




Explore the Characteristics and Common Uses of Metals
Metals are substances that develop naturally under the earth's surface. Most metals are bright or glossy. Since they are inorganic, metals are composed of materials that have never been living. A metal is very strong and durable and therefore is used to make many things. These are used for making automobiles, satellites, cooking utensils, etc. Most metals are hard but some are not.

Metal to Steel Rods
Sodium and potassium are such metals that can be cut by a knife, whereas mercury is a liquid metal at room temperature. Iron is solid. Metals make up around 75 per cent of all chemical elements that are currently understood. Most metals are found in ores (materials that include minerals), although some, like copper, gold, platinum, and silver, are commonly discovered in the free state because they do not easily react with other elements.
How are Metals made?
Metals are naturally occurring chemical elements that are often hard, shiny, and effective heat and electricity conductors. Examples include items like iron, gold, silver, copper, zinc, nickel, etc. Sodium is a metal humans consume frequently; commonly, the soft, silvery-white metal sodium joins with chlorine to make sodium chloride, also known as table salt.
Interesting Facts about Metals
The following are interesting metal facts:
The Greek term "metallon," which means to mine, dig, or remove from the earth, is the source of the English word "metal."
Metals make over 75% of all the elements in the periodic table. Different groupings of metals, including basic metals, transition metals, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, rare earth metals, lanthanides, and actinides exist.
Except for mercury, which is a liquid at ambient temperature, all metals are solids.
Aluminium is the most prevalent metal in the crust of the Earth.
Even though the Earth's crust is rich in aluminium, iron is the most common element, which makes up a sizable portion of the planet's core.
Only seven metals, known as the Metals of Antiquity, existed before the Middle Ages. The ancient metals' approximate discovery dates are as follows:
Gold (6000 BC) (6000 BC),Copper (9000 BC), Silver (4000 BC)
The majority of metals are efficient heat and electrical conductors.
The majority of metals may be formed into thin sheets or are malleable.
List of Metals on the Periodic Table
The list of the metals on the periodic table is as under, in increasing order:
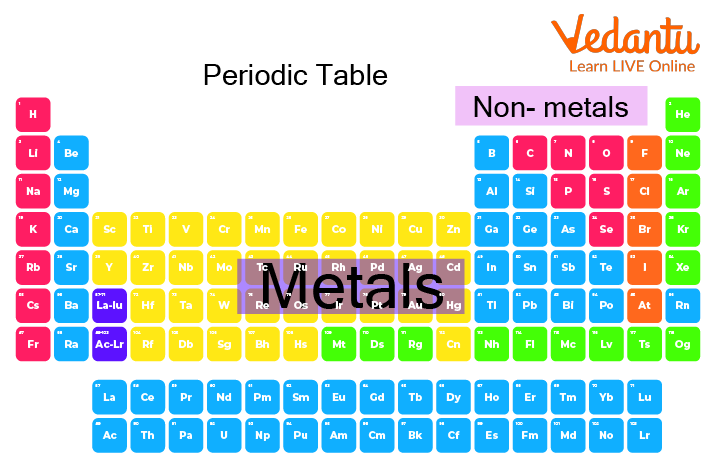
Periodic Table Showing Metal and Non-Metal
Summary
Metals are substances that develop naturally under the earth's surface. Most metals are bright or glossy. Metals are inorganic components of the earth's crust, where they are often found as metal ores and are linked to several other elements as well as each other.
Additionally, they exist naturally in dust from the atmosphere and in the rocks that have been washed by groundwater and surface water. As a result, they are present in many processes and operations, including weathering and erosion as the composition of the earth's crust is around 75% metals. The majority of metals are efficient heat and electricity conductors and can be formed into thin sheets or are malleable.
FAQs on What Are Metals? Definition, Properties & Key Facts
1. What is a metal according to the science curriculum?
A metal is a naturally occurring element that is typically solid, shiny, and an excellent conductor of heat and electricity. Chemically, metals are elements that readily lose electrons to form positive ions (cations). Common examples include iron, copper, gold, and aluminium.
2. What are the main physical properties that define metals?
Metals are primarily identified by a set of distinct physical properties. The most important ones are:
- Lustre: They have a shiny surface.
- Malleability: They can be beaten into thin sheets (like aluminium foil).
- Ductility: They can be drawn into thin wires (like copper wiring).
- Hardness: Most metals are hard solids at room temperature.
- Conductivity: They are good conductors of both heat and electricity.
- Sonority: They produce a ringing sound when struck.
3. How are metals fundamentally different from non-metals?
The primary difference lies in their physical and chemical properties. Metals are typically lustrous, malleable, and good conductors, and they tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions. In contrast, non-metals are generally dull, brittle, and poor conductors (insulators), and they tend to gain or share electrons. For example, iron is a typical metal, while oxygen is a typical non-metal.
4. Are all metals hard solids? Explain with examples.
No, this is a common misconception. While most metals are hard solids at room temperature, there are notable exceptions. Mercury (Hg) is a metal that exists as a liquid at room temperature. Furthermore, alkali metals like sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are so soft that they can be easily cut with a knife.
5. Where are metals located on the periodic table?
On the periodic table, metals occupy the majority of the space. They are found on the left side and in the center. This includes distinct groups such as the alkali metals (Group 1), alkaline earth metals (Group 2), and the large block of transition metals in the middle.
6. Why is a property like malleability so important for the use of metals?
Malleability, the ability to be hammered or pressed into thin sheets without breaking, is crucial for manufacturing. This property allows metals like aluminium and steel to be shaped into car body panels, beverage cans, and roofing sheets. Without malleability, it would be impossible to form these essential everyday items.
7. What happens at a chemical level that makes a substance a metal?
At the chemical level, an element is classified as a metal due to its atomic structure. Metal atoms have loosely held electrons in their outermost shell, which they tend to lose easily during chemical reactions. This process forms positive ions, or cations. This sea of delocalised electrons is also what allows metals to conduct electricity so effectively.
8. What key concepts about metals are covered in the CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus for 2025-26?
As per the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus for Class 8 Science, the chapter 'Materials: Metals and Non-Metals' focuses on understanding the distinction between metals and non-metals based on their physical properties (like lustre, hardness, malleability, ductility, conductivity) and key chemical properties (reactions with oxygen, water, acids, and bases). It also introduces the concept of the reactivity series and displacement reactions.









