Biological Classification Class 11 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology Biological Classification - 2025-26
1. What are the most frequently asked topics from Chapter 2, Biological Classification, for the CBSE Class 11 Biology exam 2025-26?
For the CBSE 2025-26 exams, the most important topics from Biological Classification are:
- The criteria for R.H. Whittaker's Five Kingdom Classification.
- Salient features and examples of Kingdom Monera, Protista, and Fungi.
- Key differences between the major groups within each kingdom.
- The structure and characteristics of Viruses, Viroids, and Lichens.
- Economic importance of fungi and bacteria.
2. What kind of 3-mark and 5-mark important questions can be expected from Biological Classification?
Based on previous board trends, students can expect the following types of questions:
- 3-mark questions: Often focus on differentiation (e.g., Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria) or explaining the features of a specific group like Phycomycetes or Deuteromycetes with examples.
- 5-mark questions: Typically require a detailed explanation of the Five Kingdom Classification, a comparative analysis of two or more kingdoms, or a descriptive answer on the structure and replication of viruses.
3. Why is R.H. Whittaker's Five Kingdom Classification considered such an important question for exams?
This is a cornerstone question because it tests the student's understanding of the fundamental principles of modern taxonomy. Answering it requires knowledge of multiple criteria like cell structure, thallus organisation, mode of nutrition, reproduction, and phylogenetic relationships. It forms the basis for understanding all subsequent chapters on specific kingdoms, making it a high-weightage and frequently asked concept in exams.
4. What are some potential Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) questions from this chapter?
HOTS questions from Biological Classification aim to test analytical and application skills. Examples include:
- Justifying why viruses are considered to be on the borderline between living and non-living.
- Analysing the ecological consequences if the entire Kingdom Fungi were to disappear.
- Evaluating the limitations of the Five Kingdom system with specific examples of organisms that are difficult to place, like Euglena.
5. From an exam point of view, why is it important to study viruses, viroids, and lichens?
These topics are important because they represent exceptions and complexities in biological classification that are not covered by the five kingdoms. Questions on them test a deeper understanding of biology. Examiners often ask about the key difference between a virus and a viroid (presence of a protein coat) or the symbiotic nature of lichens. These questions help differentiate high-scoring students.
6. What common mistakes should students avoid when answering questions on Biological Classification?
To score full marks, students must avoid common errors such as:
- Confusing the characteristics of Kingdom Monera and Kingdom Protista.
- Forgetting to provide specific examples when describing kingdom features.
- Writing incomplete comparisons; always use a tabular format for differentiation questions.
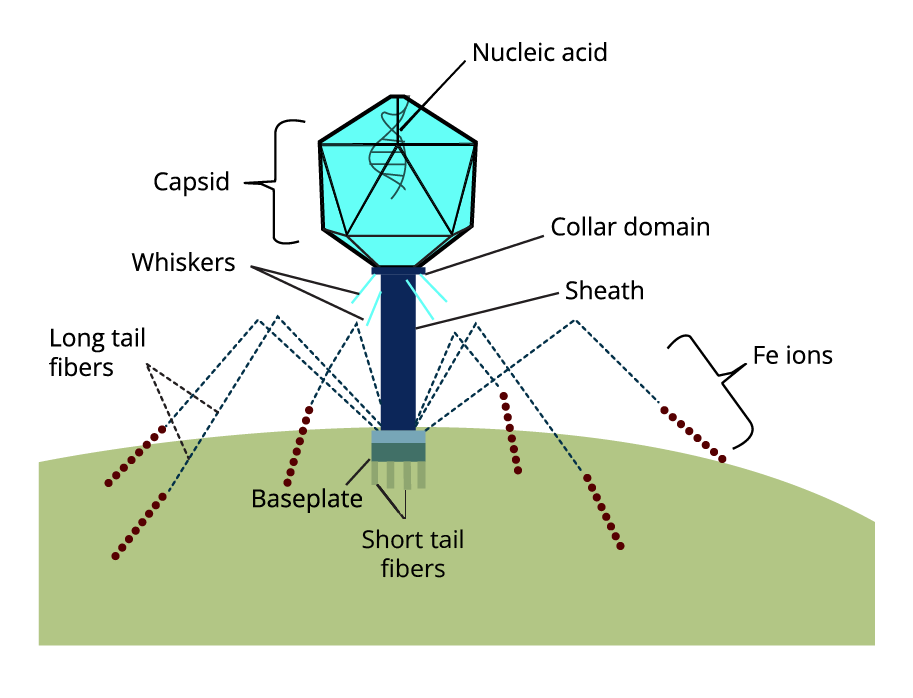
- Neglecting to draw and label diagrams where required, such as the structure of a bacteriophage.
7. How can distinguishing between different classes of Fungi be framed as an important exam question?
Questions on fungal classes are very common. A typical 3-mark or 5-mark question would ask students to differentiate between Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes based on their mycelium structure and mode of spore formation. It's crucial to mention the names of asexual and sexual spores (e.g., conidia, ascospores, basidiospores) and provide at least two examples for each class to secure full marks.
8. Besides characteristics, how might the economic importance of organisms be tested in the exam?
Questions on economic importance test the application of knowledge. Instead of a direct question, you might be asked, "Name a fungus that is a source of an antibiotic and one used in the baking industry." This requires you to recall Penicillium for antibiotics and Yeast (Saccharomyces) for baking. Similarly, questions could be framed around the role of bacteria in nitrogen fixation or causing diseases.
9. How should a student structure an answer comparing Kingdom Protista and Kingdom Plantae for a high-scoring response?
For a 5-mark comparison, use a table. The key parameters for comparison should be:
- Body Organisation: Unicellular eukaryotic (Protista) vs. Multicellular eukaryotic with tissues/organs (Plantae).
- Cell Wall: Present in some (Protista) vs. Present and made of cellulose (Plantae).
- Mode of Nutrition: Can be autotrophic or heterotrophic (Protista) vs. Primarily autotrophic (Plantae).
- Reproduction: Both asexual and sexual methods are common in both, but mechanisms differ.
10. To what extent should students prepare for the different types of protists for the 2025-26 exam?
For the CBSE exam, it's important to know the key features and one or two examples from each major group of protists. Focus on:
- Chrysophytes: Chief producers in oceans (diatoms).
- Dinoflagellates: Cause of red tides (e.g., Gonyaulax).
- Euglenoids: Mixotrophic nutrition and lack of a cell wall (e.g., Euglena).
- Slime Moulds: Saprophytic nature and formation of plasmodium.
- Protozoans: The four major groups based on locomotory structures.