
Compare the magnitude of centripetal force and centrifugal force.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint According to the third law of motion of Newton, an equal and opposite reaction occurs for any action. The two forces in magnitude and opposite in direction are equivalent. The centrifugal force does not act in motion on the body, the centripetal force is the only force that acts in motion on the body.
Useful formula
Centripetal force,
$F = m{a_c} = m{v^2}r $
Where,
$F $ is the Centripetal force.
\[{a_c}\;\] is the Centripetal acceleration.
$m $ is the mass of the object.
$v $ is the speed or velocity of the object.
$r $ is the radius.
Centrifugal force,
${F_c} = - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $
Where,
\[{F_c}\;\]is the Centrifugal force
$m $ is the mass of the object
$v $ is the velocity or speed of the object.
$r $ is the radius.
Complete step by step answer
Given by,
Compare the magnitude of centripetal force and centrifugal force.
As per the concept of the centripetal force,
Centripetal force is the force part that acts in curvilinear motion on an object that is oriented towards the rotation axis or curvature centre.
The Centripetal Force Formula is given squared, divided by the radius, as the product of mass and tangential velocity. That means that the centripetal force can quadruple when the tangential velocity is doubled.
$F = m{a_c} = m{v^2}r $
Centrifugal force:
Centrifugal force is a force that emerges from the inertia of the body and tends to work on a body that moves in a circular direction away from the core around which the body moves.
The formula of the centrifugal force is given as the negative product of square mass and tangential velocity, divided by radius. That means that the centripetal force would be quadrupled upon doubling the tangential velocity.
${F_c} = - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $
Here,
Comparison between the centripetal force and centrifugal force:
Centripetal force can be defined as the force variable acting in curvilinear motion on a body that is directed towards the curvature center or rotation axis, while centrifugal force is defined as the apparent force equal to and opposite to the centripetal force, pushing a rotating body away from the center.
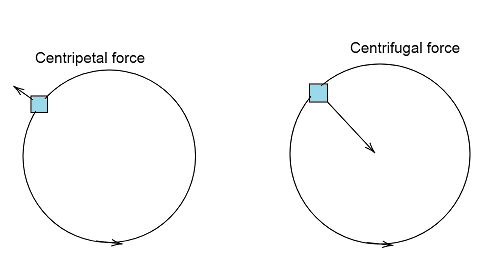
Hence,
Centrifugal force is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the centripetal force.
Note Thus, the centripetal force transmitted by the string pulls in on the mass to hold it in its circular direction while twirling a mass on a string, while the centrifugal force transmitted by the string pulls outward at the middle of the path at its point of connection. When released, the centrifugal force is often wrongly thought to cause a body to fly out of its circular direction.
Useful formula
Centripetal force,
$F = m{a_c} = m{v^2}r $
Where,
$F $ is the Centripetal force.
\[{a_c}\;\] is the Centripetal acceleration.
$m $ is the mass of the object.
$v $ is the speed or velocity of the object.
$r $ is the radius.
Centrifugal force,
${F_c} = - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $
Where,
\[{F_c}\;\]is the Centrifugal force
$m $ is the mass of the object
$v $ is the velocity or speed of the object.
$r $ is the radius.
Complete step by step answer
Given by,
Compare the magnitude of centripetal force and centrifugal force.
As per the concept of the centripetal force,
Centripetal force is the force part that acts in curvilinear motion on an object that is oriented towards the rotation axis or curvature centre.
The Centripetal Force Formula is given squared, divided by the radius, as the product of mass and tangential velocity. That means that the centripetal force can quadruple when the tangential velocity is doubled.
$F = m{a_c} = m{v^2}r $
Centrifugal force:
Centrifugal force is a force that emerges from the inertia of the body and tends to work on a body that moves in a circular direction away from the core around which the body moves.
The formula of the centrifugal force is given as the negative product of square mass and tangential velocity, divided by radius. That means that the centripetal force would be quadrupled upon doubling the tangential velocity.
${F_c} = - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} $
Here,
Comparison between the centripetal force and centrifugal force:
Centripetal force can be defined as the force variable acting in curvilinear motion on a body that is directed towards the curvature center or rotation axis, while centrifugal force is defined as the apparent force equal to and opposite to the centripetal force, pushing a rotating body away from the center.

Hence,
Centrifugal force is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the centripetal force.
Note Thus, the centripetal force transmitted by the string pulls in on the mass to hold it in its circular direction while twirling a mass on a string, while the centrifugal force transmitted by the string pulls outward at the middle of the path at its point of connection. When released, the centrifugal force is often wrongly thought to cause a body to fly out of its circular direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




