




Essential Applications and Importance of Noble Metals in EVS
There are many elements in the last column of the periodic table. These elements placed in the last column are called noble gases due to their inertness or resistance to react with any non-noble element. Due to this property, the metals that show an inert nature or resistance to reaction with other elements are called noble metals. Let's learn more about noble metals and their uses in our lives.
What are Noble Metals?
Noble metals do not react with any “non-noble” elements. They also resist attacks from oxygen or heat, which means their chemical composition doesn’t change. Examples of noble metals are silver, platinum, gold, rhodium, palladium, iridium, osmium, and ruthenium. In simple words, these metals do not rust.
The quality of these metals makes them perfect for various applications. You can see their positions in the periodic table given below. The place of an element in a periodic table also determines the chemical properties of the elements.
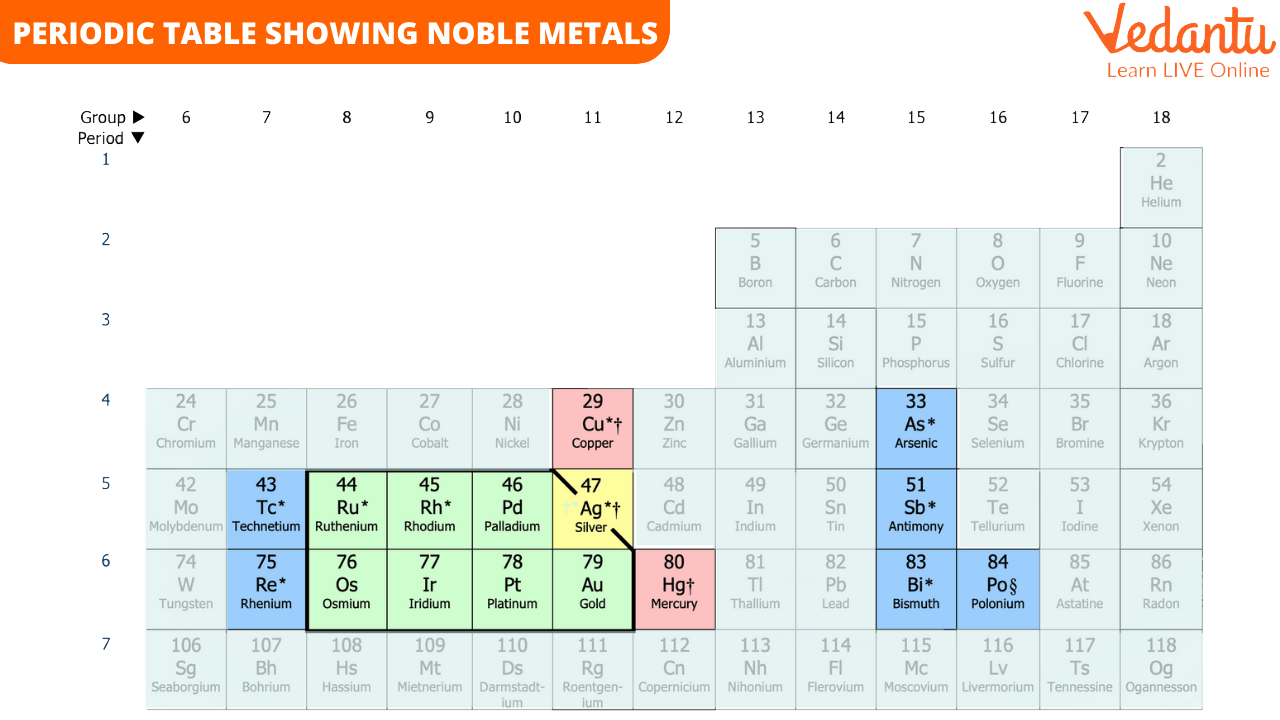
Periodic Table Showing Noble Metals
The Uses of Noble Metals
Let us discuss the uses of the most useful noble metals one by one
1. Gold
Gold is not only resistant to heat and oxidation from the air but is also malleable, which means that it can be beaten to make thin sheets. It is also ductile, which means it can be stretched to make thin wires. This is why gold is used in microelectronics, where it is used to make leads and wires. Gold is also anti-bacterial; therefore, it is one of the noble metals used in dentistry. However, the price of gold is too high. Commercial uses of this metal are too few, and it's mostly stored as wealth in the form of jewellery or coins.
2. Platinum
Due to the shine and colour of platinum, it is mostly used for making jewellery. Since the metal is durable and resistant to chemical reactions, it is used to make many types of laboratory equipment. It also acts as a catalyst that speeds up a chemical reaction but does not take part in it. Therefore, it is used in the industrial manufacturing of various chemicals like sulfuric acid. Although it is very costly and rare, it is used in places like missiles, jet engines, thermocouple wires, etc. You may be shocked to know that tiny amounts of platinum are present in objects like cigarette lighters, spark plugs, etc.
3. Platinum Family
The platinum family includes elements like ruthenium, osmium, rhodium, palladium, etc. These elements are found in Group VIII of the periodic table. These elements come under the "platinum family," as they behave similarly to platinum. Palladium is used in places like electronics and fuel cells. Ruthenium acts as a catalyst for many chemical reactions. Osmium is the highest known element and can be found in surgical implants and the tip of a fountain pen.
4. Silver
Silver is a malleable metal, but unlike gold, it tarnishes too fast. It is also less expensive than gold. It is one of the noble metals used in medicine in one of its forms; silver nitrate is used as eyedrops for newborn babies to prevent any infections. It's also used for silver plating.
5. Rhenium
Another noble metal used in medicine is rhenium. Rhenium is the last naturally occurring element that has been discovered. It is used to treat liver cancer. Apart from that, it is mixed with nickel so that it can be used in jet engines.
Conclusion
Isn’t it fascinating that such noble metals play an essential role in many processes and are present somewhere in some part of our daily lives? So today, you have learnt everything about noble metals, their types, and their uses. You have learnt that noble metals are the elements that show properties like noble gases, which are resistant to reacting easily. Examples of noble gases are gold, silver, platinum, etc. Noble metals are used in a variety of industries like medicine, dentistry, surgical implants, electroplating, etc.
FAQs on Uses of Noble Metals in Everyday Life
1. What are noble metals and which elements are considered part of this group?
Noble metals are a group of metals that are highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation in moist air. Unlike most base metals, they do not tarnish or rust easily. This chemical inertness is their defining characteristic. The most common examples of noble metals include gold (Au), silver (Ag), platinum (Pt), and other platinum-group metals like palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru), iridium (Ir), and osmium (Os).
2. What are five important uses of noble metals across different industries?
Noble metals are valued for their unique properties and are used in various fields. Here are five key applications:
- Jewellery and Ornaments: Gold, silver, and platinum are widely used for making jewellery due to their lustre, rarity, and resistance to tarnish.
- Electronics: Gold is an excellent electrical conductor that doesn't corrode, making it ideal for coating critical components like connectors and switch contacts in computers and smartphones.
- Automotive Industry: Platinum, rhodium, and palladium are essential components in catalytic converters, which convert toxic pollutants from engine exhaust into less harmful substances.
- Medicine and Dentistry: Due to their biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion, gold alloys are used for dental fillings and crowns. Platinum is used in surgical tools and implants, and silver has antimicrobial properties.
- Chemical Industry: Platinum acts as a crucial catalyst to speed up chemical reactions, such as in the large-scale production of nitric acid and sulfuric acid.
3. Why are the specific properties of gold and platinum essential for their use in jewellery and electronics?
The uses of gold and platinum are directly linked to their distinct properties. For jewellery, their value comes from being lustrous and highly resistant to corrosion. This means they won't tarnish, rust, or react with human skin, ensuring they remain beautiful and durable over time. For electronics, gold's properties of being an excellent electrical conductor and extremely malleable and ductile are critical. It can be drawn into microscopic wires and plated in thin, reliable layers on electrical contacts, ensuring a stable flow of current without risk of corrosion interrupting the circuit.
4. Which noble metals are commonly used in the medical field and what for?
Several noble metals play a vital role in medicine and healthcare because they are biocompatible, meaning they are non-toxic and do not react with the human body. Key examples include:
- Platinum: Used to make surgical instruments, pacemakers, and catheters. Certain platinum compounds are also key ingredients in anti-cancer drugs.
- Gold: Used in dentistry for crowns and fillings, and in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Silver: Known for its antimicrobial properties, silver compounds are used in wound dressings, surgical masks, and as silver nitrate drops to prevent eye infections in newborns.
- Osmium: In alloy form, it is used for surgical implants due to its extreme hardness and durability.
5. Is copper considered a noble metal? Explain why or why not.
No, copper is not considered a true noble metal, although it is more resistant to oxidation than elements like iron. True noble metals, such as gold and platinum, are exceptionally resistant to corrosion and acid attack. Copper, on the other hand, reacts with oxygen in the air over time to form a greenish layer of copper carbonate, also known as patina. This tendency to tarnish and react, even if slowly, disqualifies it from being classified as a noble metal in the strict chemical sense.
6. How does the 'nobility' of a metal relate to its resistance to corrosion?
A metal's 'nobility' is a direct measure of its low chemical reactivity. This lack of reactivity is precisely what makes it resistant to corrosion. Corrosion, like rust, is a chemical process where a metal reacts with its environment (typically oxygen and water) and breaks down. Noble metals have very stable electron configurations, which means they do not easily give up their electrons to react with other elements like oxygen. Therefore, a higher nobility means higher resistance to corrosion, allowing metals like gold and platinum to maintain their pure form indefinitely under normal conditions.









