




Why Is the Sun Important? Key Facts Every Student Should Know
The sun is the closest star to earth. It's the source of all the heat and light that we get on earth. Life wouldn't exist without it. It's also the centre of our solar system and by far its largest object. The sun was born about 4.6 billion ago. It is the source of energy of our planet earth. The Sun is composed of hydrogen and helium gases. It is believed that the sun will become a white dwarf after 5 billion years and burn up all the hydrogen.
What is Sun?
Sun is the yellow dwarf star which consists of 98% of the total mass of the entire solar system. The Sun is the source of light and energy to our planet earth. The sun is placed in the centre of our solar system and is a dwarf star that gives light. Sun also releases a stream of particles that reaches the earth as the solar wind.
The sun controls our seasons. It controls how and when food grows. It even controls when we are asleep and awake. It take-up 98% of the matter in the solar system because of its size and it has a strong gravitational pull. It keeps earth, the star, the moons and the other planets in line. Without gravity, the sun, and the earth would go spinning off into space.
The Sun
Inside The Sun
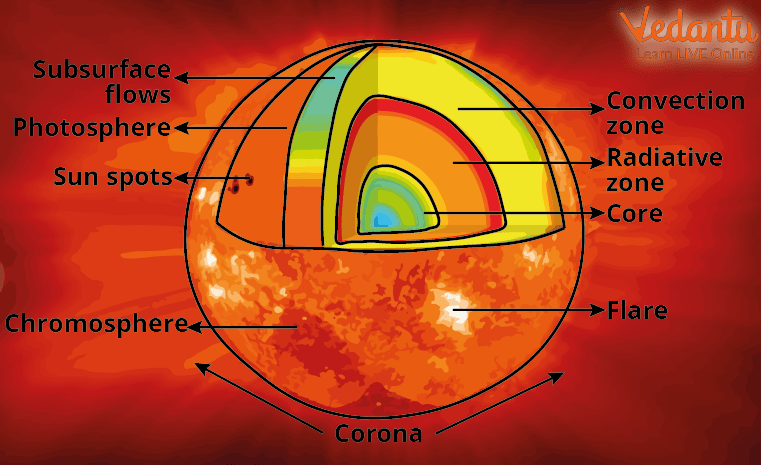
Structure of the Sun
The sun is at the centre of the solar system. It nearly perfects a sphere of hot plasma; it is divided into 2 parts: the outer layer and the inner layer.
Outer Layer
1) Photosphere - The photosphere is the sun that we can see from earth. Though it is called the surface of the sun, it is the first layer of the surface of the sun, it is the first layer of the solar atmosphere and is made of plasma.
2) Chromosphere - Chromosphere is a reddish and glowing layer of gas above a star's photosphere; it is a transition between corona and photosphere.
3) Transition Region - The transition region is a very narrow layer between the chromosphere and the corona where the temperature rises abruptly from about 8000 to abruptly 5,00,000.
4) Corona - The outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere where strong magnetic fields bind plasma and prevent turbulent solar winds from escaping. The Alfven point is when solar winds exceed the critical speed and can break free of the corona and the sun's magnetic field.
Inner Layer
1) Core: The core is at the centre. It is the hottest region where the nuclear fusion reaction that powers the sun occurs.
2) Radiative Zone: The inner layer is the Core Radiative Zone. The outer layer is the photosphere chromosphere, the transition region and the corona.
3) Convection Zone: This is the outermost layer of the solar interior. It extends from a depth of about 200,000 km right up to the visible surface.
Fun Facts About the Sun for Kids
The Sun is heating up and can kill life on earth. It becomes 10% more luminous every billion years. In fact, within just a billion years the heat from the sun will be so intense that liquid water won’t exist on the surface.
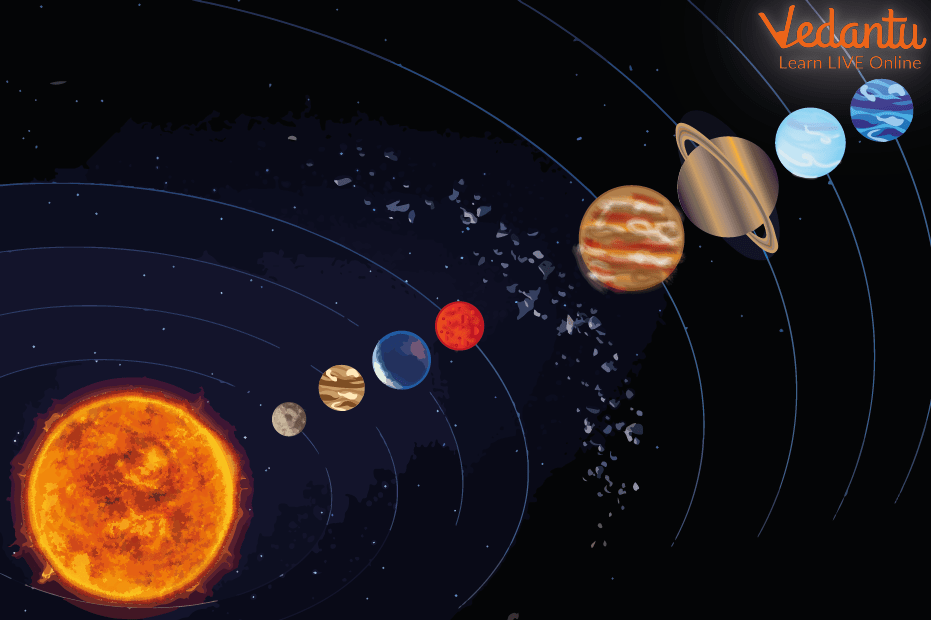
Solar System
Astronomers think that the sun formed from the solar nebula about 4.59 billion years ago.
The sun is in the main sequence stage right now, slowly using up hydrogen fuel.
After sunset. The earth, Moon, does not make its light. It shines because of the light it reflects from the sun.
This is an ordinary star. It’s just one of the billions of stars in the Milky way alone.
Summary
The sun is the star in the solar system which is at the centre. It is a nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma with an internal convection motion that generates a magnetic field via a dynamo process. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on earth.
There are three main parts to the Sun interior: The core, The radiative zone, and the constructive zone. The core is at the centre. It is the hottest region, where the nuclear fusion reactions that power the Sun occur. Moving outward next comes the radiative zone.
FAQs on Fascinating Facts About the Sun for Kids
1. What is the Sun and why is it important?
The Sun is a giant, glowing star at the centre of our solar system. It's a huge ball of extremely hot gases that produces light and heat. The Sun is vital for life on Earth because it provides the light plants need to grow and the warmth that keeps our planet from freezing, making it possible for us to live.
2. What are five amazing facts about the Sun for kids?
Here are five simple and amazing facts about our Sun:
It is a Star: The Sun is not a planet but is the closest star to Earth.
It is Huge: You could fit more than one million Earths inside the Sun.
It is Very Hot: The surface of the Sun is about 5,500 degrees Celsius, which is much hotter than any volcano on Earth.
Sunlight's Journey: The light from the Sun takes about 8 minutes to travel to Earth.
It Holds Us Together: The Sun's powerful gravity keeps all the planets, including Earth, in their orbits.
3. How big is the Sun compared to the Earth?
The Sun is enormous compared to our planet. To understand its size, imagine if the Earth was the size of a small marble. The Sun, on the same scale, would be as big as a large beach ball! It's so massive that it contains over 99.8% of all the material in our entire solar system.
4. What is the difference between the Sun and a planet?
The main difference is how they produce light. The Sun is a star, which means it creates its own light and heat through a process called nuclear fusion. Planets, like Earth, do not create their own light. They only appear bright because they reflect the light from their nearest star.
5. Why does the Sun look yellow or orange from Earth if its light is white?
While the Sun produces white light, it appears yellow or orange to us because of Earth's atmosphere. As sunlight passes through the air, shorter wavelengths of light, like blue and violet, are scattered away by air molecules. This allows the longer wavelengths, like yellow, orange, and red, to reach our eyes, especially during sunrise and sunset.
6. What would happen to Earth if the Sun disappeared?
If the Sun were to vanish, life on Earth would change dramatically. Within minutes, our planet would be in complete darkness. The temperature would drop rapidly, and the surface would begin to freeze. Plants would no longer be able to perform photosynthesis, and without the Sun's gravity, Earth would stop orbiting and drift off into space.
7. If the Sun is a ball of fire, why doesn't it burn out?
This is a great question! The Sun isn't burning like a wooden fire that needs oxygen. It shines because of a process called nuclear fusion happening in its core. It continuously converts hydrogen gas into helium, releasing an immense amount of energy in the process. The Sun has enough hydrogen fuel to keep shining for about another five billion years.









