




Overview About Wind
The term “wind” is very common, but it is important to understand what it means and how it works. Without understanding the basics of the subject, you could miss a lot of opportunities. The truth is that wind is invisible; we see only its effects. In simple terms, the wind is the visible movement of air that occurs naturally. In this article, we will learn more about wind from the basics to what makes the phenomenon worth studying in depth. In this article, we will talk about what causes wind and also know various facts about wind.

Wind
Wind Definition for Kids
According to scientific dictionaries wind definition for kids is as follows:
The wind is the motion of air over the surface of our planet. Wind can either cause a peaceful breeze or a powerful storm. When tornadoes, cyclones, and hurricanes form, the strongest winds are produced. The wind is a result of changes in the temperatures of the air, land, and water. A warm surface causes air to flow over it to heat up and rise. Cooler air can now enter thanks to this opening. The wind is the moving air.
Wind Speed
Wind speed is the speed or the moment of air in the environment. Wind speed is the phenomenon that is used in various areas to study weather and various operations related to driving aircraft or marine vehicles. High wind speed can cause various calamities whereas a blessing wind or a normal Wind can be pleasant and aesthetic for everyone.
What Causes Wind?
As the warm air rises it leads to the formation of low-pressure locations in the lower positions as the cold particles are more tightly bound up together and tend to descend into those low-pressure locations created by the vacancy of warmer air.
The wind is created by this phenomenon of the movement of cooler air to depositions of former air and the warmer air going to a higher position and vice versa, because of the molecules which move within the region of heating and cooling. This was the answer to what causes wind.
Types of Winds
The various types of winds are named after the direction from which they are coming or can also be named after the direction towards which they are moving.
Permanent Winds
These blow over larger areas and blow in the same direction the whole year. These have another name as well, they are also known as Planetary winds. Permanent winds are themselves classified into different types of winds such as:
Trade winds flow from subtropical high-pressure belts to equatorial low-pressure belts.
Westerlies flow from subtropical high-pressure belts to sub-polar low-pressure belts.
Polar winds flow from sub-polar low-pressure belts in polar areas.
Seasonal Winds
These winds, as their name is seasonal i.e. they change their direction according to the season. Seasonal winds are classified into:
Monsoon winds are often found in Asia and bring rain.
Land breeze and sea breeze, these winds flow over land and sea respectively.
Mountain breezes are the winds which fill the gap in the mountains which is made by the hot air that rises during the day.
Local Winds
These winds are the local winds blowing in a particular locality.
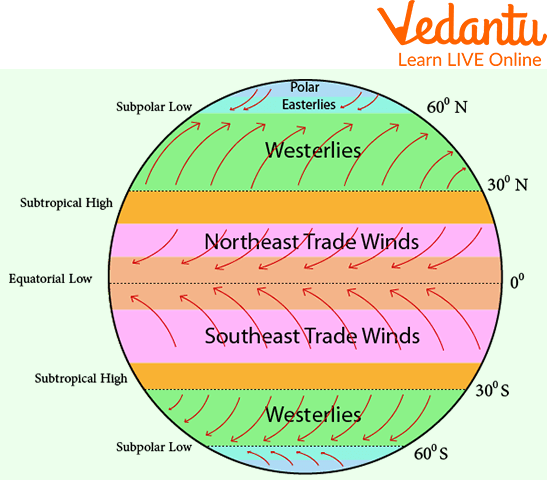
Types of Winds
Wind Facts for Kids
The wind is an astonishing naturally occurring phenomenon. Below are some interesting facts about wind:
The instrument used to measure wind speed is called an anemometer.
The unit used to measure the wind speed is called a knot.
The wind is used as the source of energy in wind turbines to produce electricity and various other kinds of energy.
The winds are the source of power that helps ships sail through the huge oceans.
Many sports are based on winds and in activities like kiteboarding, windsurfing, sailing and paragliding.
Planets that face the fastest planetary winds are Saturn and Neptune.
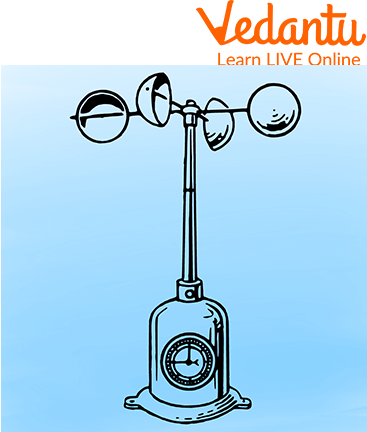
Anemometer
Summary
To conclude all the conceptual understanding regarding wind in this article we can say the wind is the movement of air in the atmosphere of our planet. It helps in bringing variations in climatic conditions and is used for varied purposes. The wind is used to harness energy. There are also various activities designed to take advantage of the wind and make our lives interesting and fun. The wind is a very useful phenomenon that helps humans and all living creatures in some ways. With this, we would like to end the learning about the wind here. We hope this article was helpful to you, in case of any other doubts feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Wind
1. What is wind, and what causes it to blow?
In simple terms, wind is moving air. The primary cause of wind is the uneven heating of the Earth by the sun. When air in one area gets warmer, it becomes lighter and rises. Cooler, heavier air from a nearby area then moves in to take its place. This movement of air from a region of high pressure (cooler air) to one of low pressure (warmer air) is what we feel as wind.
2. What is the air that forms wind made of?
The air that forms wind is a mixture of gases. The air we breathe is primarily composed of nitrogen (about 78%) and oxygen (about 21%). It also contains small amounts of other gases like argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapour. When this entire mixture of gases moves together, it creates wind.
3. How are different types of winds classified?
Winds can be classified based on their speed, direction, and impact. Some common examples include:
- Breeze: A gentle and light wind that is often pleasant.
- Gale: A very strong wind, stronger than a breeze but not as destructive as a storm.
- Storm: A strong wind accompanied by rain, snow, or other precipitation.
- Cyclone/Hurricane: Extremely powerful and destructive rotating storm systems that form over oceans.
4. How is wind helpful to us in our daily lives?
Wind is a crucial natural resource with many benefits. It helps in drying clothes, flying kites, and sailing boats. It plays a vital role in the water cycle by moving clouds. Most importantly, we harness wind's power using windmills and wind turbines to generate clean electricity, which is a form of renewable energy.
5. What is the difference between a land breeze and a sea breeze?
Land and sea breezes are local winds that occur near large bodies of water due to differences in heating. A sea breeze occurs during the day when the land heats up faster than the sea, causing cooler air from the sea to blow towards the land. A land breeze occurs at night when the land cools down faster than the sea, causing cooler air from the land to blow towards the sea.
6. How are winds named?
Winds are typically named based on the direction from which they originate. For example, a wind that blows from the west towards the east is called a 'westerly' wind. Similarly, a 'northerly' wind is one that comes from the north.
7. What tools are used to measure wind?
Two main instruments are used to measure wind. An anemometer is used to measure the speed of the wind; it usually has cups that spin as the wind blows. A wind vane (or weather vane) is used to determine the direction of the wind; it points in the direction from which the wind is blowing.
8. If wind is just moving air, why can it be powerful enough to cause destruction?
Although air is light, a massive amount of it moving at high speeds has a great deal of force and energy. In a storm or cyclone, the pressure difference between two areas is very large, causing air to move extremely fast. This high-speed movement can exert enough force to uproot trees, damage buildings, and cause widespread destruction.
9. Why is there no wind on the Moon?
Wind is moving air, and air is part of an atmosphere. The Moon has no significant atmosphere like Earth does. Without a blanket of air to heat up and move around, there can be no pressure differences and therefore, no wind can be generated on the Moon's surface.









