




Real-World Applications of Electric Motors Explained for Beginners
Have you ever wondered how a fan works or how a water pump takes water to the top of your House? The water motor takes underground water to meters tall houses just by the use of electricity? How is that even possible? What is the principle behind all these phenomena? The answer is:
All these appliances have one thing in common. What is that? An electrical device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy is an electric motor. A large percentage of electric motors work by creating force in the form of torque applied to the motor shaft through the combination of the magnetic field of the motor and electric current in a wire winding.
Electric Motor
Definition
It is a device that rotates. An electrical motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Parts of an Electric Motor
A rectangular coil- the coil is placed perpendicular to the magnet
A strong magnet
Two split rings act as commutators and reverse the current flow through the circuit
The inner side of the split rings is attached to an Axle that is free to rotate
Externally the rings are attached to brushes which in turn connect the whole circuit to the battery
Battery to supply current
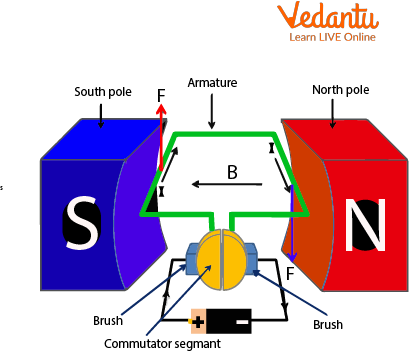
Circuit Diagram of an Electric Motor
Working of an Electric Motor
When the battery is turned on the current starts flowing through the rectangular coil in the direction A to B and the electric field generated is from the north to south direction. Therefore, according to the application of Fleming's left-hand thumb rule, a downward force is applied to the coil at portion AB. Whereas by the above principle a downward force is acting on the CD side of the coil hence the coil starts rotating
After half a turn CD replaces AB and the current starts flowing through it from C to D and the electric field applied is from north to south, therefore, CD experiences a downward force whereas AB experiences an upward force.
This hinders the rotation as we want to rotate the coil fully, not partially. And so to overcome this the current is reversed in the circuit per half a rotation.
To change the direction of the current a commutator is used in the circuit. The commutator consists of split rings and brushes attached to the battery
Now, as the coil rotates, the rings also spin with it and When the coil becomes parallel to the magnetic field, the brushes touch the small gap between the rings, and the circuit breaks
Now, due to inertia, the ring keeps on moving and so the opposite end of the ring connects with the positive end of the wire.
Split ring P is connected to coil CD whereas the split ring Q is connected to coil AB. Which in turn reverses the direction of current in the circuit.
Now, the coil CD is on the left side and AB is on the right side. Current is flowing in the coil CD is reversed i.e. from D to C. So, the force on CD is downwards and the force on AB is upwards Thus, the coil keeps rotating
This reversal of electric current occurs in every half rotation and the coil continues to rotate till the battery is turned off.
If a split ring is not used, the coil is rotated half in the clockwise direction and half in an anticlockwise direction Hence, the purpose of a split ring is to reverse the flow of current and make the coil rotate in a single direction.
Some Devices in Which Electric Motors are Used
Washing Machines
Mixers and grinders
Electric fans
Refrigerators
Electric cars
Summary
An electric motor is used for various purposes in day-to-day life from having cooling air in summers to filling water at huge heights. The basis of an electric motor works in magnetic and electric effects. Therefore we should appreciate the presence of this machine happening and make our lives easier.
FAQs on Uses of Electric Motor for Class Live Students
1. What is the main principle behind the working of an electric motor?
An electric motor works on the principle that when a rectangular coil carrying an electric current is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. This force causes the coil to rotate, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy (motion). The direction of this force is determined by Fleming's Left-Hand Rule.
2. What are the essential parts needed to build a simple electric motor?
A simple DC electric motor has a few key parts:
- An insulated copper wire coil (also called an armature).
- A strong permanent magnet (or an electromagnet) to create a magnetic field.
- A split-ring commutator to reverse the direction of the current.
- A pair of carbon brushes to make contact with the commutator.
- A battery or power source to supply the electric current.
3. Can you explain step-by-step how a DC electric motor works?
Here is a simple step-by-step explanation:
- Current flows from the battery, through the brushes, and into the coil.
- The side of the coil moving down experiences a force in one direction, while the side moving up experiences a force in the opposite direction.
- These two forces create a turning effect, causing the coil to rotate.
- After half a rotation, the split-ring commutator reverses the direction of the current in the coil.
- This reversal ensures the force continues to push the coil in the same circular direction, allowing it to rotate continuously.
4. What is the function of the split-ring commutator in an electric motor?
The split-ring commutator is a crucial part that acts as a reversing switch. Its main job is to reverse the direction of the electric current flowing through the coil every time the coil completes half a rotation. This reversal is necessary to ensure that the coil continues to spin in the same direction. Without it, the coil would just flip back and forth in one position.
5. How is an electric motor different from an electric generator?
The main difference lies in their energy conversion:
- An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy (motion). You supply electricity to make it spin.
- An electric generator does the opposite; it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. You spin it by hand or other means to produce electricity.
While they are built similarly, their purpose and energy flow are reversed.
6. Why does the coil in an electric motor keep rotating instead of just flipping once and stopping?
The continuous rotation is possible because of the split-ring commutator. After the coil makes its first half-turn, the commutator reverses the current's direction in the coil. This flips the direction of the forces on the coil's arms. The arm that was being pushed up is now pushed down, and vice versa. This clever switch ensures the turning force, or torque, always pushes the coil in the same circular path, resulting in continuous rotation.
7. What are some common examples of electric motors used in our homes?
You can find electric motors in many everyday devices around your home. Some common examples include:
- Fans (ceiling fans, table fans)
- Washing machines
- Refrigerators (for the compressor)
- Mixer grinders and blenders
- Water pumps
- Electric toys like remote-controlled cars
8. What rule helps determine the direction of force on the conductor in a motor?
To find the direction of the force experienced by the current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field, we use Fleming's Left-Hand Rule. You stretch the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your left hand so they are perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field and the middle finger points in the direction of the current, then the thumb shows the direction of the force or motion.









