




An Overview of Class 9 Biology Food Sample Test For Starch And Adulteration Experiment
Starch is a complex carbohydrate which is a polymer of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 carbon linkages. Starch containing foods are important in a balanced diet as they provide energy and help in growth and development of an organism. Adulterants are harmful ingredients added to the daily food which appears and taste like the original food but do not have the same nutrient value. Excessive consumption of such adulterants can cause cancer, stomach ulcers, brain damage, etc.
Table of Contents
Aims
Requirements
Theory
Methodology
Observations
Conclusion
Aims
(1) To determine starch content in the food sample.
Requirements
Cooked rice, potato, and bread, test tubes, Iodine solution, distilled water, dropper.
Theory
Starch is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Many moieties of glucose join together and form starch. Iodine solution is used to detect the presence of starch. Iodine converts starch containing food samples blue-black in colour.
Procedure
Add little cooked rice and water into the test tube.
Add 2-3 drops of iodine solution in the test tube and shake well.
Observe the change in colour of the sample.
Follow the same procedure for other food samples such as potato and bread and see the colour change.
Observations
After the addition of iodine solution to the various food samples, there was a formation of blue-black colouration.
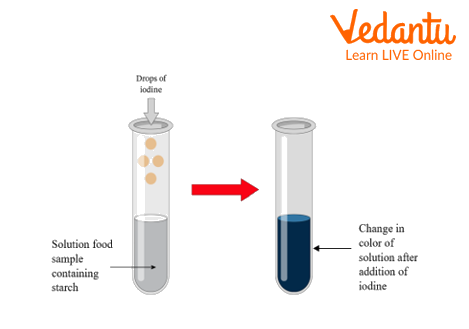
Starch detection
Result
Iodine solution when comes in contact with starch, a blue-black colour develops and hence we can conclude that the following food samples cooked rice, potato, and bread contains starch.
(2) To perform food sample tests for determining adulteration.
Requirements
Test tubes, distilled water, dropper, dal, Milk, ghee, furfural solution, conc. HCl solution, iodine solution.
Theory
A) Metanil yellow is a dye which is banned to be used as a food colour. It gives the classic yellow colour to dal and turmeric. It has harmful effects on the liver, intestine, and brain.
B) In milk, starch is used as an adulterant as it increases the solid content of the milk but reduces the fat content. As a result, adulterated milk appears thicker and heavier, same as non-adulterated milk. Pure milk when mixed with iodine solution shows coffee shade colour while adulterated milk gives a blue-black colour.
C) Vanaspati ghee is a substitute of pure cow ghee and is made from palm oil. Vanaspati ghee is partially hydrogenated vegetable oil which is cheaper and easily available as a replacement to pure ghee and hence is used as an adulterant.
Food Adulteration Experiments
Precautions
All reagents or chemicals are harmful, keep it away from eyes, nose, skin etc.
Clean the test tube before and after use.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is the stored food in plants?
Ans: The food material in plants is starch.
2. Potatoes taste sweet after a few days. Explain.
Ans: Potatoes contain starch which is made of many sugar moieties, hence as potatoes age over time, this starch is broken down into sugars and hence tastes sweet.
3. List common adulterants used in food.
Ans: Common adulterants used are:
Brick powder in red chilli powder
Urea in sugar
Mustard seeds in argemone seeds
Khesari dal in Arhar dal
4. What is the adulteration of food?
Ans: The mixing of cheaper food items with regular food which degrades the nutrients present in the food is known as adulteration of food. Adulteration is majorly done to make the product appear attractive, to make the product cheap, and to meet the daily food requirement of a rapidly increasing population.
Viva Questions
1. Name the subunits of starch.
Ans: Starch is made of glucose subunits.
2. Which is the common source of starch?
Ans: Plants are a common source of starch.
3. Reserve food material in animals?
Ans: In animals’ glycogen is the reserved food in animals.
4. Name adulterant present in milk.
Ans: A common adulterant of milk is starch which makes milk appear thick and fat.
5. Name the adulterant present in turmeric.
Ans: Adulterant present in turmeric is metanil yellow.
6. Name a chemical which assists in the detection of starch.
Ans: Iodine solution, a Brownish-yellow colour which turns blue-black comes in contact with starch.
7. Name an important chemical required to detect vanaspati adulterant.
Ans: Chemicals required to detect vanaspati in ghee is Conc. HCl and Furfural solution.
8. What does FSSAI stand for?
Ans: FSSAI stands for Food safety and Standards authority of India. It keeps a check on the quality of food supplied.
9. What do FPO and Agmrk stand for?
Ans: FPO - Food Products order
Agmark - Agriculture Marketing
10. What are adulterants of coffee?
Ans: Adulterants of coffee are powdered date seeds and tamarind powder.
Practical Based Questions
1. Name the complex carbohydrates found in plants.
Glucose
Fructose
Maltose
Starch
Ans: Starch
2. Which of the following is an example of simple sugar?
Starch
Cellulose
Table sugar
Glucose
Ans: Glucose
3. Which material is added that helps gain more profit and deteriorates the quality of the food item?
Drugs
Yellow dal
Milk
Adulterant
Ans: Adulterant
4. Shyam wanted to check the starch content of roti. Which chemical is used to test starch?
Iodine
Safranin
Methylene blue
Crystal violet
Ans: Iodine
5. Which solution is used to detect the presence of vanaspati in ghee?
Furfural solution
Iodine
Crystal violet
Formic acid
Ans: Furfural solution
6. Iodine test shows the presence of:
Carbohydrates
Sugars
Starch
Proteins
Ans: Starch
7. Which acid is used to detect adulterants in dal?
Sulphuric acid
Conc. Hydrochloric acid
Conc. Nitric Acid
Ammonia solution
Ans: Conc. Hydrochloric acid
8. Commonly used adulterant in chilli powder is?
Red colour
Pink colour
Dust
Brick powder
Ans: Brick powder
9. Which one will show a positive starch test?
Tamarind
Soyabean
Potato
Pineapple
Ans: Potato
10. Which reagent is used to detect adulteration in ghee and gives pink colour?
NaOH
H20
Furfural solution and HCl
HCl
Ans: Furfural solution and HCl
Summary
Starch is an important component of our daily diet and is a rich source for providing energy to the body. When digested starch is broken down to glucose which provides direct energy to the body. To detect the presence of the starch in a food item, a starch test is performed. Adulterants are added to the food items to contaminate them and reduce nutrient quality of the food item. It is done to gain some extra profit. Common adulterants used are starch, vanaspati, sugar syrup, papaya seeds, metanil dal, etc.
FAQs on Class 9 Biology Food Sample Test For Starch And Adulteration Experiment
1. What is the correct procedure for testing starch in a food sample, as expected for a 3-mark question in the Class 9 exam?
To answer a 3-mark question on the starch test, you should list these steps clearly:
1. Take a small quantity of the food sample and mash it.
2. Add a little water to make a paste or solution.
3. Add 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution to the sample.
4. Observe the colour change. The appearance of a blue-black colour indicates the presence of starch. Mentioning the final colour is crucial for full marks.
2. What are some important viva questions that might be asked during the practical exam on food adulteration?
During your Class 9 practical viva, a teacher might ask the following to check your understanding:
- What is an adulterant? Give an example.
- Why is food adulteration harmful?
- What is the principle behind the iodine test for starch?
- What is the chemical name for the adulterant metanil yellow?
- If a food sample does not change colour with iodine, what does that signify?
3. How do you test for metanil yellow, a common adulterant in dal, for the Class 9 practical exam?
To test for metanil yellow in dal, you should follow these steps: First, take a small amount of dal powder in a test tube and add 5 ml of water to it. Shake the mixture well. Then, add a few drops of concentrated Hydrochloric Acid (HCl). If the solution turns a magenta or pinkish-red colour, it confirms the presence of metanil yellow as an adulterant.
4. From an exam perspective, what are the key differences between the tests for starch and sugar (glucose)?
The key differences to highlight in an exam answer are:
- Reagent Used: The test for starch uses Iodine solution, while the test for sugar (glucose) uses Benedict's solution.
- Procedure: The starch test is done at room temperature, but the Benedict's test requires heating the sample.
- Positive Result: Starch gives a blue-black colour. Sugar gives a colour change ranging from green to orange or brick-red, depending on its concentration.
5. Why is it important to learn the tests for starch and adulterants for the Class 9 syllabus?
Learning these tests is important not just for scoring marks in your practical and theory exams, but also for understanding real-world science. It teaches you about the nutritional components of food and raises awareness about the serious health risks associated with food adulteration, making you a more informed consumer.
6. What is the scientific principle that causes iodine to turn blue-black in the presence of starch?
The blue-black colour appears because the iodine molecules get trapped inside the helical or coiled structure of the amylose, a component of starch. This formation of an iodine-amylose complex absorbs light differently, resulting in the characteristic dark colour. Mentioning this principle can help you score higher on HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions.
7. What could go wrong if you use a very old or improperly stored iodine solution for the starch test?
Using an old or improperly stored iodine solution can lead to inaccurate results. The iodine may have degraded or sublimated over time, making the solution too weak. This could result in a very faint colour change or no colour change at all (a false negative), even if starch is present. In an exam, this would lead to incorrect observations and loss of marks.





































