




How Clocks Work: Telling Time Through the Ages
Have you noticed the pattern of the days and seasons? Have you ever wondered who came up with the idea of time? When was the clock invented? Who invented the clock and in which year? Since ancient times different instruments have been used to measure time. Have you ever seen the ‘ Ghanta Ghar chowk’ of any old city like Delhi, Jaipur, or Hyderabad? You must have noticed that the common thing in these places is big clocks that were used in the colonial period for measuring time. Now, you can measure time on your smartphones, and smartwatch.

Clock
What is a Clock?
A clock normally displayed in a room or connected to a wall displays the time. You can see clocks of different sizes around you.
Let's see the interesting journey of the instruments that are used in measuring time.
In this article, who invented clocks, who discovered clocks is discussed.
Different Types of Time Measuring Instruments
Let’s go to the ancient time and see the different kinds of instruments used for measuring time:
Obelisks

Obelisks
See the picture; this long square-shaped tower with an end like a pyramid is Obelisk. These were first used in Egypt in 3500 BCE. With respect to the position of the sun, the shadow gives time.
Sundials

Sundial
Sundials were made up of a dial, and a stick positioned at a specific angle. The stick on the clock that denoted the time of day at any given moment cast a shadow in the sunshine. Sundials and Obelisks work only in the presence of sunlight.
Water Clock

Water Clock
The Greeks used water-based technology to create a clock that was completely powered by water around 250 BCE. The advantage of the water clock was that it could show time 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Graduate Candle Clock
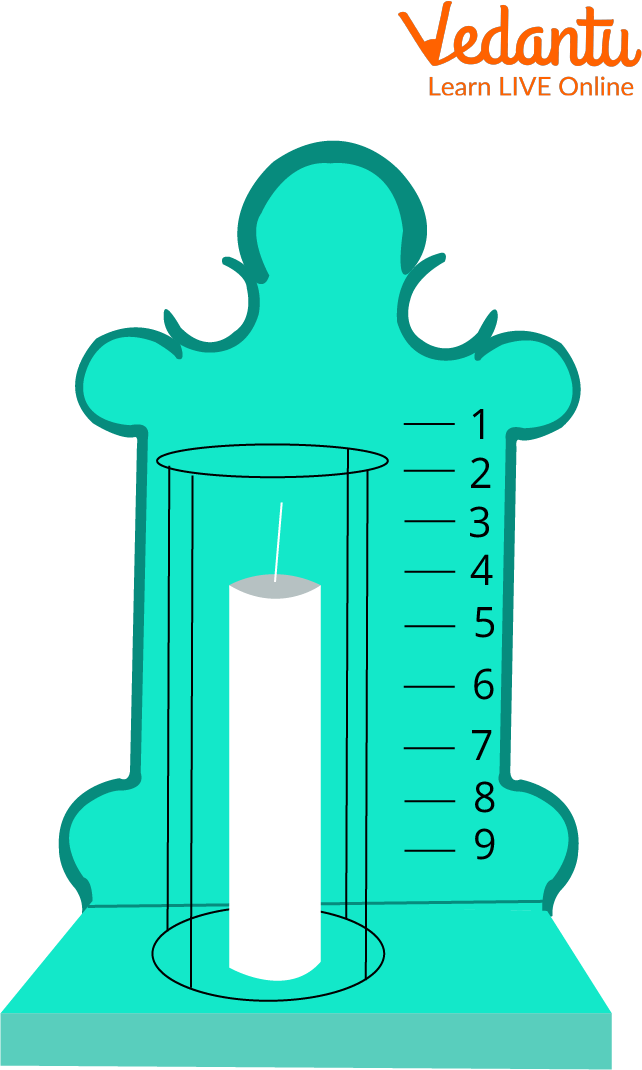

Graduate Candle Clock
Placing a big nail into a candle clock at the correct intervals might be transformed into a timer. As a result, when the candle burned down to that point, the nail clattered down onto a metal plate at the candle's base, signifying the end of the time interval.
You can make these candles on your own at home, do try to make one.
Hourglass
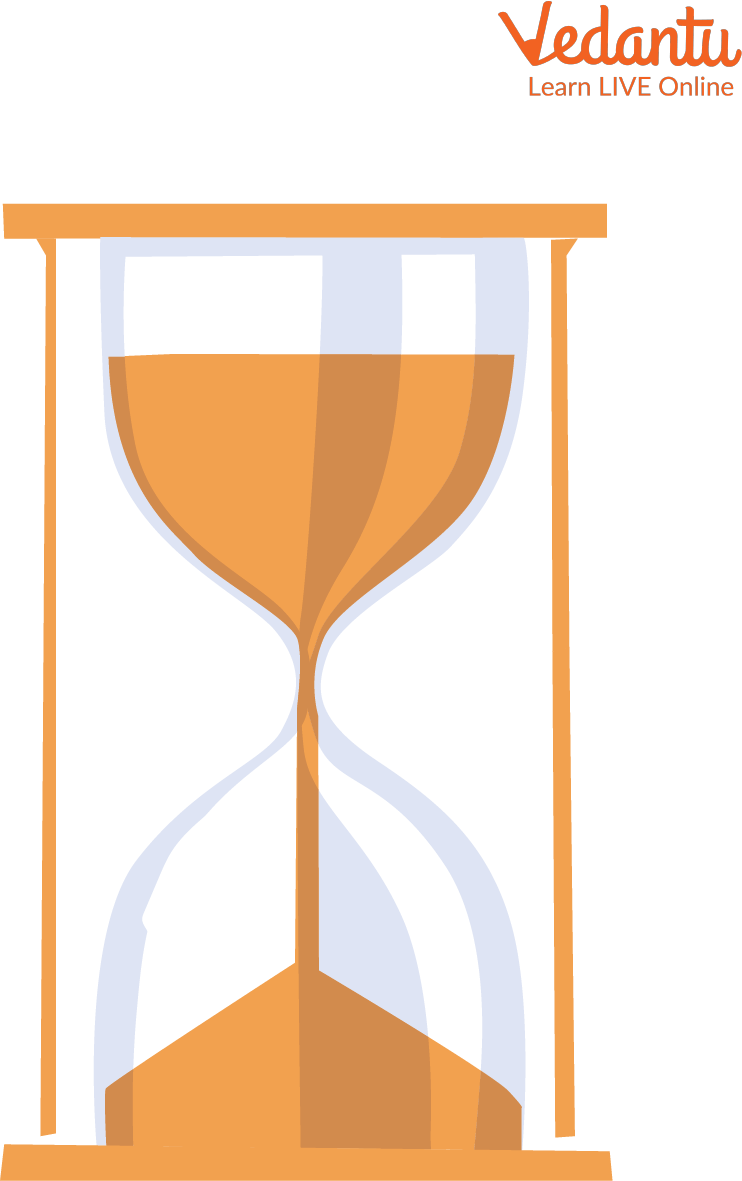

Hourglass
An hourglass was an early instrument for measuring time intervals. These are also known as sandglass or log glass. It comprises two pear-shaped glass bulbs that are joined at their apexes and have a little passage between them. The bulbs contain a quantity of sand (or, on rare occasions, mercury).
These were the clocks used in ancient times. Let’s see the clocks that were used in Mediaeval times.
Western historians refer to the period as "mediaeval times," but they also refer to it as "the Dark Ages." Because of their circumstances, their perception prevailed across Europe at the time. However, the equivalent Muslim areas prospered during that period.
In their time-keeping devices, they used flowing water. In this context, some well-known names who invented clocks include:
1. The Castle Clock of Al-Jazairi (12th century)
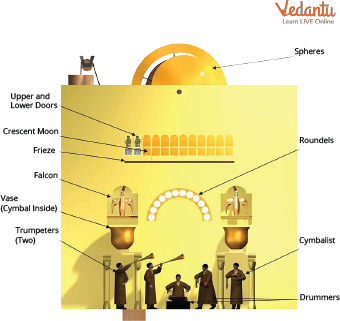
The Castle Clock of Al-Jazairi
2. Ridhwan al-Sa'ati is noted for building a clock for Damascus' mosque.

Clock on Damascus' Mosque
3. Al-Kaysarani created the first clock of its sort, known as the striking clock, in about 1154.

Striking Clock
Now, let's learn about modern instruments.
Mechanical Clocks
Mechanical Clock
Levi Hutchins, an American inventor, was the first to build a mechanical clock in 1787. In 1878, a region's Standard Time was established. Later, mechanical devices incorporating spiral (round) springs were used to create wristwatches and timepieces on tables and sideboards.
Pendulum Clock

Pendulum Clock
A pendulum clock keeps time using a swinging weight called a pendulum. To work, pendulum clocks needed to be level and motionless. Any motion or acceleration will impact the pendulum's motion, causing it to lose or gain speed and beat.
Wrist Watches

Wristwatch
The concept evolved from public clock towers to individual and personal time-keeping devices over time. Wristwatches used to be powered by circular springs that had to be wound once every 24 hours.
Digital Clocks or Watches

Digital Clock
Digital clocks are one of our society's most common pieces of technology. The electronic wristwatch has experienced major evolutionary changes and dozens of offshoots that include everything you could imagine cramming into a wristwatch.
Atomic Clocks
An atomic clock is a sophisticated time measuring instrument that can measure time at a very high degree of accuracy and precision. The typical accuracy of the atomic clock is an error of 1 second every 100 million years.
Summary
You have seen the wonderful journey of the clocks. So, one can divide the clocks based on when they were discovered:
1. Ancient Period instruments:
Obelisks
Sundials
Water clock
Graduate Candle clock
Hourglass
2. Mediaeval Period:
The Castle Clock of Al-Jazairi (12th century)
Ridhwan al-Sa'ati is noted for building a clock for Damascus' mosque.
Al-Kaysarani created the first clock of its sort, known as the striking clock, in about 1154.
3. Modern Period:
Mechanical clocks
Pendulum clocks
Atomic clocks
Wristwatches
Digital watches/ clocks
FAQs on Types of Clocks: Meaning, Uses, and Inventions
1. What are the main types of clocks that have been used throughout history?
Clocks have evolved significantly over time. They can be broadly categorised based on the period of their invention:
- Ancient Instruments: These were the earliest forms of timekeeping and included Sundials, Obelisks, Water Clocks, graduated Candle Clocks, and Hourglasses.
- Mediaeval Clocks: This era saw the development of more complex devices, often using flowing water or early mechanical systems, like the striking clock.
- Modern Clocks: This period includes the invention of Mechanical clocks, Pendulum clocks, Wristwatches, Digital clocks, and the highly precise Atomic clocks.
2. Which ancient clocks could only work during the day, and why?
Ancient instruments like the Sundial and the Obelisk could only measure time on sunny days. This is because their entire mechanism was based on tracking the moving shadow cast by the sun. On cloudy days or during the night, no shadow would be cast, making it impossible to tell the time.
3. What was the main advantage of using a water clock over a sundial?
The primary advantage of a water clock, also known as a clepsydra, was its ability to function continuously, 24 hours a day. Unlike a sundial, it did not rely on sunlight to work. This made it a far more reliable method for keeping time, especially at night or on overcast days, marking a significant advancement in timekeeping technology.
4. How does a simple pendulum clock keep accurate time?
A pendulum clock keeps time using a swinging weight called a pendulum. The key to its accuracy is that a pendulum of a specific length takes a very consistent amount of time to complete one swing. This regular, repeating motion controls the clock's internal gears, which then move the hands on the clock face at a steady, constant speed. For this to work correctly, the clock must be kept level and motionless.
5. What is the difference between an analog and a digital clock?
The main difference lies in how they display the time. An analog clock uses a face with numbers and continuously moving hands (an hour hand and a minute hand) to indicate the time. A digital clock, on the other hand, displays the time directly with digits, such as '10:30', making it a direct numerical reading.
6. Why are atomic clocks considered the most accurate timekeeping devices?
Atomic clocks are incredibly accurate because they use the natural, constant vibration of atoms (like caesium atoms) as their time reference. These atomic vibrations are extremely stable and predictable, far more so than any mechanical part like a pendulum or spring. This allows atomic clocks to measure time with such high precision that their margin of error is as small as one second in over 100 million years.
7. Who invented the first mechanical alarm clock?
The first mechanical clock with a practical alarm function was invented by Levi Hutchins, an American inventor, in 1787. While mechanical clocks existed before him, his invention was specifically designed to wake him up for work at a set time, making it the forerunner of modern alarm clocks.





















