




Why Is Helium Important? Key Uses Simplified for Easy Learning
Just like Hydrogen, Helium is a chemical element in the periodic table. In today’s world, this chemical element is used for various purposes. Helium is recognised with the symbol “He”, and its atomic number is 2.
Interestingly, Helium is a family of noble gases. Helium is called a noble gas because it does not readily react with anything in general. Other noble gases are Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Neon, Radon, and Oganesson. Further in this article, we will talk about the application of helium, why helium is used in diving apparatus, commercial uses of helium, and many more.
What is Helium?
Helium is not found in a solid state but in gas form. This gas does not have any colour; some say it is slightly grey. It is an odourless, tasteless, inert, non-toxic gas and is the first noble gas. This makes this gas's boiling point and melting point the lowest in the periodic table.
Helium is the second-lightest and second-most element that is observable in the universe. On the other hand, hydrogen is the lightest gas in the universe. The density of helium is 0.1786 g/L when it is in gas form. When Helium is turned into a liquid form, the density becomes 0.145 g per centimetre cube.
In the Earth’s atmosphere, it is quite rare to find Helium. Today, Helium is generated by heavy radioactive elements' natural decay. Some heavy radioactive elements are thorium and uranium.

Helium
What is Helium Used for?
Helium is not a very common element found in the atmosphere but has many uses. Large companies and factories use Helium quite a lot. Normally, Helium is used as a cooling medium for the Large Hadron Collider. They are highly used while experimenting with other gases and in labs.
As for science background, Helium is highly used to keep satellite instruments cool. It is also used to cool down liquid oxygen and hydrogen, mostly used in Apollo space automobiles. Basically, this chemical element is mostly used to cool down heating objects. Some other uses of Helium are as follows:-
Helium is used for welding metals such as aluminium in rocket propulsion.
It is highly used in cryogenics as a coolant because it is the coldest substance on Earth.
Helium is also used as a high-pressure breathing operation, in which it is mixed with oxygen while scuba diving and caisson work.
Helium is found in meteorites and rocks, and that helps cool down objects near them.
By a combination of Helium and oxygen, doctors produce a heliox gas that is used for treatments.
These are some of the scientific uses of Helium. Scientists use Helium for various experiments and outer space as well.

Helium Being Used for Welding Purposes
Helium Uses in Everyday life
Helium is not only used for scientific purposes but for our daily lives as well. Yes, this chemical element is used by various manufacturing companies. Some daily uses of Helium are the following:-
It is used to fill decorative balloons, weather balloons and some other similar things.
Helium is used to make medicines for patients who have lung issues.
This chemical element enables better gas penetration to the alveoli in the lungs.
Interestingly, Helium is also used for laparoscopic surgeries.
While diving in water bodies helium replaces nitrogen. This helps the divers to go deeper under the water without having any issues. This is the answer for why is helium used in diving apparatus.
Meteorologists use helium to fill weather balloons.

Helium Balloon
Commercial Uses of Helium
Helium is highly used to manufacture medicines for patients with lung problems. Some commercial uses of Helium are the following:-
It is popular in welding mixtures.
This chemical element is used in electronics as well. It is used for the production of semiconductors or flat screens.
It is used to perform the manufacturing process, particularly for its reinforcements.
Applications of Helium
Balloons are the common object where Helium is used most. But, we should know that they are a minor part of all Helium uses. Helium is used in some parts by looking at its properties as well. Here are some applications of Helium:-
Controlled Atmosphere - Helium is highly used as a protective gas in growing germanium and silicon crystals. This is because it is an inert gas.
Arc Welding - It is used as a shielding gas on materials that are at welding temperatures.
Industry Leak Detection - Helium is used to detect any leak in an industry. It diffuses through solids three times faster than air.
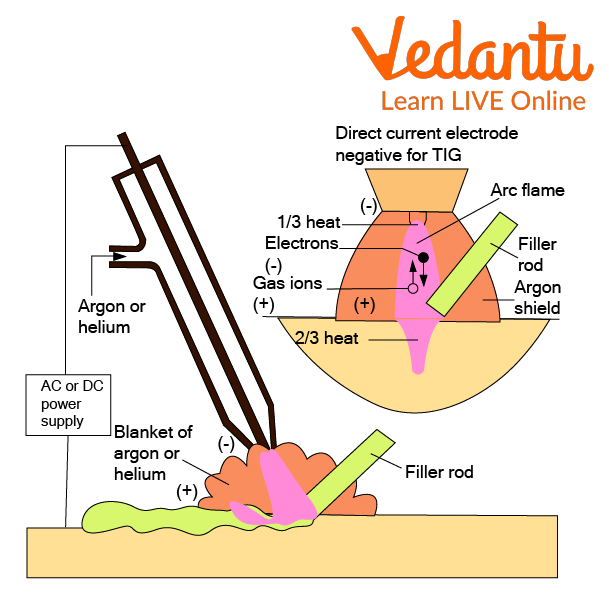
Arc Welding
Summary
Helium is surely an important chemical element in our daily life. The uses of this chemical gas are increasing as the world progresses. As the gas is lighter than air, it is used in airships and balloons. Moreover, Helium has become an essential element in our daily lives and commercial industry. We have learned about this essential element i.e helium in this article. We discussed its uses, applications and its importance.
FAQs on Uses of Helium: Applications and Benefits for Students
1. What are the primary physical and chemical properties of helium?
Helium (symbol He, atomic number 2) is the first element in the noble gas group. Its key properties include:
- It is a colourless, odourless, and tasteless gas.
- Chemically, it is almost completely inert, meaning it does not easily react with other elements.
- It has the lowest boiling and melting points of all elements, making it exist as a gas except under extreme conditions.
- It is the second-lightest element after hydrogen, making it lighter than air.
2. What are five common uses of helium in industry and science?
Helium's unique properties make it essential in various fields. Five major applications are:
- Cryogenics: Used as a cooling agent for superconducting magnets in MRI scanners and scientific research equipment like the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
- Lifting Gas: Filling weather balloons, airships, and decorative balloons due to its low density.
- Welding: Used as a shielding gas in arc welding to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination.
- Leak Detection: Its small atoms can diffuse through tiny cracks, making it ideal for detecting leaks in industrial systems and vacuum equipment.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Used to create a protective, controlled atmosphere during the manufacturing of silicon wafers and fibre optics.
3. Why is helium used in deep-sea diving equipment?
Helium is mixed with oxygen to create a breathing gas called Heliox for deep-sea divers. Unlike nitrogen (the main component of air), helium is far less soluble in blood under high pressure. This is crucial because it helps prevent a dangerous condition known as decompression sickness, or "the bends," which can occur when a diver ascends too quickly and dissolved nitrogen forms bubbles in their bloodstream.
4. How does helium's inert nature contribute to its most important applications?
Helium's inertness, or its chemical non-reactivity, is fundamental to its use. In applications like arc welding and the production of semiconductors, it provides a protective atmosphere that prevents oxygen and other reactive gases from interfering with or damaging the materials. This ensures a cleaner weld and a purer silicon crystal, which are critical for high-quality manufacturing.
5. What makes helium a better lifting gas than hydrogen for applications like weather balloons?
Although hydrogen provides slightly more lift, helium is overwhelmingly preferred for safety reasons. The key difference is that hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive when mixed with air, as seen in the Hindenburg disaster. In contrast, helium is completely non-combustible and inert, eliminating the risk of fire or explosion and making it the much safer choice for both manned and unmanned aircraft like weather balloons and airships.
6. Where is helium found on Earth and how is it commercially extracted?
Helium is a non-renewable resource found trapped in underground natural gas deposits. It is not created on Earth but is a product of the natural, slow radioactive decay of heavy elements like uranium and thorium in the Earth's crust. Commercially, helium is extracted from natural gas through a process called fractional distillation, where the gas mixture is cooled to extremely low temperatures, causing other gases to liquefy while helium remains in its gaseous state and can be separated.
7. Is it dangerous for humans to inhale helium gas?
Yes, inhaling helium can be very dangerous. While a very small amount from a balloon causes a temporary squeaky voice, inhaling it directly from a pressurised tank can be fatal. Helium displaces the oxygen in your lungs, and breathing it in can lead to asphyxiation. This can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness, and even death within minutes by starving your body of essential oxygen.









