




An Overview of Class 9 Biology Animal Kingdom Experiment
Biology Experiment - Animal Kingdom
The animal kingdom is the largest kingdom containing various life forms. It includes all the organisms which show movement and locomotion. Organisms belonging to this kingdom are multicellular and eukaryotes. Most of them are heterotrophic and depend on other plants or animals for food and nutrition. No members of this kingdom contain chlorophyll. Members of this kingdom are further divided into 10 phyla depending on the complexity of their body design. Each phylum has special structures which help the organisms to survive in a particular niche or their habitat.
Table of Contents
Aim
Requirements
Theory
Methodology
Observations
Conclusion
Summary
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To observe the given specimens of earthworm, cockroach, bony fish, and bird and study their adaptive characteristics with respect to its habitat and classic features of the phylum.
Requirements
Preserved specimens of pigeon, fish, cockroach and earthworm, notebook, etc.
Theory
Adaptation is a specialised biological mechanism which helps a particular organism to adjust to the variations occurring in its habitat, in the climate and the environment as a whole. The concept of natural selection and survival of the fittest is dependent on these adaptive characteristics that an organism obtained during the process of evolution. These adaptations are the reason due to which some organisms survive while some perish.
Procedure
Observe the given specimens properly.
Identify which phylum it belongs to.
Note the characteristics of a phylum and the adaptive characteristics of the specimen.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Observations
Earthworm
Phylum - Annelida.
Classic features of this phylum:
They are hermaphrodites.
Body is segmented internally and externally, these segments are known as metameres.
Setae is the locomotory organ and is made up of chitin.
Examples - Leeches, Earthworms etc.
Adaptive features:
Earthworm lives in the soil generally in a burrow and hence has the following adaptations:
The body is long and cylindrical.
Prostomium is a sensory lobe present over the mouth and helps in digging of soil.
Excreta of earthworms contains fine soil which increases the fertility of the soil.
Castings are ring-shaped which are released through the anus.
Skin is always moist due to the presence of mucus glands.
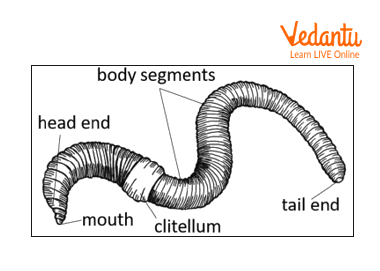
Diagram of earthworm
Cockroach
Phylum- Arthropoda.
Classic features of this phylum:
They contain jointed appendages with three pairs of legs.
Body is divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen.
Largest phylum of the animal kingdom.
Examples - Cockroaches, Crabs, etc.
Adaptive features:
Members of this phylum reside in wet, dark, and warm places. They are nocturnal.
Their body is covered with chitinous cuticles which prevent the movement of water inside the body.
They contain two compound eyes and a triangle head which helps to move through drainage pipes and sewers.
There are spiracles on either side of the body which assist in respiration.
Antennae contain tactile receptors which help in the detection of physical objects in dark.
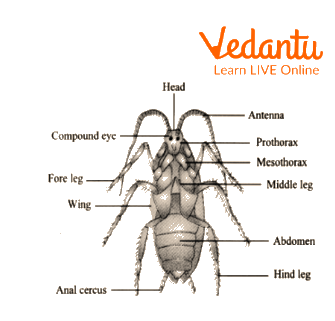
External features of cockroach
3. Bony fish
Phylum- Chordata, Subphylum- Vertebrata, Class- Pisces.
Classic features of this phylum:
They contain a well-developed notochord.
They contain a post-anal tail.
Classic features of class Pisces:
They contain paired gills covered with operculum.
They are exclusively aquatic.
Contain a terminal mouth.
Adaptive features:
Bony fishes are exclusively aquatic. Following are its adaptive features:-
Entire body is covered with scales.
Body is streamlined for ease in swimming.
Fins are used for locomotion. Dorsal and Pelvic fins assist in movement and balancing, Pectoral fins behave like brakes whereas navigation is done by the caudal fin.
Specialised air bladder provides buoyancy.
Eye is protected by the nictitating membrane.
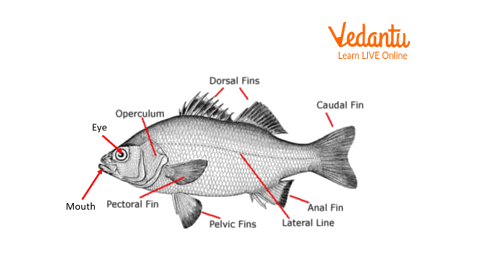
External features of Bony fish
Bird
Phylum- Chordata, Subphylum- Vertebrata, Class- Aves.
Classic features of this phylum:
They contain a well-developed notochord.
They contain a post-anal tail.
Classic features of class Aves:
They contain wings which are modified forelimbs.
They show oviparous modes of reproduction.
They contain specialised beaks which are used for catching twigs and eating food.
Adaptive features:
They have an aerial mode of life. Following are its adaptations:
Body is streamlined which reduces resistance to air when flying.
They contain hollow bones which reduce the weight of birds.
Feathers help in flying and provide insulation.
Eyes are protected by a nictitating membrane.
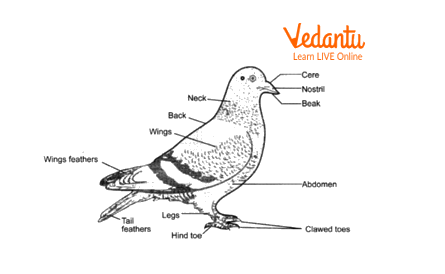
External features of pigeon
Result
Various animals of phylum Annelida, Arthropoda, and Chordata were observed and their adaptive characteristics were studied.
Precautions
All the specimens should be carefully handled and diagrams should be neat and accurately labelled.
Lab Manual Questions
1. Name the phylum to which leeches, crabs, bony fish, and sparrows belong to.
Ans: Leeches belong to phylum Annelida, Crabs belong to phylum Arthropoda, and bony fish and sparrows belong to phylum Chordata.
2. Clitellum is found in which body segment?
Ans: 14-16 segments of the earthworm contains the clitellum.
3. State two most important adaptive characteristics of Aves.
Ans: Hollow bones which decrease the weight of the body and Nictitating membrane to protect the eye.
4. What is the use of antennae in cockroaches?
Ans: Antennae in a cockroach are sensory in function and contain various receptors such as olfactory, tactile, thermal, etc. which detect smell, physical objects, temperature etc.
Viva Questions
Which animal class do birds belong to?
Ans: Birds belong to class Aves of Subphylum- Vertebrata, phylum- Chordata.
State two adaptations of cockroaches.
Ans: Chitinous exoskeleton and Antennae with various receptors.
What are adaptations?
Ans: Modifications of an organism which assist it to survive in a particular habitat are known as adaptations.
Why is the skin of earthworms always moist?
Ans: Moist skin helps in better respiration, hence skin of earthworm is moist so that it can breathe under the soil.
Which structure helps earthworms sense the soil?
Ans: Prostomium is a smally sensory lobe present over the mouth which helps in sensing soil.
What is the advantage of a streamlined body?
Ans: Streamlined body reduces the resistance faced by the organism body due to water currents or fast winds.
State the meaning of the word amphibians.
Ans: Amphibians mean which can survive in two habitats or can have two modes of life, i.e., one in water and other on land. Example - Frogs, toads etc.
How do cockroaches survive in damp places?
Ans: Due to the chitinous exoskeleton, cockroaches can survive in damp places.
Which organ is vestigial in humans but not in birds and fishes?
Ans: Nictitating membrane.
Importance of feathers in birds.
Ans: Feathers are useful in flying and also provide insulation to birds.
Practical Based Questions
1. Meaning of arthropod is_____
Compound eyes
Joint appendages
Streamline body
Pseudocoelom
Ans: Joint appendages
2. Exoskeleton of cockroaches is of
Lignin
Cellulose
Pectin
Chitin
Ans: Chitin
3. Annelids do not contain______.
Nephridia
Metameric segmentation
Prostomium
Notochord
Ans: Notochord
3. For preserving old animal specimens the following is used?
Alcohol
Water
Formalin
HCL
Ans: Formalin
4. What are the special characters of phylum Chordata?
Streamline body
Presence of notochord
Presence of wings
Presence of gills
Ans: Presence of notochord
5. Which of the following is a true fish?
Star fish
Jellyfish
Golden fish
Bony fish
Ans: Bony fish
6. Jaws of birds contain:
10 teeth and beak
20 teeth and beak
32 teeth and beak
Beak and no teeth
Ans: Beak with no teeth
7. Which of the following belongs to the Animal kingdom?
Dogs
Funaria
Amoeba
Mushrooms
Ans: Dogs
8. Which of the following is the diagram of earthworm?
Ans: B
9. Mode of reproduction in birds is:
Viviparous
Oviparous
Ovoviviparous
Brooding
Ans: Oviparous
Summary
Animal kingdom is a diverse kingdom harbouring various animals from the primitive forms such as sponges to advanced forms such as humans. Animals belonging to each phyla have specific adaptive characters which assist them in adjusting to their habitat.
FAQs on Class 9 Biology Animal Kingdom Experiment
1. What are the three most important features used for the primary classification of animals as per the CBSE Class 9 syllabus?
The primary basis for classifying animals for your exam involves three key features:
- Levels of Organisation: Whether the animal has a cellular (e.g., Sponges), tissue (e.g., Coelenterates), organ, or organ-system level of organisation.
- Body Symmetry: This describes whether the body can be divided into identical halves. It includes asymmetry (Sponges), radial symmetry (Coelenterates), or bilateral symmetry (most other animals).
- Nature of Coelom: The presence or absence of a true body cavity (coelom) between the body wall and the gut wall is a major classification point. Animals can be acoelomates, pseudocoelomates, or coelomates.
2. Differentiate between an open and a closed circulatory system with an example of a phylum for each.
This is a frequently asked question in exams. The main differences are:
- An open circulatory system is where blood is pumped out of the heart and flows through body cavities called sinuses, directly bathing the tissues. This is characteristic of the phylum Arthropoda (e.g., cockroach).
- A closed circulatory system is where blood is always contained within vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) and circulates throughout the body. This is seen in the phylum Annelida (e.g., earthworm) and all Chordates.
3. List three defining characteristics of the phylum Arthropoda. Why is this phylum considered the most successful in the animal kingdom?
Three defining characteristics of Phylum Arthropoda that are important for exams are:
- They possess a hard chitinous exoskeleton which provides protection, prevents water loss, and supports the body.
- They have jointed appendages (like legs and antennae) which are adapted for various functions like walking, feeding, and sensing.
- Their body is typically segmented into a head, thorax, and abdomen.
Arthropoda is considered the most successful phylum because it includes over 80% of all known animal species and they have successfully adapted to nearly every habitat on Earth, from deep oceans to high mountains.
4. What are the four main features of Class Reptilia that distinguish them from Amphibia?
For your Class 9 exams, remember these four key features of Class Reptilia:
- Cold-blooded (Poikilothermic): They cannot regulate their internal body temperature and depend on the environment.
- Respiration: They breathe exclusively through lungs throughout their entire life.
- Heart: They typically have a three-chambered heart (except crocodiles, which have four chambers).
- Reproduction: They lay hard-shelled, amniotic eggs on land, which prevents them from drying out and removes their dependence on water for reproduction.
5. What is a notochord, and why is it a significant feature in the classification of animals?
A notochord is a flexible, rod-like structure that runs along the dorsal (back) side of an animal during its embryonic stage. Its significance in classification is fundamental:
- Animals that possess a notochord at any stage of their life are classified under the phylum Chordata.
- Animals that completely lack a notochord are grouped as Non-chordates.
In vertebrates, a sub-phylum of Chordata, the notochord is replaced by the vertebral column (backbone) in the adult stage.
6. Justify with two important points why an earthworm is called a 'farmer's friend'.
An earthworm is considered a 'farmer's friend' because its activities are highly beneficial for soil health. Two key reasons are:
- Soil Aeration and Porosity: By continuously burrowing through the soil, earthworms create micro-tunnels. These channels allow air and water to penetrate deeper, improving aeration and drainage which is crucial for healthy plant roots.
- Nutrient Enrichment: Earthworms ingest soil and decaying organic matter. Their excretions, known as worm castings, are rich in essential plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This process of vermicomposting naturally enhances soil fertility.
7. What is the key evolutionary difference between Amphibia and Reptilia regarding their dependence on water for reproduction?
The key evolutionary difference lies in their egg structure and life cycle, which is a very important concept for exams:
- Amphibians (like frogs) are tied to water for reproduction. They lay soft, shell-less eggs that would dry out on land. Their larvae (tadpoles) are also aquatic and breathe through gills.
- Reptiles (like lizards) made a major evolutionary leap by developing the amniotic egg. This egg has a tough, protective shell that prevents dehydration, allowing them to lay their eggs on land and be completely independent of water for reproduction.
8. Why is bilateral symmetry considered a more advanced feature than radial symmetry in the animal kingdom?
Bilateral symmetry is considered a significant evolutionary advantage because it is directly linked with cephalization. This is the formation of a distinct head region where sensory organs (eyes, antennae) and the brain are concentrated. This arrangement allows a bilaterally symmetrical animal to move purposefully in a forward direction, actively seeking food and better detecting and responding to threats from its environment. Radially symmetrical animals, in contrast, are often stationary (sessile) or slow-moving and react to stimuli from all directions equally.
9. State three important differences between Chordates and Non-chordates that are likely to be asked in an exam.
For the CBSE Class 9 (2025-26) exam, the three main differences to remember are:
- Notochord: Chordates possess a notochord at some life stage, while Non-chordates do not.
- Nerve Cord: In Chordates, the central nerve cord is dorsal (on the back), hollow, and single. In Non-chordates, it is ventral (on the front), solid, and often double.
- Heart Position: If a heart is present, it is located on the ventral side of the body in Chordates. In Non-chordates, the heart is typically on the dorsal side.





































