




What Are the Main States of Matter? Definitions & Examples
We can say that matter is the substance which occupies space, which has definite mass, which can exert pressure, can produce physical resistance, and whose existence can be felt by our senses.
For example - Air and water; hydrogen and oxygen; sugar and sand; silver and steel; iron and wood; ice and wine; milk and oil; carbon dioxide and steam; carbon and sulphur; Rocks and minerals etc. These are different types of matter that have mass and volume and occupy space.
Properties of Matter for Kids
The Properties of Matter can be general or specific. General properties of matter are those whose characteristics are common to all bodies:
Quantity or Extent: The space occupied by a body.
Weight: The force exerted by gravity on bodies.
Porosity: The space that exists between particles.
Inertia: The characteristic that prevents matter from moving without interference from an external force.
Impenetrability: The property that one body cannot use the space of another body at the same time.
Divisibility: The ability of matter to be divided into smaller parts.
It is important to emphasise that its properties are always influenced by the gravitational forces of the environment in which they are found and by the forces of attraction between the molecules that make up it.
Types of Matter
Substances are divided into two categories based on composition:
Physical Structure
Chemical composition
Physical Structure:
The substances in this structure depend entirely on the existing intermolecular forces between their molecules. Based on physical structure, the matter is divided into three groups – solid, liquid, and gas.
Chemical Composition:
The matter is divided into three groups - elements, compounds, and mixtures.
States of Matter
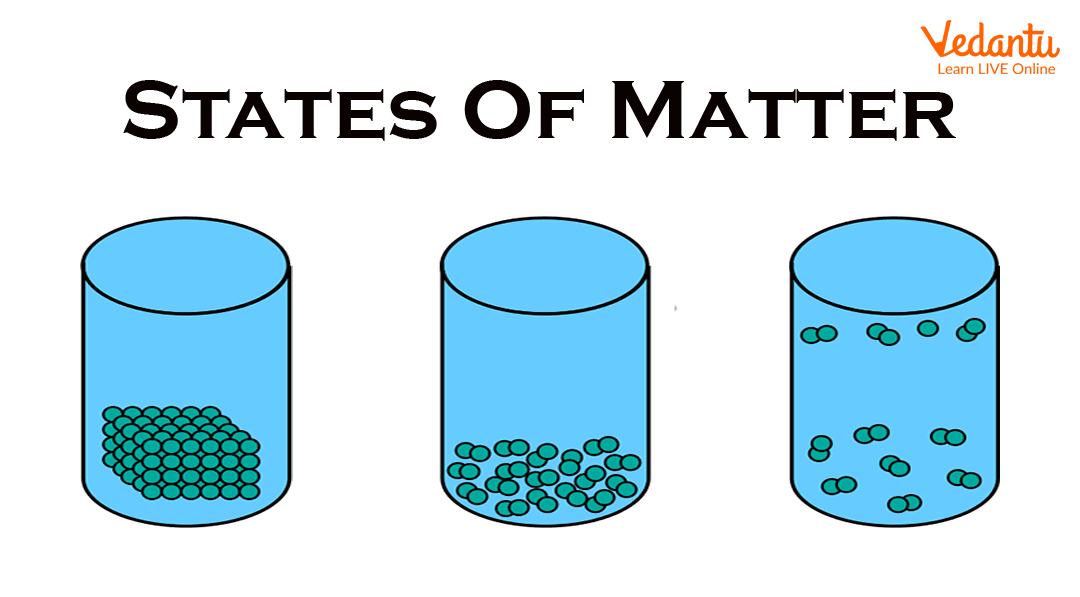
States of Matter
Physical States of Matter:
Based on their physical states, substances are classified into three main classes: solid, liquid, and gas. The fourth state of plasma has also been considered. The fifth state is Bose-Einstein condensate.
Solid State: The state of matter in which its shape and volume are fixed. Like iron, gold, wood, salt, diamond etc. When the force of attraction between the molecules of a substance is stronger than the separating force, the substance remains in a solid state. Due to the strong force of attraction, solids are densely condensed, that is, they are very close together and their positions are fixed.
Liquid State: Liquid is that state of matter in which its volume is fixed but its shape is uncertain, e.g., milk, water, oil, mercury etc. The size of the liquid depends on the vessel in which it is kept. When the force of attraction in a substance is only slightly stronger than the separating force, the substance remains in a liquid state.
Thus, the mutual attraction between the molecules of a liquid substance is weaker than that of the solid state. For this reason, the molecules in liquids are less densely condensed and free to move.
Gaseous State: Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, chlorine etc. are gaseous substances. Matter in the gaseous state has neither shape nor volume. Due to the very weak force of attraction, the molecules of a gaseous substance are much farther away from each other than solid and liquid substances and are free to move in all possible directions.
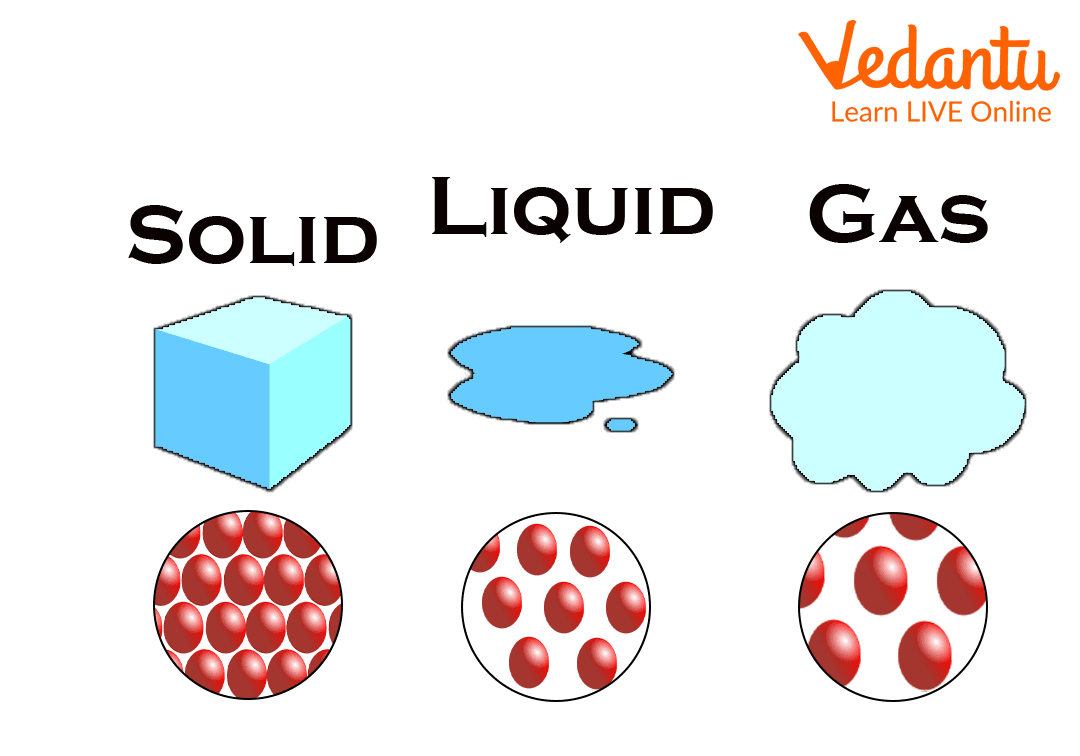
States of Matter: Solid, Liquid, and Gas
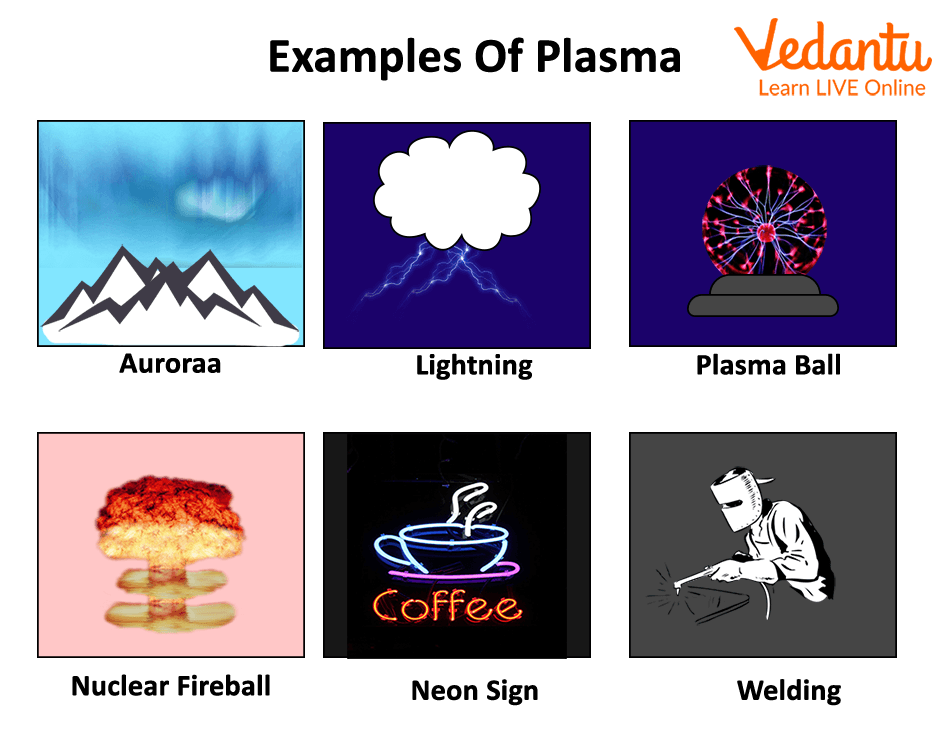
Examples of Plasma

Bose-Einstein Condensate
Solved Questions
1. Write the name of the physical state of matter that has an indefinite shape and a definite volume.
Ans: Liquid is the state of matter that has an indefinite shape but a definite volume.
2. What is the physical state of matter whose shape and volume are both uncertain?
Ans: Gas is the physical state of matter whose shape and volume are both uncertain.
Learning by Doing
1. Which of the following are substances?
Chair
Air
Affection
Smell
Hatred
Almond
Thought
Cold Soft Drink
The Fragrance of the Perfume
2. How many states of water are found in nature?
Summary
The matter is that which occupies space and has weight. There are three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. Both the shape and volume of a solid substance are fixed. The volume of a liquid is fixed but the shape is not fixed. Both the volume and shape of the gas are uncertain.
FAQs on Examples of States of Matter
1. What is matter, and what is it made of?
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). Everything in the universe, from the smallest dust particle to the largest star, is made of matter. It is composed of tiny particles, primarily atoms and molecules, which are the fundamental building blocks of all substances.
2. What are the three main states of matter with everyday examples?
The three most common states of matter found on Earth are solid, liquid, and gas. Each has unique properties:
- Solids: Have a fixed shape and volume. Examples include a wooden block, ice, a book, and a metal spoon.
- Liquids: Have a fixed volume but take the shape of their container. Examples include water, milk, honey, and juice.
- Gases: Have no fixed shape or volume and will expand to fill any container completely. Examples include air, oxygen, steam (water vapour), and helium.
3. What is the main difference in particle arrangement between solids, liquids, and gases?
The primary difference between these states lies in the energy and arrangement of their particles:
- In solids, particles are packed tightly in a fixed, orderly pattern. They have low energy and can only vibrate in place.
- In liquids, particles are close together but not in a fixed pattern. They have enough energy to slide past one another, allowing the liquid to flow.
- In gases, particles are very far apart and have high energy. They move randomly and quickly, which is why a gas expands to fill its container.
4. How does a substance change from one state of matter to another?
A substance changes its state when energy, typically heat, is added or removed. This process changes how its particles move. The main transitions are:
- Melting: Solid to liquid (e.g., ice turning into water).
- Freezing: Liquid to solid (e.g., water turning into ice).
- Evaporation/Boiling: Liquid to gas (e.g., water boiling into steam).
- Condensation: Gas to liquid (e.g., water vapour forming droplets on a cold surface).
5. Are there other states of matter besides solid, liquid, and gas?
Yes, scientists have identified several other states of matter that exist under extreme conditions. The two most well-known are:
- Plasma: A superheated, ionised gas where electrons have been stripped from atoms. It is the most abundant state of matter in the universe, found in stars like our Sun and in lightning.
- Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC): A state that occurs at temperatures near absolute zero. At this point, atoms cool down and clump together, behaving as a single 'superatom'.
6. Why does a gas spread out to fill a room, but a liquid does not?
This happens due to the differences in intermolecular forces and kinetic energy. Gas particles have very high kinetic energy and extremely weak forces holding them together, so they move freely and independently, spreading out as much as possible. In a liquid, the intermolecular forces are strong enough to keep the particles together, so while they can flow and change shape, they cannot escape the container's volume easily.
7. Can a substance, like water, exist in all three states at the same time?
Yes, under a specific condition of temperature and pressure known as the triple point, a substance can coexist in a stable equilibrium of solid, liquid, and gas phases simultaneously. A more common, though less perfect, example is a glass of ice water. You have the solid (ice) and the liquid (water) together, while some of the water is constantly evaporating into a gas (water vapour) in the air above it.
8. Is fire considered a state of matter?
Fire itself is not a distinct state of matter but rather a chemical reaction called combustion. The visible flame is a complex mix of hot gases, glowing solid soot particles, and, most importantly, plasma. Because it contains plasma, fire involves a state of matter, but it is more accurately described as an energetic process.









