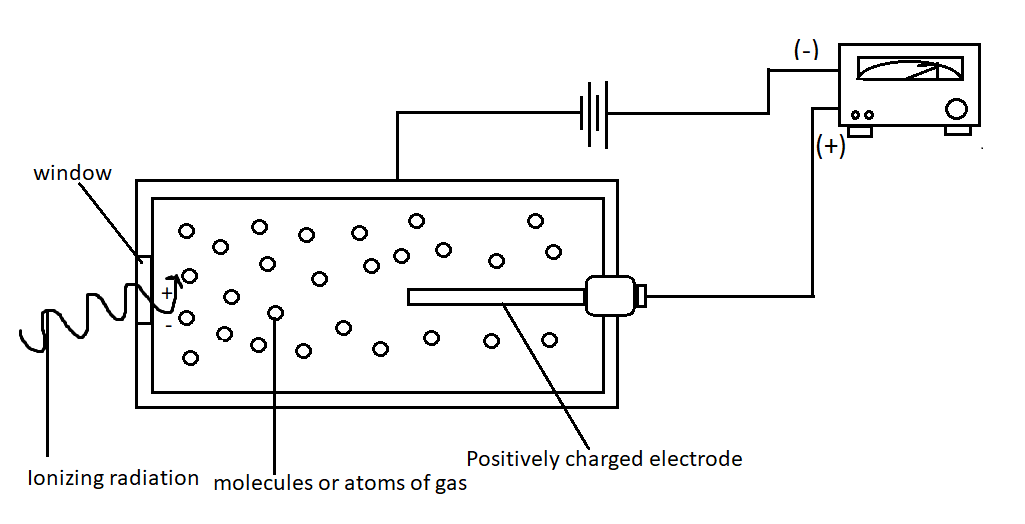
Construction:
The GM counter consists of a hollow metallic chamber as shown in the figure that acts as a cathode.
A thin wire anode is also placed along its axis.
The chamber has a sealed window, through which the radiation enters the chamber.
The chamber is filled with an inert gas at low pressure.
There is a counter connected to this system to measure the radiation.
Working
The chamber is filled with an inert gas (helium, neon, or argon) at low pressure. A high voltage is applied to this chamber. The metallic chamber will conduct electricity. When radiation enters the chamber through the window, the photons in the radiation will ionize the inert gas inside the chamber. This will make the gas conductive. The electrons produced due to ionization are accelerated due to the potential that we applied and these electrons cause even more ionization. The ionized electrons travel towards the anode. The anode is connected to a counter. The counter counts the electrons reaching the anode. This is how we measure radiation.
NoteThe major limitation of the Geiger Muller counter is that it does not have the ability to differentiate different types of radiations. Another major limitation is that it cannot measure high radiation rates. This is because, after each ionization, there will be a 'dead time’. This is an insensitive time during which further incident radiation does not count.
Step by step solution

Construction:
The GM counter consists of a hollow metallic chamber as shown in the figure that acts as a cathode.
A thin wire anode is also placed along its axis.
The chamber has a sealed window, through which the radiation enters the chamber.
The chamber is filled with an inert gas at low pressure.
There is a counter connected to this system to measure the radiation.
Working
The chamber is filled with an inert gas (helium, neon, or argon) at low pressure. A high voltage is applied to this chamber. The metallic chamber will conduct electricity. When radiation enters the chamber through the window, the photons in the radiation will ionize the inert gas inside the chamber. This will make the gas conductive. The electrons produced due to ionization are accelerated due to the potential that we applied and these electrons cause even more ionization. The ionized electrons travel towards the anode. The anode is connected to a counter. The counter counts the electrons reaching the anode. This is how we measure radiation.
NoteThe major limitation of the Geiger Muller counter is that it does not have the ability to differentiate different types of radiations. Another major limitation is that it cannot measure high radiation rates. This is because, after each ionization, there will be a 'dead time’. This is an insensitive time during which further incident radiation does not count.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




