




Why Is Coal Important? Uses, Formation & Quick Questions
Coal is one of the most important primary fossil fuels which is a solid carbon-rich material that is usually black and most often occurs in stratified sedimentary deposits. The energy that we get from coal comes from the energy that plants absorbed from the sun millions of years ago.
The use of coal is especially prevalent in developing countries like India because it is affordable with its easy availability and low technological requirements for working with it. Let's check out some interesting coal facts and learn more about its uses and properties. Let’s dive in and learn what is coal.

Burning Coal
Information About Coal
Did you know that coal contributes to approximately 40% of the world’s electricity production? In other words, the world has always relied on this fossil fuel for energy production more than any other energy source, including natural gas, oil, nuclear sources, the sun, water, and the wind.
Now, several coal deposits present will most probably last for another 300 years, but after that, as it is an exhaustible natural resource, there will be none of this fossil fuel left.
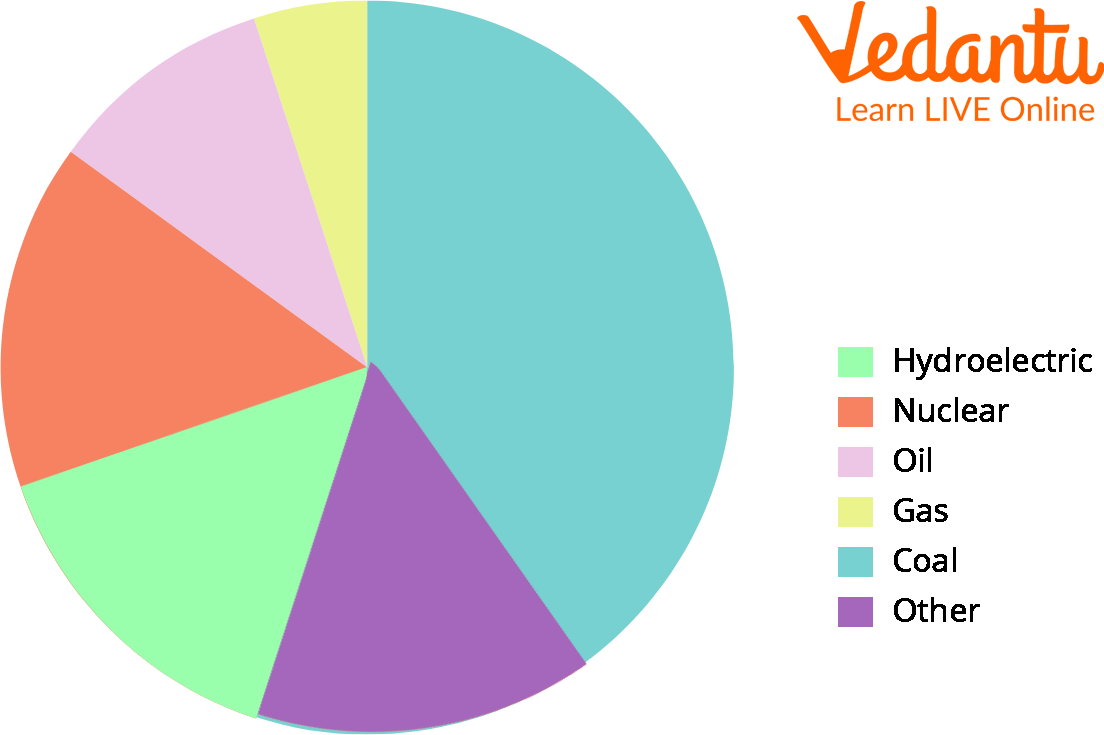
A Pie Chart Showing Resources
Uses of Coal
In many European nations such as Germany and Austria, the use of coal has decreased due to the high price of its emissions compared with other fuels such as natural gas or renewable energy sources like solar panels. As a result, these nations have experienced a sharp decline in carbon dioxide emissions over recent years that has shifted their reliance away from fossil fuels like coal towards cleaner forms of energy production.
It is used to generate electricity and heat.
It is used in households & in various industries to accomplish tasks.
It is the cheapest source of power fuel.
The iron and steel industry depends on this fossil fuel for energy.
It is also used to produce products such as coke, tar, and coal gas.
This fossil fuel was responsible for the Industrial Revolution of the 19th century.
Types of Coal
Coal is divided into 4 main types, which are anthracite, bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite. Their ranking is done by the amount and the type of carbon that is present inside the coal and its ability to produce heat when it is burned. The rank of the coal deposit determines the amount of heat and pressure that has acted on the dead and decayed matter over a prolonged period.
Coal Facts and Figures
Some interesting facts on coal are as follows:
Coal largely consists of carbon but also contains other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur and nitrogen.
Different types of coal contain different amounts of carbon content. Lignite contains around 60 to 75%, while anthracite contains more than 92%.
Anthracite is a hard, shiny, black coal which burns with a blue, smokeless flame. While the majority of coal is associated with sedimentary rock, anthracite undergoes metamorphism and is linked to metamorphic rocks.
Coal has been burned for a very long time to create electricity and heat. Its use is increasing every year, in 2006 the world consumed over 6,000,000,000,000 kilograms of coal!
Coal is the world’s largest energy source in electricity production.
Coal is converted to electricity after it is burned in a furnace with a boiler. The boiler water is further heated until it becomes steam, with the smoke then spinning turbines and generators to create the electricity.
Nearly 70% of China’s electricity comes from coal.
Coal mining and the subsequent burning of coal can have harmful effects on both humans and the environment. Examples of this include waste products, acid rain, contaminated water, poisonous emissions, high levels of carbon dioxide and increased risks of lung cancer for coal plant workers.
Summary
In this article, we learned about what coal is and its types. How coal contributes to the production of 40% of the world's electricity and can be used in household works, etc. were also discussed. We now know how coal has different types which are ranked according to the carbon content they have. Further, various facts about coal were studied, like how it also features hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur and oxygen except for just carbon and it may also cause pollution when we burn it to get heat and electricity. We hope you enjoyed reading this article; visit our website to read more such interesting topics.
FAQs on Coal Facts Every Student Should Know
1. What exactly is coal and how is it formed?
Coal is a black or brownish-black combustible sedimentary rock that can be burned for fuel and used to generate electricity. It is composed primarily of carbon, along with other elements like hydrogen, sulphur, oxygen, and nitrogen. The formation process, known as carbonisation, began millions of years ago when dense forests in swampy wetlands died and were buried under layers of sediment. Over time, intense heat and pressure transformed this organic matter into coal.
2. Why is coal referred to as a 'fossil fuel'?
Coal is called a fossil fuel because it originates from the fossilised remains of plants that lived millions of years ago. The energy stored in coal is the solar energy that these ancient plants captured through photosynthesis. When we burn coal, we are releasing this ancient, stored energy. The term 'fossil fuel' also applies to other energy sources like petroleum and natural gas, which formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms.
3. What are the main uses of coal in industries and daily life?
The primary uses of coal are widespread and critical for many sectors. Its most important applications include:
- Electricity Generation: A significant portion of the world's electricity is produced by burning coal in thermal power plants.
- Steel Production: Coal is converted into coke, which is an essential material for smelting iron ore in the manufacturing of steel.
- Industrial Fuel: Various industries, including cement and paper manufacturing, use coal as a direct source of heat and energy.
- Domestic Use: In some regions, coal is still used for heating homes and for cooking.
4. What are the main products obtained when coal is processed?
When coal is heated strongly in the absence of air (a process called destructive distillation), it breaks down into several useful products. The three main products are:
- Coke: A tough, porous, and almost pure form of carbon. It is primarily used as a fuel and a reducing agent in steel manufacturing.
- Coal Tar: A thick, black liquid with an unpleasant smell. It is a mixture of many substances used to make dyes, drugs, explosives, perfumes, and synthetic materials.
- Coal Gas: A flammable gas produced during the process, which is used as a fuel in industries located near coal processing plants.
5. How are the different types of coal, like Anthracite and Lignite, different from each other?
The main difference between types of coal lies in their carbon content, moisture level, and heating value, which are determined by the extent of transformation they have undergone.
- Anthracite: This is the highest rank of coal. It is hard, brittle, and has the highest carbon content (over 90%), producing a lot of heat with little smoke.
- Bituminous Coal: This is the most common type. It has a high heating value but also a high sulphur content. It is used extensively for generating electricity and making coke.
- Lignite: Also known as brown coal, it is the lowest grade of coal with a low carbon content and high moisture. It produces more smoke and less heat compared to other types.
6. If both coal and petroleum are fossil fuels, what is the key difference in their formation?
The primary difference between the formation of coal and petroleum lies in their source material and environment. Coal was formed from the remains of dense terrestrial vegetation like trees and ferns in ancient swampy forests. In contrast, petroleum (crude oil) and natural gas were formed from the remains of tiny marine organisms, such as algae and zooplankton, that sank to the bottom of ancient oceans and were buried under sediment.
7. Why is burning coal considered harmful to the environment?
Burning coal is considered harmful primarily because it releases a significant amount of pollutants into the atmosphere. When coal is burned, it produces large quantities of carbon dioxide (CO₂), a major greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming and climate change. Additionally, it releases other harmful substances like sulphur dioxide, which causes acid rain, and particulate matter (soot), which can lead to respiratory health problems.
8. What are the main chemical elements that make up coal?
Coal is not a single substance but a complex mixture of chemical elements. The primary element is carbon (C), which is the main source of its energy. In addition to carbon, coal contains varying amounts of other elements, including hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and sulphur (S). It also contains small amounts of mineral matter, which forms ash when the coal is burned.









