




What are Resources?
Resources are anything that has utility and adds value to your life. Air, water, food, plants, animals, minerals, metals, and everything else that exists in nature and is useful to mankind is a 'resource'. The value of each such resource depends on its usefulness and other factors. For example, the metals gold, silver, copper, or bronze have economic value; That is, they can be replaced with money. However, mountains, rivers, seas, or forests are also resources that do not have economic value.
Anything and everything that is naturally available on the earth is a natural resource. We can further divide them into:
Renewable resources are almost all elements of nature that can renew themselves. For example, sunlight, wind, water, forest, and so on. Whereas non-renewable resources are limited in their quantity. Like fossil fuels and minerals. Although these resources take millions of years to form, they will be exhausted in our lifetime if we use them continuously.

Sources of Renewable Energy
What are Renewable Resources?
Renewable resources are those resources that can be naturally regenerated or renewed over time. Water, wind, solar energy, etc. are all renewable resources. An environment can effortlessly renew these resources. Some renewable resources have an essentially endless supply, such as solar power, wind power, and geothermal pressure. In contrast, other resources are considered renewable even if some time or effort is put into their renewal (eg, wood, oxygen, leather, and fish) can go with time.
Five Important Renewable Resources
Uses of Renewable Resources: There are many renewable energy sources and their uses. But the most common are:
1. Solar Energy (Energy from Sun)- According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, "the amount of energy that falls to Earth in one hour from the Sun is not used by everyone in the world in a year." Today, we use the sun's rays in many ways.
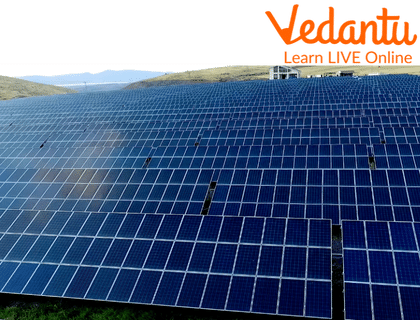
Solar Energy
2. Wind Energy - A windmill is usually attached to a generator that is powered by its rotation. Wind power is not only used to produce electricity but to perform repetitive mechanical tasks, such as pumping water from wells or grinding grain.

Wind Energy: Wind Turbines.
3. Hydro Energy - Hydropower is one of the most commercially developed energy sources. This renewable energy source generates electricity by using a dam or barrier to control the flow of water.
4. Geothermal Energy - By harnessing the natural heat beneath the Earth's surface, geothermal energy can be used directly in homes or to generate electricity.
5. Tidal Energy - It is another form of hydroelectricity that uses tidal currents to drive turbine generators.
Why is Renewable Energy Important for Sustainable Development?
Sustainable development means fulfilling the needs of the present without compromising the needs of future generations.
Renewable energy sources play an important role in achieving sustainable energy with low emissions. It is already recognised that renewable energy technologies can substantially cover electricity demand and reduce emissions. In recent years, the country has developed a sustainable route for its energy supply.
Uses of Alternative Sources of Energy
Bio Energy: We generate bioenergy from organic matter known as biomass or biofuel. Some examples would be wood and the byproducts of a recently living animal or plant. Ethanol is an example of a biofuel that many people are familiar with.
Nuclear Power: Nuclear energy is created through heat through the fission process of atoms. The initial fission process produces energy and triggers a chain reaction that repeats the process and produces more energy. In nuclear power plants, the heat generated by fission produces steam. The steam then spins a turbine, which produces electricity.
Wave Energy: Wave energy is an alternative energy source from waves travelling across the water. Wave energy uses power generators placed on the surface of the ocean. Wave energy is eco-friendly, renewable, and harmless to the environment.
What Will Happen If We Keep Using Non-renewable Resources?
Most of the world relies on non-renewable resources such as coal and oil that are used for domestic and industrial purposes. If we keep using them recklessly, there will be a time when no more resources will be left for future consumption. Developing technologies that efficiently use renewable energy sources is also critical to our future.
Solved Questions
Write True or False.
1. Wood is not a renewable resource. - False.
2. Methane is a composition of biogas. - True.
3. Renewable energy does not cause pollution. - True.
4. Transportation of renewable energy is difficult - True.
5. Renewable energy causes an ecological imbalance - False.
Learning by Doing
Kids Activity: List as many items from renewable natural resources as you can.
Hint: Go for a short walk outside, consider taking a walk around the neighbourhood or even a trip to your backyard. (This will help you to make a list of many more items.)
Summary
We have already studied many things related to "resources". As we know, renewable resources are very important to maintain the dynamics of the universe. So we have to update technology and make sure that there will be no more waste of resources. We should take proper care of our environment without damaging natural resources. We should use renewable resources effectively and efficiently by upgrading our technology.
FAQs on Uses of Renewable Resources
1. What are the common applications of renewable resources that are often tested in Class Science board exams?
Renewable resources like solar, wind, hydro, and biomass energy are extensively used for electricity generation, powering homes and industries. They also find crucial applications in heating and cooling systems, transportation (e.g., electric vehicles powered by renewable grids), and agricultural processes such as irrigation and crop drying. Understanding these diverse uses is essential for scoring well in your examinations.
2. Why are renewable energy sources considered crucial for future sustainability, a concept highly emphasized in the 2025-26 CBSE syllabus?
Renewable energy sources are vital for environmental sustainability because they produce minimal or no greenhouse gas emissions, directly helping combat climate change. They also contribute significantly to energy independence by reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels, and their abundant availability ensures a continuous supply for future generations. This emphasis aligns with the CBSE curriculum's focus on responsible resource management and ecological balance.
3. Identify and briefly explain the most widely utilized types of renewable resources relevant for your Class Science studies.
The most widely used renewable resources include:
- Solar energy: Harnessed from sunlight using photovoltaic cells (solar panels) for electricity or solar water heaters.
- Wind energy: Captured by large wind turbines to generate electricity, particularly effective in areas with consistent strong winds.
- Hydropower: Produced by the force of flowing water (e.g., rivers) turning turbines in dams, making it a major electricity source globally.
- Biomass energy: Derived from organic matter like agricultural waste, animal manure, or dedicated energy crops, converted into heat, electricity, or biofuels.
- Geothermal energy: Utilizes heat from within the Earth's crust for power generation or direct heating, commonly found in geologically active regions.
4. What are the primary challenges or drawbacks associated with the widespread adoption of renewable energy, a common subject for descriptive answers?
Despite their numerous benefits, renewable energy sources face several significant challenges:
- Intermittency: Sources like solar and wind depend on variable weather conditions, making their energy output inconsistent and unpredictable.
- Storage issues: Effectively storing large amounts of energy generated during peak production for use during off-peak times is technically challenging and expensive.
- High initial investment: Setting up new renewable energy infrastructure (e.g., solar farms, wind parks) often requires substantial upfront capital.
- Geographic limitations: The availability and efficiency of certain renewable resources, like geothermal or large-scale hydropower, are restricted to specific geographical regions.
- Land requirements: Large-scale renewable energy projects, particularly solar and wind farms, can require significant land areas, potentially impacting ecosystems.
5. How does the 'photovoltaic effect' enable solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity, and why is this a fundamental concept in renewable energy?
The photovoltaic effect is the core scientific principle that allows solar cells to transform light energy into electrical energy. When sunlight (composed of photons) strikes a semiconductor material (most commonly silicon) within a solar cell, it excites electrons, causing them to break free from their atomic bonds. These freed electrons then move, creating a flow of electric current. This effect is fundamental because it provides a direct, clean, and efficient method of converting radiant energy into usable electricity without any moving parts, making solar power a key renewable solution.
6. Compare and contrast the primary uses and long-term implications of renewable versus non-renewable resources, a common topic for analytical questions in exams.
Renewable resources, such as solar, wind, and hydro, are primarily used for sustainable electricity generation, heating, and eco-friendly transportation. Their long-term implications include reducing carbon emissions, mitigating climate change, and ensuring energy independence due to their natural replenishment. In contrast, non-renewable resources, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are currently dominant for large-scale electricity production, as fuel for vehicles, and as raw materials in various industries. Their long-term implications are severe, leading to resource depletion, significant environmental pollution, and contributing to global warming, as they are finite and take millions of years to form.









