




Key Stages and Importance of the Human Gestation Period
Everything in this universe comes with prep time! Food, clothes, house, humans? Why this prep time you ask me, well everything that exists around us is super complex and has to be built up atom by atom, cell by cell.
Now there are very complex sounding yet simple processes as well as simple-sounding complex processes that basically involve this whole building up of things around us.
One such fascinating phenomenon of building up a ‘human’ from the smallest of cells is gestation.
Would you believe me if I say that humans are organisms containing trillions of cells but we all actually started as a couple of really small cells? Scroll through to dive into this splendid biological affair.
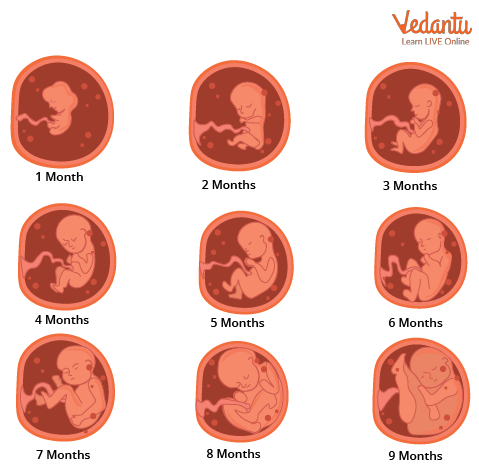
Gestation
What is Gestation?
Gestation, commonly called pregnancy, is the period of full development of a baby inside the mother’s womb. It involves the physical, mental, and overall nourishment of the baby before it is ready for birth into the world.
Duration of Human Gestation
Humans are relatively complex species. As mentioned earlier we’re made of trillions of cells. Can you roughly guess how long it will take for the formation of a trillion cells from just two cells? The answer to that question is roughly 40 weeks which is around 9-10 months. So, when a little human is kicking in the womb it actually takes at least 9 months before they are out and about in the real world.
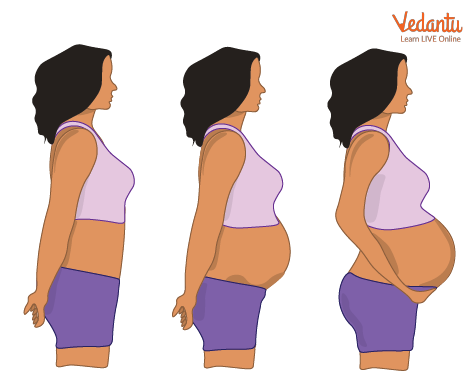
Pregnancy
In this crucial period, the baby grows in size, develops its fundamental organs, and starts kicking (for real!) There are several changes that take place in the mother’s body to accommodate the growing baby, the most important of which is the growth of the womb to give space for the baby which is seen as the baby bump as shown above.
Stages of Gestation
In humans, the 9 months of gestation are divided into 3 trimesters ( trimester meaning 3 months; tri-3) which gives us three separate phases to deal with in detail.
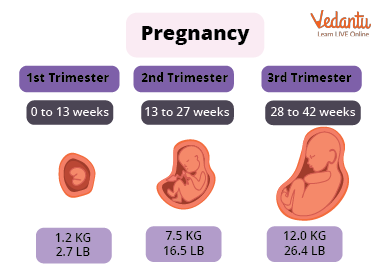
Trimesters
The First Trimester
Once the baby is nice and snuggly placed in the womb (At this stage called the embryo) it starts to exhibit fast and vital signs of growth.
These can be seen as follows:
The neural tube develops closing the brain and spinal cord
Development of heartbeat
Formation of ears and eyes
Development of hands and toe
Development of genital parts
Placement of intestines in the abdominal region
It is an interesting factor to note that the baby is just weighing 14 grams and is around 2.5 inches in length at the end of the first trimester (9-12 weeks) now called a foetus (another fancy-sounding name for a small baby) is roughly the size of a plum!
Embryo
The Second Trimester
Now that the foetus looks more like a human baby, further growth and maturation take place in the second trimester (13-27 weeks).
The baby which was earlier just a bunch of cells now starts to look more human-like with mature features
Urine excretion into the surrounding amniotic fluid sac
The umbilical cord is connected to the placenta
Thickening of bones
Nails begin to develop
Hair becomes visible
Baby can hear and it responds to voice and sudden movements
Lungs develop
The baby is around 820 g in weight and 9inches in length. At the end of the 27th week, the baby is the size of a cauliflower!
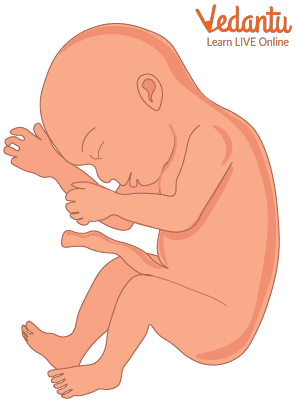
Foetus
The Third Trimester
The final trimester bringing this heroic journey sure ends with a bang. The third trimester (28-40 weeks) completes the period of gestation at the end of which the baby is ready to come to this world. Some of the notable changes in this trimester include:
Baby starts kicking and stretching
Rapid weight gain
The baby is sensitive to light
The chest becomes more prominent
Head turns down ( for easier birth for the mother)
The baby weighs approximately 3400 grams and is around 14 inches in length. At the end of gestation, the baby is the size of a jackfruit!
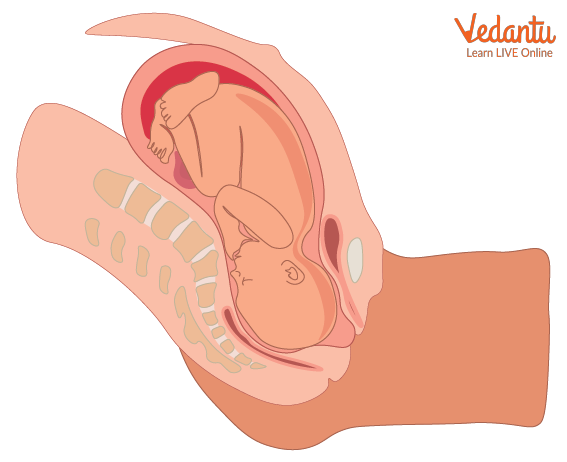
Full Growth of Baby
Summary
Gestation is the process of development and maturation of a human baby in the mother’s womb for a period of around 40 weeks.
Also known as pregnancy, gestation is divided into 3 trimesters each having distinctive developmental phases for the baby.
Initially clusters of cells, the baby slowly develops through various stages from the size of poppy seeds to plums to cauliflower and finally to that of a jackfruit.
At the end of 40 weeks, the baby is ready for birth and is brought out by a process called ‘parturition’ (also known as childbirth).
FAQs on Gestation Period in Humans: Complete Guide
1. What is the gestation period in humans?
The gestation period in humans refers to the time a fetus develops inside the mother's uterus, from conception until birth. On average, the human gestation period lasts for about 280 days, which is equivalent to 40 weeks or approximately 9 calendar months. This duration is crucial for the complete development of the fetus.
2. Why is human pregnancy sometimes described as 9 months and other times as 10 months?
This common confusion arises from two different ways of calculating the duration. Medically, pregnancy is calculated from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period (LMP), which totals about 40 weeks or 10 lunar months (of 28 days each). However, conception typically occurs about two weeks after the LMP. Counting from the actual date of conception gives a duration of about 38 weeks, which is closer to 9 calendar months. The 40-week model is the standard used by healthcare professionals.
3. What are the key stages of the human gestation period?
The human gestation period is divided into three main stages called trimesters, each lasting about three months. Each trimester is marked by specific fetal development milestones:
- First Trimester (Week 1-12): This is a critical period where the basic structure of the body and major organs form. The heart begins to beat, and by the end of this stage, the fetus has arms, legs, fingers, and toes.
- Second Trimester (Week 13-27): The fetus grows rapidly in size and weight. Details like fingerprints, eyebrows, and eyelashes form. The mother can usually start to feel fetal movements during this stage.
- Third Trimester (Week 28-40): This is the final stage of maturation. The lungs, brain, and other vital organs complete their development to function outside the womb. The fetus gains significant weight and positions itself for birth.
4. What is the difference between a full-term, pre-term, and post-term pregnancy?
These terms describe the timing of birth in relation to the normal gestation period:
- A full-term pregnancy is one that lasts between 38 and 42 weeks. This duration allows for the baby to be fully developed and ready for life outside the womb.
- A pre-term (or premature) birth occurs before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Pre-term babies may face health challenges as their organs, especially the lungs, may not be fully mature.
- A post-term pregnancy extends beyond 42 weeks. This can also pose risks to both the mother and the baby, often requiring medical monitoring or intervention.
5. How does the gestation period in humans compare to that of other mammals?
The length of the gestation period varies significantly across different mammal species, often correlating with the animal's size, complexity, and the developmental state of the newborn. For example, an elephant has one of the longest gestation periods at around 22 months, resulting in a well-developed calf at birth. In contrast, smaller mammals like cats have a much shorter period of about 9 weeks, and a squirrel's gestation lasts only about 6 weeks.
6. Why is completing the full-term gestation period so important for a baby's health?
Completing the full-term period is crucial because the final weeks of gestation are vital for significant development. During this time, the baby's brain and lungs fully mature. The baby also builds a layer of fat, which helps in regulating body temperature after birth. Furthermore, it acquires important antibodies from the mother, which provides initial immunity against illnesses. Babies born full-term generally have lower risks of respiratory issues, feeding problems, and other long-term health complications compared to premature babies.
7. What are some key factors that can affect the length of the human gestation period?
While the average gestation period is 40 weeks, several factors can influence its actual length. These include the mother's age and overall health, whether she has pre-existing conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure, and lifestyle factors such as nutrition and stress levels. Another significant factor is carrying multiple fetuses (e.g., twins or triplets), which often leads to an earlier, pre-term delivery.









