




Overview of the Nitrogen
Have you ever wondered why the chip packets are so fluffed with some gas? What is the gas filled in those bags of chips? Does it harm our bodies? Does it spoil our food? The gas that is being talked about is called Nitrogen. It is used in food packaging because it displaces oxygen present here. It is a non-reactive gas used for varied purposes by humans due to its unique properties. Nitrogen is used for the production of fertilisers, nitric acid, dyes, etc. This gas is most abundant and immediate in our surroundings yet cannot be used by us directly. In this article, we will learn more facts about nitrogen, its properties of nitrogen and much more. So let’s start learning.
A Packet of Chips Filled with Nitrogen
Who Discovered Nitrogen?
We learnt what nitrogen is and where it is found in the above portion of the article. Who discovered nitrogen and identified and placed it as a unique element? 78% of the air in the atmosphere is nitrogen gas only. Daniel Rutherford discovered nitrogen. Rutherford discovered the element nitrogen officially in 1772.
Boiling Point of Nitrogen
The boiling point of Nitrogen is 195.8 degrees Celsius. And that is why Nitrogen stays as a gas in our atmosphere due to nitrogen's very low boiling point.
Characteristics of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a gaseous element on the periodic table. Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the earth's atmosphere, meaning it makes up the greatest portion of the gases we breathe in.
Nitrogen is a very major component in the bodies of both humans and plants. It is essential for their lives to continue and to translate into future generations.
Scientifically nitrogen is denoted as the alphabet N.
It is the seventh element on the periodic table.
Nitrogen has an atomic mass of 14 Atomic mass units.
Nitrogen has a density of about 1.25 grams per litre.
Nitrogen has two stable isotopes, which are N-14 and N-15. N-15 has one additional number of neutrons than that of N-15 in its atom.
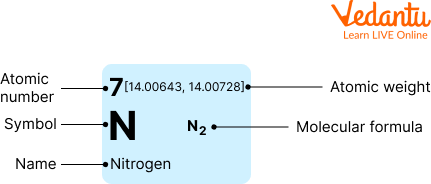
Information About Nitrogen
Properties of Nitrogen
The properties of nitrogen element are as follows:
Nitrogen is colourless, odourless, and tasteless.
It is very active and can react very easily.
Nitrogen cannot be utilised or used by living organisms directly.
Nitrogen molecules support plant growth and contribute to animal protein synthesis.
When temperatures are very low, nitrogen turns into a liquid. In that state, it can freeze dry food and maintain the coldness of food throughout long-distance transportation.
Ammonia and nitric acid are the two most noteworthy nitrogen molecules used in industrial and commercial settings. Many additional nitrogen compounds are prepared using the gas ammonia. A liquid called nitric acid is used to make explosives, fertilisers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
Uses of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a very useful element in various industries for varied purposes therefore, below are enlisted various uses of nitrogen:
Food Industry- Nitrogen gas is employed to provide unreactive conditions. Due to this, it is used to preserve foods.
Nitrogen in Bulb: Nitrogen is filled into the bulb because the bulb filament reacts easily when it comes in contact with air therefore, nitrogen provides an unreactive environment.
Fire Compressor: Nitrogen is used to make fire compressor systems
Aircraft: Nitrogen is also used as fuel in aircraft engines
Preservation: Nitrogen is also used to pressurise and preserve various drinking products.
Steel: Nitrogen is also used in steelmaking to increase the boiling point of the material being made, as the boiling point of nitrogen is very high.

Nitrogen Used as a Cooling Agent
Facts About Nitrogen
Here are some most interesting facts about nitrogen :
Nitrogen in its liquid state is very cold and can cause severe frostbite and damage to the skin if it comes in contact with liquid nitrogen.
Nitrogen is seventh on the list of most abundant elements found on earth.
About 3 per cent of our body mass is made up of nitrogen.
Fusion, a process that takes place deep inside stars, creates it.
Nitrogen plays a vital role in the formation and duplication of DNA or our genetic material.
Summary
To conclude all the learnings from this article, we can say nitrogen is one of the most important elements on earth. It is used in various life processes as well as industrial processes. Nitrogen is colourless, odourless and tasteless. It is an essential part of human DNA. we also looked at the element information of nitrogen and the boiling point of nitrogen which is as high as minus 195 degrees Celsius. Nitrogen is used in the food industry in bulbs, fire compressors, aircraft, etc. Then we also looked at some astonishing facts about nitrogen, like it makes up 3 per cent of the human body mass. Nitrogen can react very actively in nature. With this, we would like to end this article. We hope we were easy and understandable, and fun to learn with.
FAQs on Facts About Nitrogen
1. What are five key facts about the element nitrogen?
Here are five key facts about nitrogen:
It is the most abundant element in Earth's atmosphere, making up about 78% of the air we breathe.
Nitrogen is a non-metal with the atomic number 7 and the chemical symbol N.
In its pure gaseous form, it is colourless, odourless, and tasteless.
It is essential for all life, as it is a key component of amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) and nucleic acids (like DNA).
Saturn's largest moon, Titan, has a dense atmosphere that is composed of over 98% nitrogen.
2. Where is nitrogen found on Earth?
Nitrogen is found in several key places on Earth. The vast majority, about 78%, exists as a gas in the atmosphere. It is also present in the Earth's crust, dissolved in water bodies, and is a fundamental component of all living organisms, including plants and animals. Crucially, it is found in soil, where it exists in various compounds that plants can absorb to grow.
3. What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is the natural process by which nitrogen moves and changes form between the atmosphere, soil, water, and living organisms. This circulation is vital for making nitrogen available to life. The main steps are:
Nitrogen Fixation: Special bacteria or lightning convert atmospheric nitrogen gas (N₂) into usable forms like ammonia (NH₃).
Assimilation: Plants absorb these nitrogen compounds from the soil to build proteins. Animals get nitrogen by eating plants.
Ammonification: When organisms die, decomposers break them down, returning nitrogen to the soil as ammonia.
Denitrification: Other bacteria convert these compounds back into nitrogen gas, which returns to the atmosphere, completing the cycle.
4. If the air is mostly nitrogen, why can't plants and animals use it directly?
Although we are surrounded by nitrogen gas (N₂), most living things cannot use it directly because the two nitrogen atoms in the N₂ molecule are held together by a very strong triple covalent bond. This bond is extremely difficult to break. Plants and animals lack the necessary enzymes to split these molecules. Therefore, we depend on the nitrogen cycle, where certain bacteria and natural phenomena like lightning 'fix' the nitrogen, converting it into accessible compounds like ammonia and nitrates that can enter the food web.
5. What makes nitrogen so essential for all living organisms?
Nitrogen is essential for life because it is a core building block of several vital organic molecules. Without an adequate supply of nitrogen, organisms could not create:
Proteins: These molecules perform countless functions, from building muscle tissue and hair to acting as enzymes that control chemical reactions in our cells.
Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA): These master molecules carry the genetic code that directs the growth, function, and reproduction of every living thing.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): This is the primary molecule used for storing and transferring energy within cells.
6. What are some common uses of nitrogen in industry and everyday life?
Due to its properties, especially being relatively inert, nitrogen has many important uses:
Fertilisers: Its most significant application is in producing ammonia for fertilisers, which is crucial for growing the world's food crops.
Food Packaging: Nitrogen gas is used to flush oxygen out of food packages, such as bags of crisps, to prevent spoilage and keep the contents fresh.
Electronics: It creates a non-reactive atmosphere during the manufacturing of sensitive electronics to prevent defects from oxidation.
Liquid Nitrogen: In its cryogenic liquid form, it is used for freezing and preserving biological samples, in medicine for dermatology, and in producing stainless steel.
7. How is nitrogen used to keep packaged foods fresh?
Nitrogen gas is used in a technique called modified atmosphere packaging (MAP). During the packaging process, the regular air inside the bag, which contains about 21% oxygen, is replaced with pure nitrogen. Oxygen causes food to spoil by enabling the growth of aerobic microbes and causing fats to become rancid (oxidation). Because nitrogen is an inert gas, it does not react with the food, effectively preserving its flavour, texture, and crispness for a much longer period.
8. What are the main physical properties of nitrogen gas?
At standard room temperature and pressure, nitrogen gas (N₂) has several distinct physical properties. It is a colourless, odourless, and tasteless gas. It is also non-toxic and is slightly less dense than air. A key property is its very low boiling point; nitrogen becomes a liquid at -195.8°C (-320.4°F) and freezes into a solid at -210°C (-346°F).
9. Who is credited with the discovery of nitrogen?
Nitrogen was officially discovered by the Scottish physician and chemist Daniel Rutherford in 1772. While experimenting with air, he removed oxygen and carbon dioxide from a sample and found that the remaining gas would not support combustion or living organisms. He called this component "noxious air." Although other scientists like Carl Scheele and Henry Cavendish were working on it simultaneously, Rutherford is widely credited with its formal discovery.









