




Fascinating Elephant Facts for Curious Students
Have you ever visited a zoo? Have you seen an elephant? Let’s learn more about it. Elephants are the largest terrestrial creatures on the planet. The African Savanna elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant are the three types of elephants. These animals belong to the elephant family. This family also included mammoths and mastodons, which are now extinct. Keep reading to know more about elephants.
Picture of Elephants
A Herd of Elephants
Life Cycle of An Elephant
Elephants are divided into two genera: African and Asian, based on genetic and ecological evidence. However, they all share comparable life cycles and phases of growth. African bush elephants prefer the savannas of Sub-Saharan Africa, whereas forest elephants prefer the rainforests. In India and Southeast Asia, Asian elephants can be found in tropical and scrub woods, as well as open grasslands.
What is the Colour of Elephants?
Generally, Elephant colours vary from grey to brown or black. Thus, the colour of elephants are grey, brown or black. Colour of elephants in Africa is mostly grey.
Elephant calves, on average, weigh 265 pounds at birth. Calves are able to sight, smell, and walk within an hour of birth. They normally start sucking within a few hours of birth and are completely reliant on their mothers' milk for the first three months of their existence. Infants are nursed not only by their mothers but also by other nursing females in the herd. Calves acquire their motor skills during the first three months of their lives. They start feeding on their own around the age of 3 to 4 months, but nurse for another two or three years.
Even after they've been weaned, young elephants stay with their original herd. Both male and female elephants grow and develop at similar rates over the first 10 years of their lives. The growth rates of adolescent elephants begin to decline between the ages of 10 and 12. Play is an important part of life for young elephants. Young male elephants chase and spar with other young males, while young female elephants chase birds with other females across the grass.
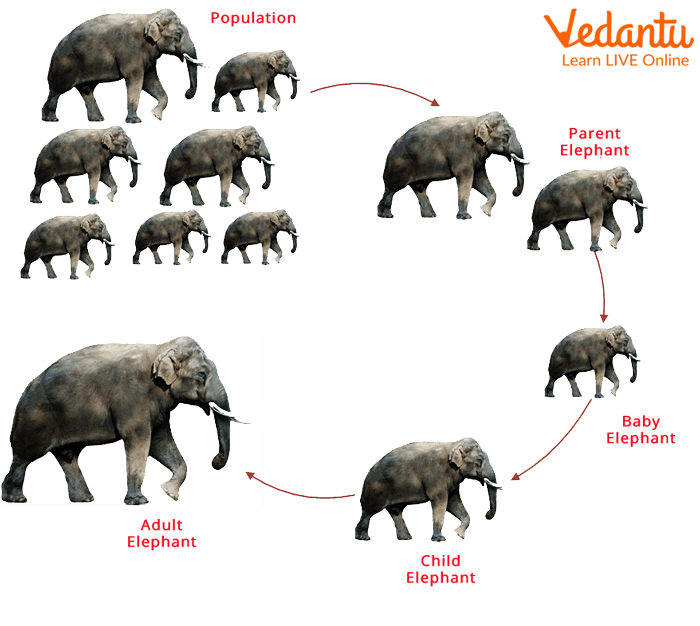
Life Cycle of An Elephant
Male African grey elephants can reach heights of up to 12 feet at the shoulders and weigh up to 5 tonnes, making them the world's largest terrestrial mammals. Females are shorter than males, with an average height of 9 feet at the shoulders. Asian elephants have smaller ears and are slightly smaller than African elephants. Female Asian elephants, unlike their African counterparts, do not develop tusks. Elephants can live to be 70 years old and continue to grow for the rest of their life. As they become older, their growth rate slows, though there is evidence that males have a second growth spurt around the age of 20.
Characteristics of Elephants
Elephants have a big trunk, curved tusks, large ears, and wide legs, which distinguish them from other animals. Elephants can grow to be 11 feet tall and weigh up to 6000 kilograms (13,000 pounds). Elephants in Africa are substantially larger than elephants in Asia, with greater ears and tusks. They have wrinkled skin and a gloomy grey tint. Asian elephants, on the other hand, have grey and brown skin that is less wrinkled. Elephants' skin can grow up to 1 inch thick.
Diet of Elephants
Elephants are herbivores, meaning they eat only plants (plant eaters). They consume leaves, roots, fruits, grasses, and tree bark. They eat by breaking the branches of trees with their trunks. They can sometimes completely destroy the tree they are eating. In a single day, an elephant can consume roughly 300 pounds (140 kg) of food and drink up to 30 gallons of water.
Habitat of Elephants
Elephants are present on both the African and Asian continents in two different species. Because they frequently need to bathe to cool their bodies during the day, they like woodlands and reside near ponds. Elephants can also be seen in arid savannas. These elephants have developed particular adaptations to help them survive in the desert.
Summary
Elephants have been utilised as transportation and labour animals by humans since prehistoric times. They are still used for these purposes throughout Asia today. Elephants that have been trained also feature in circuses all over the world. Human activities, on the other hand, have put the survival of wild elephants in jeopardy. Many elephant habitats have been destroyed by humans. Many elephants have also been murdered for the ivory in their tusks. Ivory is carved into pieces of art, jewellery, and other artefacts by humans. So, this was all about our learning about elephants. Hope you enjoyed it!
FAQs on Everything About Elephants: Life, Habitat, and Food
1. What is an elephant and why is it considered a special animal?
An elephant is a very large mammal known for its long trunk, large floppy ears, and thick, grey skin. They are special because they are the largest land animals on Earth. Elephants are also highly intelligent and social animals that live in family groups called herds, showing deep family bonds.
2. What are the main types of elephants found in the world?
There are two main species of elephants, each living on different continents. The key differences are:
African elephants: They are generally larger, have big ears shaped like the continent of Africa, and both males and females typically grow tusks.
Asian elephants: They are smaller, have more rounded ears, and usually only the males grow large tusks.
3. Why is an elephant's trunk so important for its survival?
An elephant's trunk is a vital, multi-purpose tool essential for survival. It functions as a nose for smelling, a hand for grasping food and objects, a straw for drinking water, and a horn for making sounds. With its incredible strength and flexibility, the trunk allows an elephant to perform delicate tasks like picking a single berry and powerful actions like lifting heavy branches.
4. What is a baby elephant called and how is it cared for in the herd?
A baby elephant is called a calf. From birth, a calf receives protection and care not just from its mother but from all the female elephants (cows) in the herd. It drinks its mother's milk for several years and learns crucial survival skills, like how to find food and interact with others, by observing and imitating the adults.
5. How do elephants use their large ears?
An elephant's large ears serve two main functions. Firstly, their size helps capture sounds from far away, giving them an excellent sense of hearing. Secondly, they act as a natural cooling system. By flapping their ears, elephants increase air circulation and cool the blood flowing through the numerous vessels in their ears, which helps regulate their body temperature in hot climates.
6. Is the elephant the largest animal on Earth?
This is a common misconception. While the elephant is the largest animal on land, the largest animal on the entire planet is the blue whale, which lives in the ocean. The blue whale is significantly larger and heavier than any elephant, making it the biggest animal known to have ever existed.
7. What kind of food do elephants eat?
Elephants are herbivores, which means they have a plant-based diet. They spend a large part of their day eating a wide variety of vegetation, including:
Grasses
Leaves and tree bark
Roots
Fruits and twigs
An adult elephant needs to eat a huge amount of food each day to sustain its massive body.
8. Why do elephants live together in herds?
Elephants live in herds for safety, social bonding, and shared knowledge. The herd, led by an older female called a matriarch, works as a team to protect the young from predators, find sources of food and water, and pass down survival skills through generations. This social structure is crucial for their well-being and success in the wild.
9. How do elephants communicate if they are far apart?
Elephants have a remarkable ability to communicate over long distances. Besides loud trumpet calls, they use low-frequency sounds known as infrasound. These deep rumbles are too low for humans to hear but can travel for miles through the ground. Other elephants can 'hear' these vibrations through their feet and trunks, allowing the herd to stay in contact even when spread out.
10. In a comparison of size, which animal is bigger: an elephant or a rhinoceros?
An elephant is much bigger than a rhinoceros. An adult African bush elephant, the largest species of elephant, can stand over 10 feet tall and weigh over 6 tonnes. In comparison, the white rhino, the largest rhino species, is significantly shorter and lighter. While both are massive land animals, the elephant holds the title for being larger.









