What Is the Simple Future Tense? Definition, Forms, and Uses
FAQs on Simple Future Tense Made Easy: Rules, Examples, and Practice
1. What is the simple future tense?
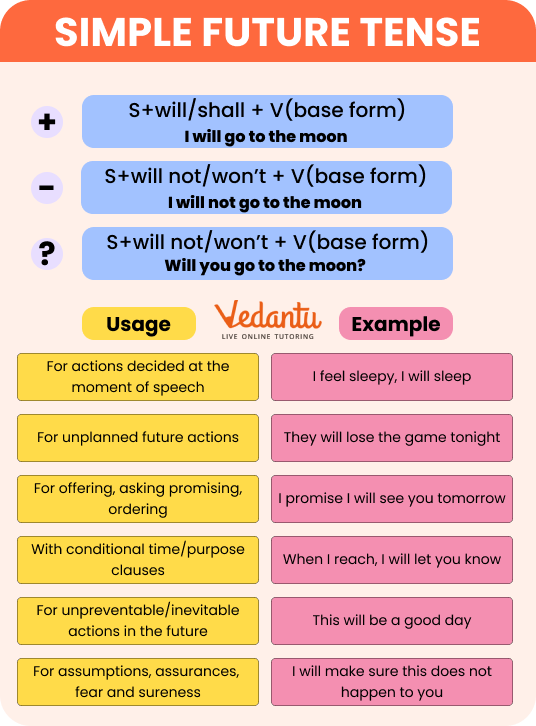
The simple future tense describes actions that will happen after the present time. It uses "will" or "going to" followed by the base form of the verb.
2. What are the Simple Future Tense rules?
The formula is: Subject + will + base form of the verb + the rest of the sentence. For example, "She will go to the store."
3. What is the difference between 'will' and 'going to'?
"Will" is used for decisions made at the moment of speaking or for predictions. "Going to" is used for plans or intentions already decided before speaking.
4. How do you form negative sentences in the simple future tense?
Add "not" after "will" to form negatives. For example, "They will not (won't) arrive on time."
5. How do you ask questions in the simple future tense?
Start with "Will" followed by the subject and the base form of the verb. For example, "Will you attend the meeting?"
6. Can you give examples of positive sentences in the simple future tense?
"I will finish my homework." "She will visit her grandparents next week."
7. How do you use the simple future tense to make predictions?
Use "will" followed by a base verb. For example, "It will rain tomorrow."
8. How can I use 'going to' in sentences?
Use "am/is/are going to" followed by the base form of the verb to talk about future plans. For example, "I am going to start a new job."
9. Are there any exceptions or irregular forms in the simple future tense?
There are no irregular forms in the simple future tense. The structure remains consistent.
10. How do you use the simple future tense in formal writing?
The structure remains the same, but ensure clarity and formality in your language. For example, "The company will release its new product next quarter."
11. What are some common mistakes with the simple future tense?
Common mistakes include using incorrect forms like "will be going" instead of "going to" or omitting "will" in positive sentences.
12. How can I practise using the simple future tense?
Practice by writing sentences, completing exercises, and using the tense in everyday conversations.
13. Can the simple future tense be used for offering or requesting?
Yes, use "will" for offers or requests. For example, "Will you help me with this task?"
14. How do you distinguish between the simple future tense and other future tenses?
The simple future tense uses "will" or "going to" and focuses on future actions or events, while other future tenses might involve different structures and aspects.