




How Do Mirrors Reflect Light? Principles, Examples & Everyday Impact
Have you ever imagined what will happen if you take the Mirrors available in your home into space? Will it form the same kind of image as it does at your home? Will it break down and not form any kind of image? So many questions right ! We find mirrors everywhere around us. From the mirror used in the house to see how we are looking to the mirrors used as rear mirrors in cars to see the objects coming from behind. In this article, we will discuss all the facts regarding mirrors, what mirror reflections are and do mirrors work in space. So, let's start learning!

Reflection in the Mirror
What are Mirrors?
A mirror is an object that has a smooth surface and forms images of the objects nearby. Mostly, the regular Mirrors are made out of a sheet of glass that has a shiny metal coating on its back side.
Mirrors on a large scale are made in factories where there is availability of specialised machinery. By using the machinery, first, the sheet of glass is polished and made smooth. Then the back side of the glass is covered with a layer of any metal like silver, aluminium. After that, the metal used is covered with another layer of any copper, varnish or any kind of paint so that it is protected from environmental attacks and scratches.
Types of Mirrors
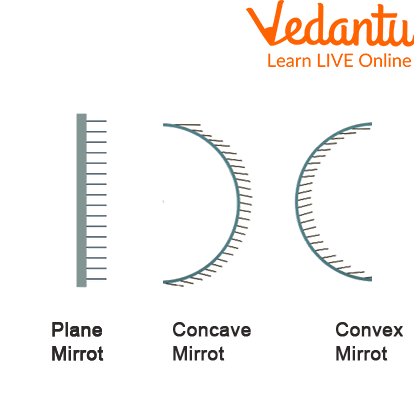
Generally, the mirrors found around us are flat and are referred to as plane mirrors. Images formed in plane mirrors are laterally inverted. For example, if you stand in front of a mirror and raise your left hand while looking into the mirror you will notice that the image formed in the mirror will appear to you as if you have raised your left hand.
Different Types of Mirrors
There can be two more kinds of mirror also namely convex and concave mirror.
The convex mirrors are bulged outwards and curved outwards.
The convex kind of mirrors form images that are smaller and reverse than their actual size.
Whereas, the concave Mirrors are curved in words and forms images that are upside down then the real object
What are Mirror Reflections?

Mirror Reflection
The formation or appearance of an image of any object into a mirror is called the phenomenon of reflection. The phenomenon of reflection occurs when light hits the surface of any object. Generally when light is passed through any surface it gets reflected back. Most of the surfaces absorb some amount of the light which is passed through it and reflects back a little amount of it. Mirrors usually reflect all of the light that hits them. This happens due to the metallic coating on the back of the mirrors.
When we stand in front of a mirror, bodies reflect the pattern of the light falling on it and follow it to the mirror and those patterns of light bounce back and form the image of ourselves in the mirror that we see and perceive through our eyes. Below are attached some mirror reflection images which will help you understand how light falls and is reflected by various surfaces and kinds of mirrors.

Reflection Through Different Types of Surfaces
Reflection Through Convex and Concave Mirrors
The phenomenon of reflection occurs in surfaces that are shiny or polished like glass, water or any polished metal. These objects or surfaces mentioned above, reflect the light with the same angles with which it hits the surface.
The angle with which any ray of light hits the reflecting surface or any smooth surface is called the angle of incidence. Whereas, the angle with which the reflected rays bounce back is called an angle of reflection.
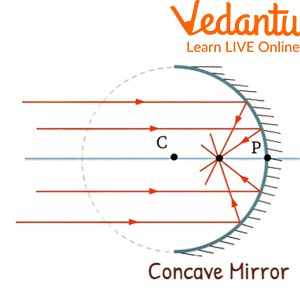
Concave Mirrors
Reflection through Concave Mirror
Concave Mirrors are used in telescopes to form the reflection of sources that are faint high up in the sky and condense the faint light coming from them to form a sharp image into the telescope which is visible to our naked eyes.
In the concave mirrors the light coming from various sources travel in a straight line towards the mirror and are reflected to meet at a certain point called the focal point.
Concave mirrors are used in shaving mirrors, astronomical telescopes, headlights of automobiles etc.
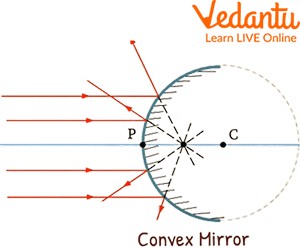
Convex Mirrors
Reflection of Light Through Convex Mirror
In the convex mirrors the light coming from the source reflects outwards and away from the focal point of the mirror. Which makes a small size and erect image of the object.
Convex Mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles and in shops for security for a wider vision of field
Do Mirrors Work in Space?
Till now we have looked at all the properties of the mirrors and how they perform the phenomenon of reflection. To answer the question whether mirrors work in space or not. We can say that mirrors actually work the same as they do on earth in space. Because mirrors are used in telescopes and various other instruments that are carried into space by astronauts to observe the outer space and environment outside the earth.
Summary
To conclude all the learnings from this article we can say that Mirrors are very useful for daily life activities for humans they are used for dressing up and also used for very highly specified purposes like astronomy. Mirrors have a very valuable space in human life. We cannot imagine the foundation of devices like cameras, telescopes etc. without the discovery of mirrors. With this we would like to end this article and hope that our work is clear and understandable enough to clear all your doubts regarding Mirrors and their properties. However, if you still have any doubts you can write it down in the comment section below.
FAQs on Understand Mirror Reflections in EVS: Key Concepts & Uses
1. What is a mirror and how does it work?
A mirror is a surface, typically made of glass coated with a reflective material, that bounces back light to form an image. It works based on the principle of specular reflection. When light rays from an object strike the smooth surface of the mirror, they reflect at the same angle, creating a clear, reversed image of the object in front of it.
2. Do mirrors work in the vacuum of space?
Yes, mirrors work perfectly in space. The process of reflection does not depend on gravity or air. A mirror simply needs a source of light to reflect. So, if an astronaut in space shines a light on a mirror, or if the mirror is positioned to catch light from the Sun, stars, or a spacecraft, it will create a reflection just as it does on Earth.
3. Why is a light source necessary for a mirror to show a reflection?
A mirror itself does not produce an image; it only reflects existing light. An object becomes visible when light from a source (like the sun or a lamp) bounces off it. The mirror then catches these bouncing light rays and reflects them to our eyes. In complete darkness, there are no light rays to bounce off an object, so the mirror has nothing to reflect, and you will see only blackness.
4. What are the main types of mirrors and how do their reflections differ?
The three main types of mirrors are distinguished by their shape and the kind of image they form:
- Plane Mirrors: These are flat mirrors, like the ones in your bathroom. They produce a virtual image that is upright, the same size as the object, and laterally inverted (left and right are swapped).
- Concave Mirrors: These mirrors curve inward. They can form magnified, upright images when the object is close (used in makeup mirrors) or smaller, inverted images when the object is far away (used in reflecting telescopes).
- Convex Mirrors: These mirrors curve outward. They always produce images that are smaller than the object, allowing them to show a wider field of view. This is why they are used for security mirrors in shops and as side-view mirrors on vehicles.
5. If you hold a mirror in space, what would you see in its reflection?
If you were an astronaut holding a mirror in space, you would see a reflection of whatever is in front of the mirror. This would include your own face and spacesuit, parts of your spacecraft, the Earth if it is in view, and the deep blackness of space dotted with distant stars. The reflection itself would be clear, as its function is independent of the environment.
6. How is looking in a mirror different from looking at a photograph?
Looking in a mirror and looking at a photograph are different in key ways. A mirror shows a real-time, dynamic reflection that changes as you move. The image is also laterally inverted. A photograph, on the other hand, is a permanent, static record of a past moment. It captures light on a sensor or film and is not inverted, presenting the scene exactly as the camera saw it.
7. What is the actual colour of a perfect mirror?
Theoretically, a perfect mirror that reflects all wavelengths of light equally would be white, as white is the combination of all colours in the visible spectrum. However, common household mirrors are not perfect. They reflect green light slightly better than other colours. This faint green tint can be seen if you look into a 'mirror tunnel' created by placing two mirrors facing each other.
8. Does a mirror have mass and can it wear out over time?
Yes, a mirror has mass because it is made of physical materials like glass (silicon dioxide) and a thin layer of metal (like silver or aluminium), all of which are composed of atoms. A mirror can also wear out. The reflective coating on the back can tarnish or get scratched, and the glass itself can be chipped or broken, degrading the quality of the reflection.









