




Understand How Eyes and Brain Work Together to Make Us See Clearly
Have you ever wondered how we can see all the beautiful things around us like our parents, friends, flowers, or butterflies? Yes, you guessed it right, we can see because of our eyes, and that is why our eyes work like windows to the world. Do you know that our eyes work just like a lens and around 80% of everything we learn comes through the eyes? So here, we will learn how our eyes work and how we are able to see this beautiful world.
How Do the Eyes See?
The eyes can see things because of the light. Light bulbs, the sun, and fire are a few sources of light. The light that comes from these sources travels in a straight line, so when they strike an object, they bounce and travel in another direction.
So when we look at an object, these light rays enter our eyes through a front layer called the cornea and that is how we can see light rays. As you know that our eyes work just like a camera lens, so let us understand in detail how our eyes work?
Light rays enter our eyes through the cornea. The light rays then continue to travel and reach the iris. If you have ever wondered why some people have green, blue, brown, or black eyes, it is because of their Iris. It is that part of the eyes that gives them their colour.
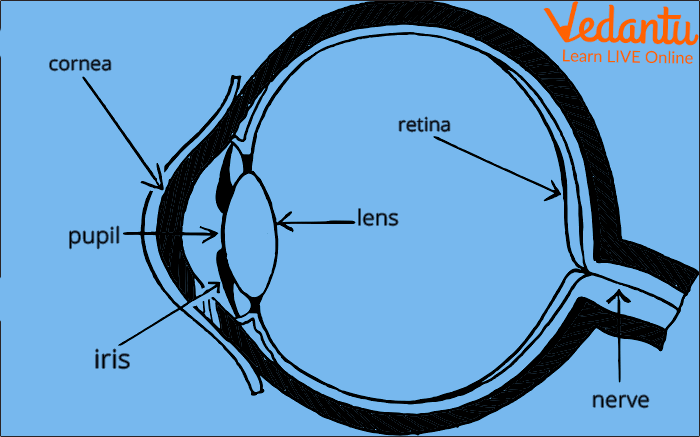
Different Parts of the Eye
The light rays then pass through a lens behind the pupil. The lens bends and focuses the light so that we can see the image clearly, but due to this, the image in our eyes is formed upside down.
There is a small black hole in the iris called the pupil. The light rays enter the pupil but do you know the iris has muscles that help the pupil control the amount of light that enters?
The sharp focused, upside-down image is formed on the retina that is on the back of our eyes. The retina is a layer that responds to light because it has special cells called rods and cones. Rods allow us to see shapes, while cones allow you to see colours. You are able to see that your friend is wearing red clothes and has a black bag because of your retina.
How Do We See the Right Image?
Now you must be wondering if you can see images just the way they are and not upside down. So how are you able to see the right image?
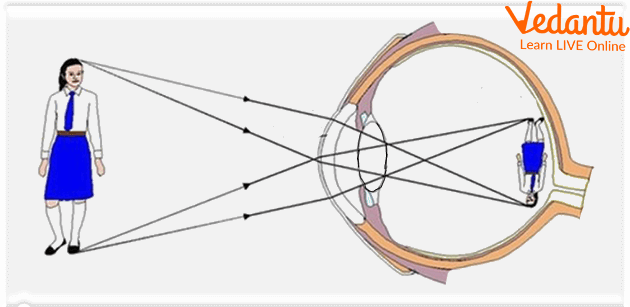
Mind Flipping the Image
This is because the retina changes this information into electrical signals so that our brain can understand what we see. These electrical signals reach the brain through the optic nerve which is at the very back of your eyes. The optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that contains more than one million nerve cells. When your brain receives the electrical signals, it slips the image back the right way up, helping you to understand what you are seeing.
Summary
80% of everything we learn comes through the eyes. You will be surprised to know that our eyes work just like a camera lens. The light rays enter our eyes through the cornea and continue to travel and reach the iris. There is a small black hole in the iris called pupil. The iris has muscles that help the pupil control the amount of light that enters our eyes. The retina is a layer that responds to light because it has special cells called rods and cones. These electrical signals reach the brain through the optic nerve, which is at the very back of your eyes.
FAQs on How Do We See? The Science Behind Our Eyes
1. How do we see things around us? A simple explanation.
We see things through a two-part process involving our eyes and our brain. First, light from a source like the sun or a bulb bounces off an object and enters our eyes. The eye acts like a camera, capturing this light. Then, it sends signals to our brain, which interprets these signals to form the image of the object that we recognise and understand.
2. What is the step-by-step process of seeing an object?
The process of seeing involves several quick steps:
Light Reflection: Light rays travel from a source, hit an object, and reflect off it.
Entering the Eye: This reflected light enters your eye through the opening called the pupil.
Focusing: The lens inside your eye focuses the light, creating an upside-down image on the back of your eye, on a screen-like part called the retina.
Signal to Brain: The retina converts this light image into electrical signals.
Image Interpretation: These signals travel through the optic nerve to the brain. The brain flips the image the right way up and tells you what you are looking at.
3. How does our brain help us understand what we are seeing?
The brain does the most important job in vision. While the eye just collects light and sends signals, the brain acts as a supercomputer. It receives the raw signals from the optic nerve and processes them. It deciphers patterns, identifies colours, recognises faces and objects from memory, and helps us understand the size and distance of what we are seeing. Without the brain, the signals from our eyes would be meaningless.
4. Why can't we see things clearly in the dark?
Our ability to see depends entirely on light. In a dark room or at night, there are very few or no sources of light like the sun or a lamp. This means there is not enough light to bounce off objects and enter our eyes. When very little light reaches our retina, our eyes cannot gather enough information to send to the brain, making it difficult or impossible to see clearly.
5. How are we able to see different colours?
We see colours thanks to special cells in our retina called cones. There are three types of cones, and each type is sensitive to a different primary colour of light: red, green, or blue. When light from an object hits the retina, these cones get activated in different combinations. The brain interprets the unique combination of signals from these cones to perceive the entire spectrum of colours that we see.
6. Why is it important to protect our eyes from very bright screens or sunlight?
Staring at bright screens or directly at the sun for long periods can cause eye strain and fatigue. This happens because the intense light forces the muscles in our eyes to work too hard. It can lead to headaches, blurred vision, and tired, dry eyes. Protecting our eyes by taking regular breaks from screens, avoiding extreme brightness, and not looking at the sun helps keep them healthy and working properly.
7. How is the human eye similar to a camera?
The human eye and a camera work in very similar ways to capture images. The lens in our eye focuses light, just like a camera's lens. The pupil widens or narrows to control the amount of light coming in, similar to a camera's aperture. Finally, the retina at the back of the eye acts like the camera's sensor or film, where the image is captured before being processed.









