How Prepositional Phrases Improve Your Sentences
FAQs on What Is a Prepositional Phrase? Simple Guide for Students
1. What is a prepositional phrase in simple terms?
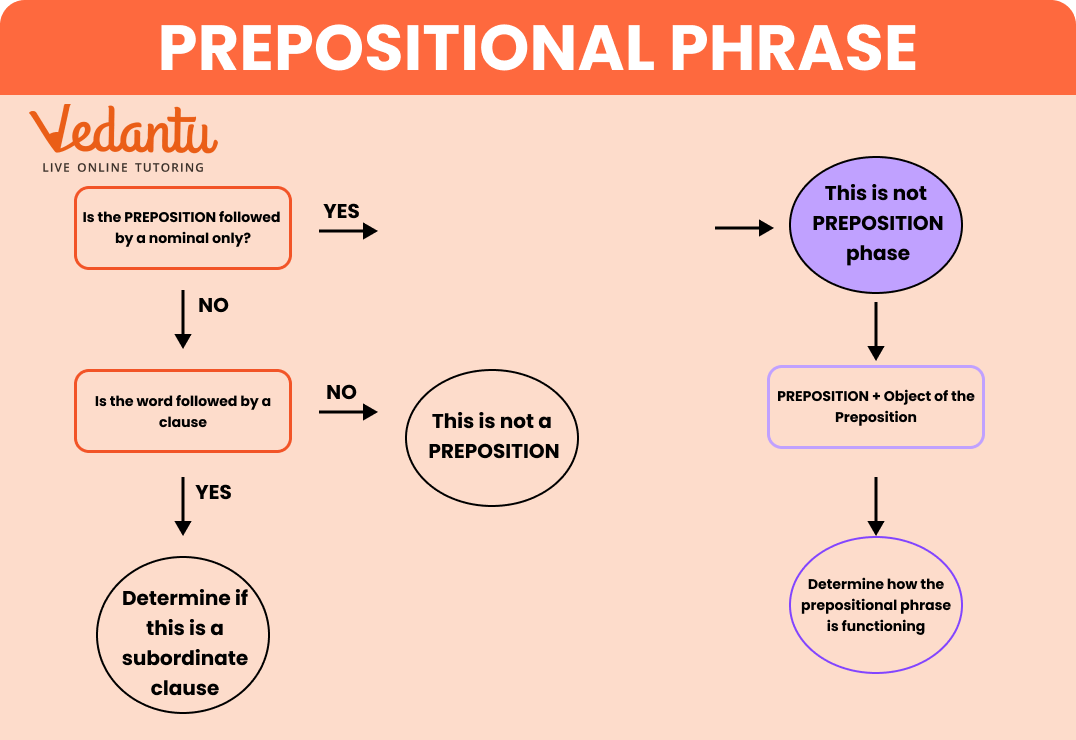
A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begins with a preposition (e.g., in, on, at, under, with) and ends with a noun or pronoun, called the object of the preposition. This entire phrase acts as a single unit to add more information to a sentence, usually describing a noun or a verb.
2. What are the essential parts of a prepositional phrase?
Every prepositional phrase has two core parts:
- The Preposition: The word that starts the phrase (e.g., after, by, for, to).
- The Object of the Preposition: The noun or pronoun that follows the preposition (e.g., school, him, the table).
3. How can you identify a prepositional phrase in a sentence?
To find a prepositional phrase, first look for a preposition. Once you find one, identify the noun or pronoun that it connects to. The preposition, its object, and any words in between (like adjectives or articles) make up the complete phrase. For example, in "The cat is sleeping on the warm blanket," the phrase is "on the warm blanket."
4. Can you give some examples of prepositional phrases?
Certainly. Prepositional phrases can describe location, time, or manner. Here are a few examples:
- Location: under the bridge, near the school, inside the box
- Time: after the class, during the night, in the morning
- Manner: with a smile, by a long shot, in a hurry
5. What are the two main types of prepositional phrases?
The two main types are distinguished by what they describe:
1. Adjectival Prepositional Phrases: These modify a noun or pronoun. Example: "The book on the table is mine." (describes the book).
2. Adverbial Prepositional Phrases: These modify a verb, adjective, or adverb. Example: "He ran with great speed." (describes how he ran).
6. How does a prepositional phrase make a sentence more detailed?
A prepositional phrase adds detail by answering important questions within the sentence. It provides context by telling the reader Where? (e.g., at the park), When? (e.g., before noon), Which one? (e.g., the dog with brown spots), or How? (e.g., with enthusiasm). This turns a simple sentence into a more descriptive and informative one.
7. What is the key difference between an adjectival and an adverbial prepositional phrase?
The key difference is the word they modify. An adjectival phrase always describes a noun or pronoun. Think of it as doing the job of an adjective. An adverbial phrase, however, describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb, doing the job of an adverb. Always ask: "What is this phrase telling me more about?" to find its type.
8. Can a sentence start with a prepositional phrase?
Yes, it is grammatically correct and very common to start a sentence with a prepositional phrase. This technique is often used to create variety in sentence structure. When a prepositional phrase starts a sentence, it is usually followed by a comma. For example: "After a long day at school, I like to relax."
9. What is a common mistake to avoid when using prepositional phrases?
A very common mistake is placing the prepositional phrase incorrectly, creating confusion. This is called a misplaced modifier. The phrase should be placed as close as possible to the word it is describing. For instance, "I saw a bird in the sky with my binoculars" is confusing. A better structure is, "With my binoculars, I saw a bird in the sky."
10. Why is it important to use prepositional phrases correctly in writing?
Using them correctly is crucial for clarity and precision. They allow you to add layers of detail, paint a vivid picture for the reader, and express complex ideas clearly. Proper placement ensures your reader understands exactly what you mean, making your writing more effective, professional, and engaging.