




Introduction
The process of connecting multiple computers together for the purposes of sharing data, offering technical support, and communicating is known as computer networking. The technology that connects various computer systems is known as the internet. The world has undergone a revolution thanks to networking technology, which has also opened up new opportunities for each country's overall growth.
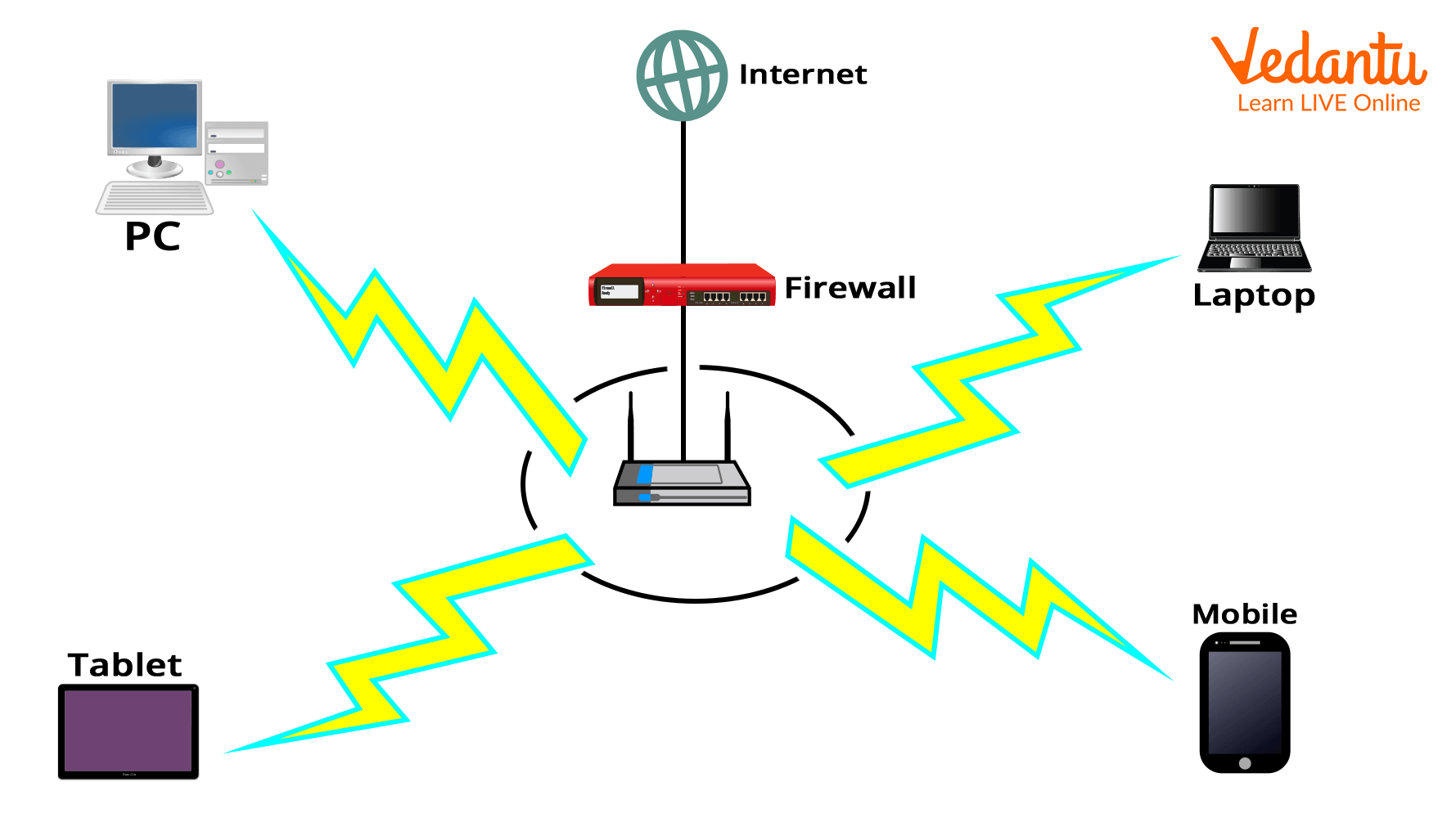
Computer Networking
Types of Networks
A Computer Network is typically classified based on its size and purpose. The following are the most commonly used computer networks:
LAN i.e. Local Area Network
WAN i.e. Wide Area Network
MAN i.e. Metropolitan Area Network
PAN i.e. Personal Area Network
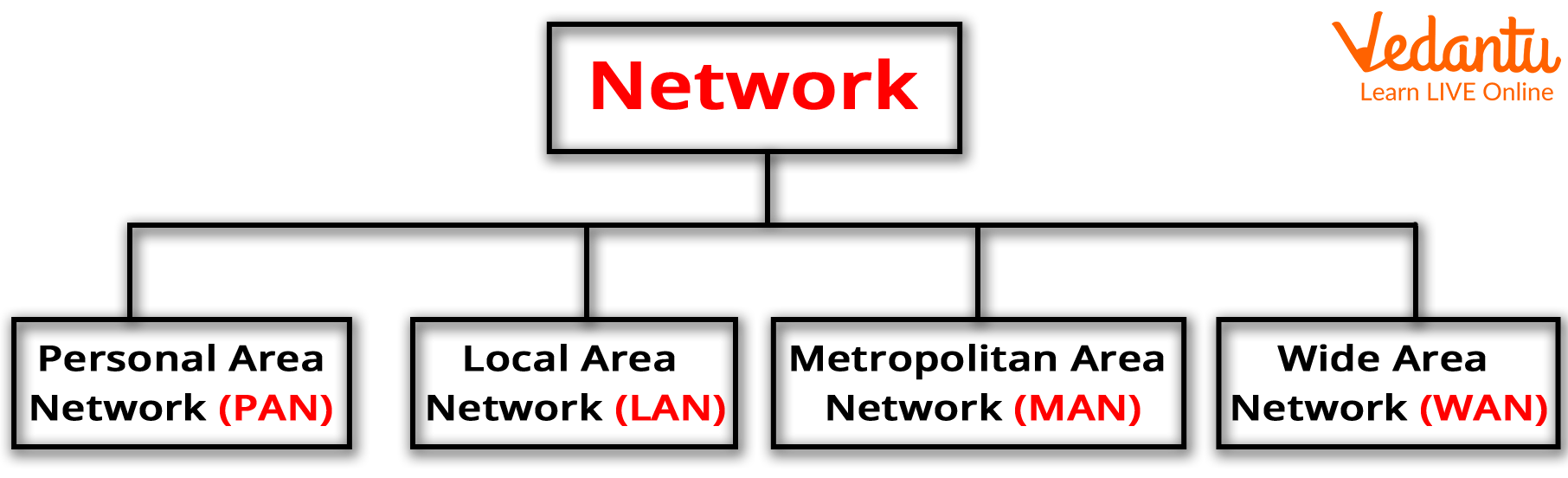
Different Types of Networks
Let's discuss them in detail.
LAN (Local Area Network)
A Local Area Network, or simply LAN, is a method of connecting a few computers in a given location. It is typically used for a single commercial office, residential apartment, school etc.
The main goal of such interconnectivity is to create a communication system to make work easier. However, in such connections, other devices such as laser printers, fax machines, and so on can be attached. It covers an area ranging from 10-15 kilometers.
Uses of LAN Network
To rapid transfer of data over a limited geographical area.
To allow for quick interconnections between individual computer units.
The number of users on a local area network can range from two or three to thousands.
Software and hardware can be used together.
With the use of emails, chats, and web forms, LAN offers its users quicker and highly customized services.
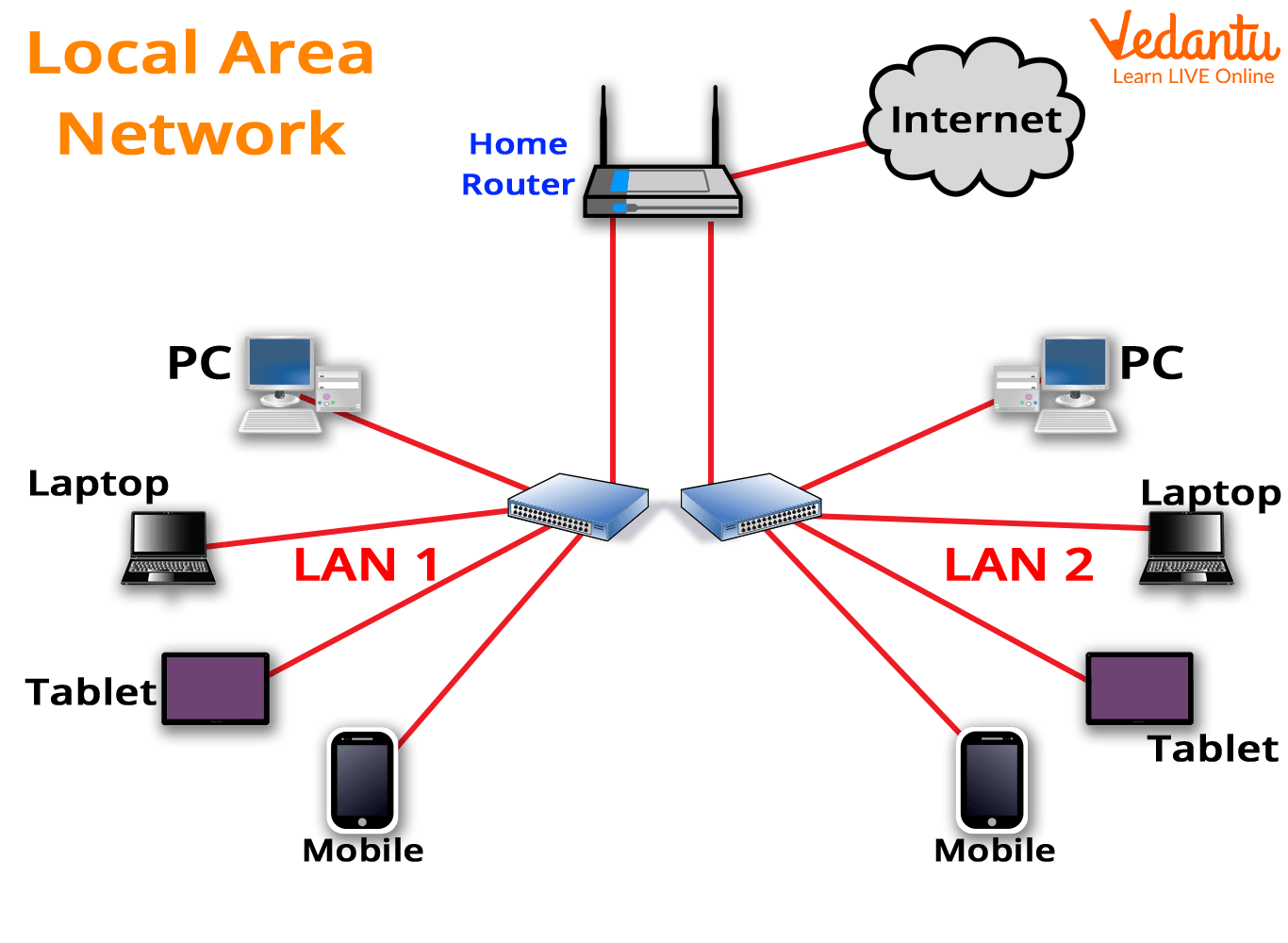
Local Area Network
WAN (Wide Area Network)
It is a network system that extends a large geographical area around the world. WAN services are provided by both Government and private organizations. The network also allows you to access databases that are located in different locations. The WAN system is extremely beneficial to MNCs and other large corporations that are offering online services. The internet is one of the world's largest WANs.
Uses of WAN Network
To enable organizations with international branches to communicate, exchange information, and stay connected between branches.
When employees arrive at work, WANs enable them to access the data they require to complete their tasks.
It enables businesses to share information with clients and partners even if they are in other countries.
It involves communication via a variety of different technologies. Point-to-point WANs such as Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) are examples of these technologies.
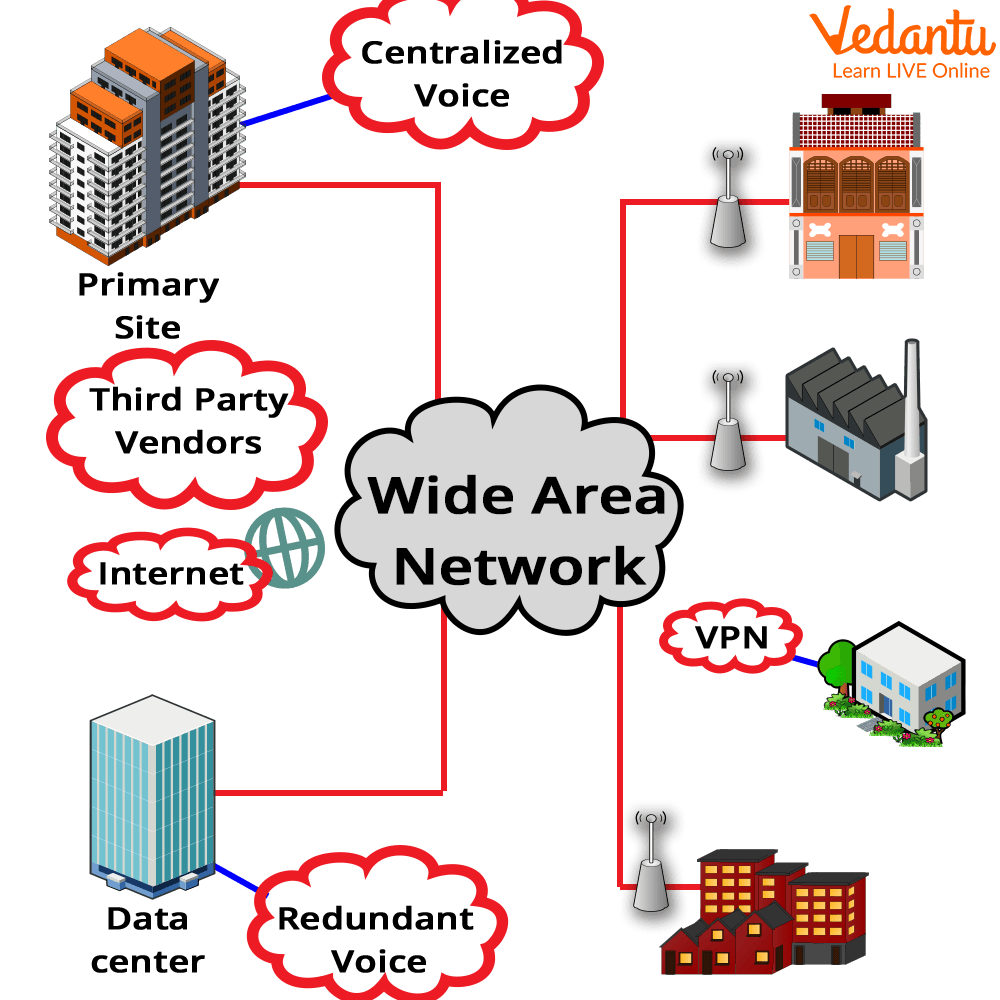
Wide Area Network
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
It is a network that connects multiple LANs to form a larger network that covers a larger geographic area. Government agencies use MAN to communicate with citizens and private businesses. MAN connects various LANs to one another via a telephone exchange line. It has a greater range than a Local Area Network (LAN).
Uses of MAN
To communicate between city banks.
It is applicable to airline reservations.
It could be used in a city college.
It can also be used for military communication.
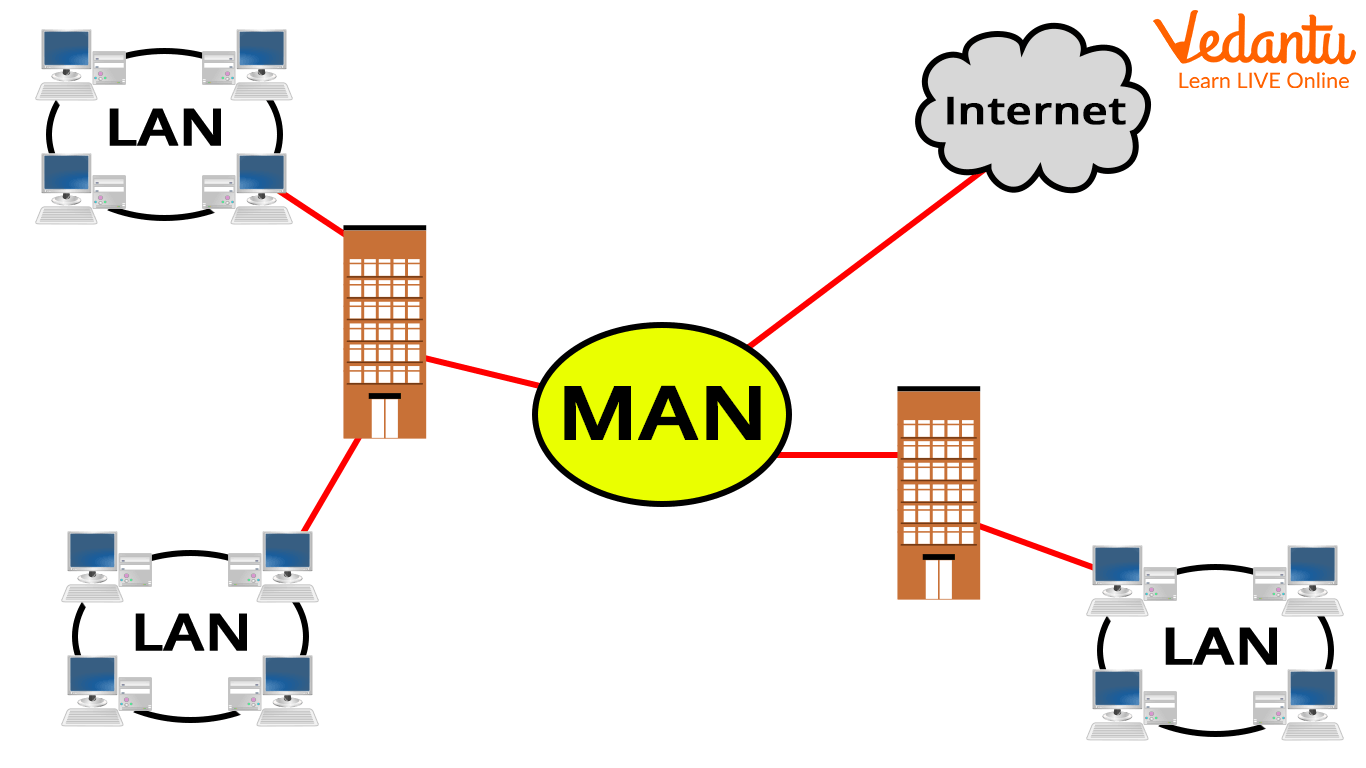
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
PAN (Personal Area Network)
It is a network that is set up by a single person, typically within a 10-meter radius. It is used to connect computer devices for personal use. It has a 30-foot radius. Personal computer devices used to develop a personal area network include laptops, mobile phones, and play stations.
Uses of PAN
It is mostly personal devices networked in a small area.
Allows you to manage the interconnection of IT devices in a single user's environment.
It can connect to the internet wirelessly via WPAN.
PAN appliances include cordless mice, keyboards, and Bluetooth systems.
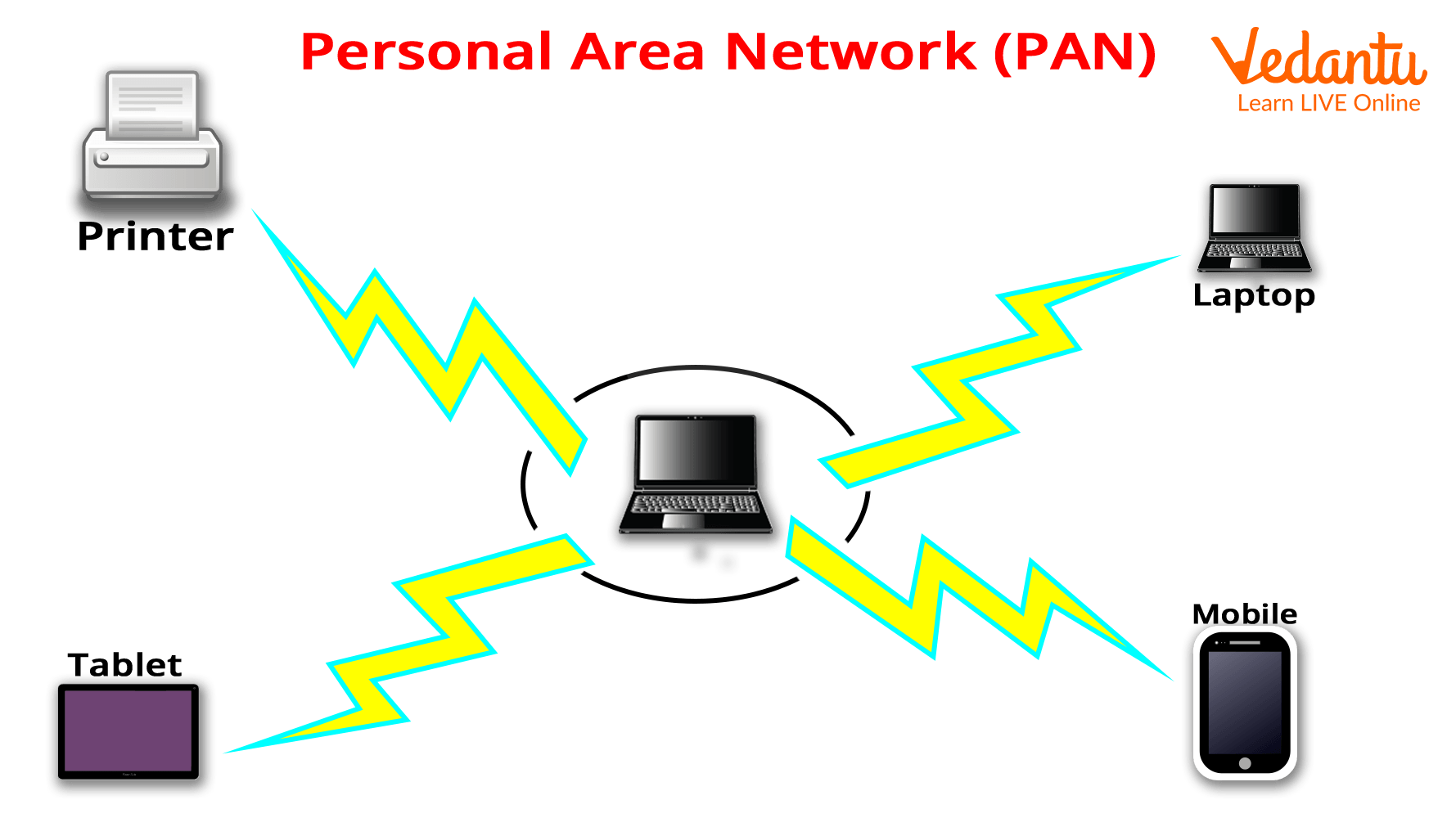
Personal Area Network
Things to Know
The Personal Area Network concept was first proposed by Thomas Zimmerman, a research scientist.
Due to restrictions on size and distance, networks can only be a certain size.
A local area network's speed can easily be increased to or exceed 1 Gbps.
Learning by Doing
1. Write abbreviations for:
ATM
HDLC
PPP
PSTN
2. Which of the following is considered the world's largest network?
Usenet
Ethernet
Internet
PSTN
None of the above
3. Which of these uses a WAN the most frequently?
University
School
MNCs Company
Local Company
Sample Questions
1. What are types of LAN?
Ans: Client/server LANs and Peer-to-Peer LANs are the two main types of LANs or local area networks. A client/server LAN is made up of various client devices that are linked to a central server. The server manages application access, device access, file storage, and network traffic.
There is no central server in a peer-to-peer local area network, and it cannot handle heavy workloads like a client/server local area network. This type of LAN is smaller in size, with each device contributing equally to network operation.
2. Which network has the smallest geographical coverage?
PAN
MAN
WAN
LAN
Ans: D) LAN i.e. Local Area Networks
3. What are the advantages of networking?
Ans: Here are some of the most significant benefits of networking.
Improve business relationships.
Networking is about giving rather than taking.
Get new ideas.
Increase your visibility.
Increase your knowledge.
Get career advice and support
Increase your confidence.
Summary
We place a high value on networking. The majority of the work is dependent on computer networks. This chapter taught you about various types of networks: LAN, WAN, PAN and MAN
FAQs on Different Types of Networks
1. What are the four main types of computer networks based on their geographical area?
The four primary types of computer networks, classified by their geographical scope, are:
- Personal Area Network (PAN): Covers a very small area, typically for a single user.
- Local Area Network (LAN): Connects devices within a limited area like a building or a campus.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Spans a larger area, such as an entire city.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): Extends over a large geographical area, connecting cities, countries, or even continents.
2. What is a Local Area Network (LAN) and where is it commonly used?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a private network that connects computers and other devices within a limited geographical area, such as a single office building, a school, or a home. Its primary purpose is to allow for the sharing of resources like files, printers, and a single internet connection among multiple users. Due to its limited size, a LAN typically offers high data transfer speeds.
3. What defines a Wide Area Network (WAN), and what is a prime example of it?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers a broad geographical area, often using public or leased communication lines to connect multiple LANs. It is used to connect offices of a multinational corporation or to provide connectivity to a global user base. The most prominent and largest example of a WAN is the Internet itself, which connects billions of devices worldwide.
4. How is a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) different from a LAN and a WAN?
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) serves as an intermediary between a LAN and a WAN. The key differences are:
- Scope: A MAN covers an entire city or a large campus, making it larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
- Infrastructure: It often connects multiple LANs within a city. For example, a university with several campuses across a city might use a MAN to connect them.
- Ownership: A MAN can be owned by a single private entity or can be a service provided by a public utility like a telecommunications company. A common example is a city's cable TV network, which can also provide internet services.
5. What is a Personal Area Network (PAN), and what kind of devices does it connect?
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is the smallest type of computer network, typically set up for an individual's personal use within a range of about 10 meters. It is used to connect a person's own devices. Common examples include connecting a laptop to a wireless keyboard, a mobile phone to a Bluetooth headset, or a gaming console to its controllers.
6. Why would a school use a LAN instead of just connecting all computers directly to the internet (a WAN)?
A school uses a LAN for several critical reasons beyond just internet access:
- Speed: Data transfer between computers on a LAN is significantly faster than over the internet, which is essential for sharing large files locally.
- Resource Sharing: A LAN allows all connected computers to share expensive resources like high-quality printers, scanners, and local file servers efficiently.
- Security and Control: A LAN is a private network, giving the school administration greater control over security, content filtering, and user access, which is much harder to manage on a public network like a WAN.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It is more economical to share a single high-speed internet connection among all users on a LAN than to provide a separate one for each computer.
7. What are the two main architectural types of a LAN?
The two main architectural models for a Local Area Network are:
- Client-Server LAN: In this model, one or more central computers, called servers, manage and provide resources like files, applications, and network access to other devices, known as clients. This architecture is robust and suitable for managing large networks.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) LAN: In this model, there is no central server. Every device on the network is equal (a peer) and can share its files and resources directly with any other device. This is simpler to set up and is typically used in small environments like homes or small offices.
8. Beyond geographical size, what key factors differentiate network types like PAN, LAN, and WAN?
Besides their geographical range, network types are differentiated by several other key factors:
- Ownership: A PAN is owned by an individual, a LAN is typically owned by a single private organization (like a company or school), while a WAN often involves multiple owners and public carriers.
- Data Transfer Speed: Generally, LANs offer the highest speeds, followed by MANs, and then WANs, as speed tends to decrease as the distance covered increases.
- Technology Used: LANs commonly use technologies like Ethernet and Wi-Fi. WANs rely on technologies designed for long-distance communication, such as MPLS, satellite links, and fiber optic cables.
- Maintenance and Cost: LANs are relatively inexpensive and easier to maintain by a local administrator. WANs are complex, costly to set up, and require specialized personnel to manage the network over large distances.
9. What are the basic components required to set up any computer network?
To establish a functional computer network, several essential components are needed. These include:
- Clients and Servers: The computers that request services (clients) and provide services (servers).
- Transmission Media (Channels): The physical or wireless pathways for data travel, such as twisted-pair cables, fiber optic cables, or radio waves.
- Network Interface Devices: Hardware that connects devices to the network, like a Network Interface Card (NIC), Wi-Fi card, router, or switch.
- Network Operating System (NOS): Software that manages network resources and allows devices to communicate.























