




Why Knowing Nitrogen’s Atomic Structure Matters for Students
The first element in column 15 of the periodic table is nitrogen. The class of "other" non-metal elements includes it. Seven electrons, seven protons, and five electrons in the outer shell make up the nitrogen atom.

Symbol of Nitrogen
Through the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen has a significant impact on the survival of plants and animals on earth. A nitrogen molecule has a mass of 28 units since it is made up of two bonded atoms. The majority of the air in the earth's atmosphere is made up of the gas nitrogen (important gas), an element of chemistry. N represents nitrogen as a symbol.
Who Discovered Nitrogen?
Now, we might have some questions like who is the discoverer of nitrogen? Or who found nitrogen? Daniel Rutherford, a Scottish chemist, isolated nitrogen for the first time in 1772. "Noxious air," he referred to the gas as nitrogen. French chemist Jean-Antoine Chaptal gave nitrogen its name in 1790. When he discovered that nitre contained the gas, he gave it the name nitre. Other names for nitrate include saltpetre and potassium nitrate.
Even though we frequently refer to the air we breathe as "oxygen," nitrogen is the most prevalent element. Nitrogen gas makes up 78 percent of the Earth's atmosphere. The Earth's crust has extremely little nitrogen despite the high nitrogen content of the atmosphere. Some relatively uncommon minerals, like saltpetre, include it. All living things on Earth, including plants and animals, have nitrogen. In both proteins and nucleic acids, it is crucial.
Interesting Facts about Nitrogen
The following are some interesting facts about Nitrogen. Other nitrogen compounds exist in the air, rain, soil, and ocean.
Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and will instantly cause frostbite and severe damage to flesh upon contact.
It is estimated to be the universe's eighth most abundant element in terms of mass.
In terms of mass, nitrogen makes up the fourth most of the elements in the human body. About 3% of the mass of the human body is made up of it.
Fusion, a process that takes place deep inside stars, creates it.
In DNA molecules, nitrogen plays a vital role.
Nitrogen has two stable isotopes, 14 and 15, respectively. Nitrogen-14 makes up more than 99 per cent of the universe's nitrogen.
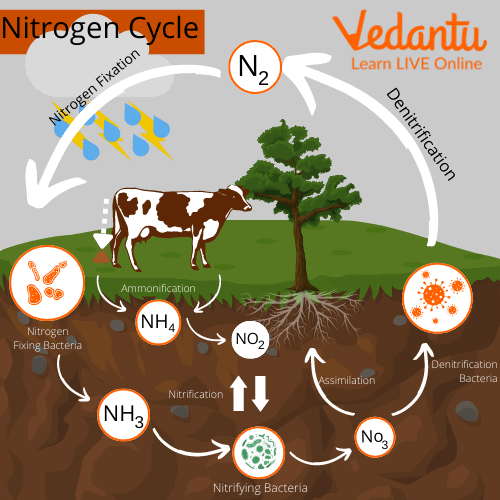
Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen Uses
Making ammonia is nitrogen's main industrial usage. The Haber’s Process, in which nitrogen and hydrogen are mixed to produce ammonia, is the method by which nitrogen is used to manufacture ammonia (ammonia). After that, ammonia makes explosives, nitric acid, and fertilisers. Nitrogen is a component of several explosives, including TNT, nitroglycerin, and gunpowder.
Nitrogen gas is used in incandescent light bulbs, producing stainless steel, preserving fresh food, decreasing fire threats, and other processes. To keep things cold, liquid nitrogen is utilised as a refrigerant. Additionally, it is employed in the cryopreservation of blood and biological materials. Liquid nitrogen is frequently used by scientists in low-temperature science research.
Summary
With the atomic number 7 and the chemical symbol N, nitrogen is a gaseous chemical element. It is a tasteless, odourless, colourless gas that makes up 78 per cent of the atmosphere on earth and it is a component of all living things. It can be used as an inert atmosphere or dilute other gases because it is the almost completely inert diatomic molecule N2. Free nitrogen is also present in many meteorites, the gases from mines, volcanoes, and some mineral springs, as well as some stars and nebulae, in addition to the air.
FAQs on How Many Atoms Are in a Nitrogen Element?
1. What is the fundamental difference between a nitrogen atom (N) and a nitrogen molecule (N₂)?
A single nitrogen atom (N) is the basic unit of the element nitrogen. However, in the atmosphere and under standard conditions, nitrogen is stable as a diatomic molecule (N₂). This molecule consists of two nitrogen atoms joined together by a very strong triple covalent bond, making it chemically inert and different from a single, highly reactive nitrogen atom.
2. What is the atomic number of nitrogen and what does it signify?
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. This is a fundamental property that signifies two key things about a nitrogen atom: it has exactly 7 protons in its nucleus, and in a neutral state, it has 7 electrons orbiting the nucleus. The atomic number uniquely identifies nitrogen as an element on the periodic table.
3. How many atoms of nitrogen are in common compounds like ammonia (NH₃) and nitric acid (HNO₃)?
The number of nitrogen atoms in a compound is shown by the subscript in its chemical formula.
- In one molecule of ammonia (NH₃), there is one nitrogen atom.
- In one molecule of nitric acid (HNO₃), there is also one nitrogen atom.
4. What are the key properties of nitrogen gas (N₂)?
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is known for being:
- Colourless, odourless, and tasteless under normal conditions.
- The most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, making up approximately 78%.
- Largely inert or unreactive due to the strong triple bond between its two atoms, which requires a large amount of energy to break.
5. If nitrogen gas is so unreactive, why is it considered essential for all living things?
While nitrogen gas (N₂) is inert, nitrogen atoms are a vital component of many organic molecules essential for life. Organisms cannot use nitrogen gas directly from the air. Instead, it must be 'fixed' (converted into usable forms like ammonia or nitrates) through the nitrogen cycle. Once fixed, nitrogen is used to build:
- Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
- Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which carry genetic information.
- ATP, the molecule that provides energy for cellular processes.
6. How can you determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a standard nitrogen atom?
For the most common isotope, Nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N), the subatomic particles can be determined as follows:
- Protons: The number of protons is equal to the atomic number, which is 7.
- Electrons: In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons, so there are 7 electrons.
- Neutrons: This is calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number (14 − 7), which equals 7 neutrons.
7. What is the difference between the atomic mass and mass number of nitrogen?
The mass number is the total count of protons and neutrons in a single atom's nucleus and is always a whole number (e.g., 14 for the most common isotope). In contrast, the atomic mass of nitrogen (approximately 14.007 u) is a weighted average of the masses of all its naturally occurring isotopes. This is why the atomic mass on the periodic table is not a whole number.
8. Why can nitrogen exhibit a valency of both 3 and 5 in different compounds?
Nitrogen's valency, or combining capacity, depends on how it shares its 5 valence electrons.
- It most commonly shows a valency of 3 by forming three covalent bonds, as seen in ammonia (NH₃). This allows it to achieve a stable octet.
- It can also exhibit a valency of 5 in compounds with highly electronegative elements like oxygen (e.g., in N₂O₅), where it uses all five of its valence electrons in bonding.









