




An Overview of Class 12 Chemistry Introduction To Basic Laboratory Equipment Experiment
The science laboratory is an environment where basic experimental skills are taught through the systematic performance of a set of prescribed and properly designed experiments. Students must follow the rules and regulations in the laboratory and be familiar with the general facilities and equipment. The typical science laboratory consists of a working table, some items of common utility, and a storage space for equipment, chemicals, and glassware. Here students learn about preparing, identifying, and estimating chemical substances. The student must know where to get the necessary apparatus and where to place the chemicals before starting an experiment.
Table of Content
Aim
Theory
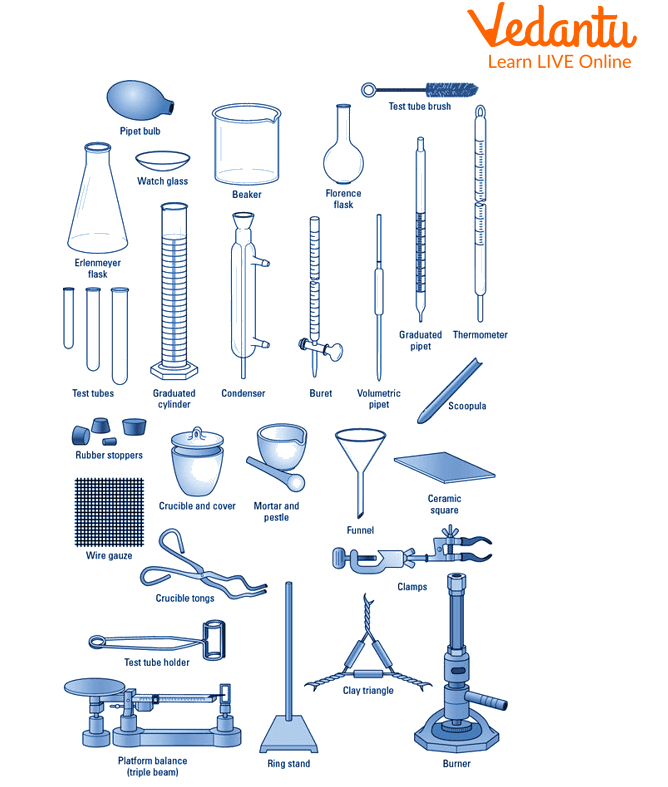
Apparatus required
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Aim
To give an introduction to the basic laboratory equipment.
Theory
All the chemistry lab equipment serves different purposes. For example, test tubes can be used to store and mix reagents during chemical reactions, beakers can be used for storing, heating, or mixing substances. Measuring cylinders are narrow cylindrical-shaped instruments used for measuring liquid volumes, and wire gauzes are used to hold flasks or beakers while heating.
Apparatus Required
Working table
Fume cupboard
Side Shelves
Exhaust Fans
Balance Room
Test tubes
Beakers
Funnel
Conical flask
Measuring cylinder
China dish
Glass rod
Tripod Stand
Wire gauze
Bunsen burner
Wash bottles
Procedure
Students must familiarise themselves with the following fittings in chemistry laboratories.
Students working table: Concrete or wooden tables are given for work. Each seat contains:
Sinks and Water Taps: Every two reagent shelves have a sink and a water faucet. Two taps on either side of the sink usually supply water.
Reagent Shelves: Reagents used in the laboratory are placed on the reagent shelf. For example, acids such as HCl, H2S04, HN03, etc., and bases like NH4OH, NaOH, etc.
Gas Taps: These are fitted on the seats for gas supply to the burners.
Fume Cupboard: The laboratory includes at least one fume cupboard where experiments release harmful gases or vapours.
Side Shelves: Two large shelves are provided on the laboratory's walls. Chemicals and reagents are not frequently used and are put on these shelves. Sometimes, solid chemicals may be placed on a different shelf.
Exhaust Fans: Two exhaust fans are provided at the laboratory's two comers to remove poisonous gases and vapours from the laboratory.
Balance Room: In this room, a collection of balances is used for weighing the substances in each laboratory.
Common Lab Instruments Name List:
Test tubes are usually cylindrical glass pipes with circular openings on one side and rounded bottoms on the other. They are available in different sizes, but the most common is 18x150 mm. A test tube is one of the most important apparatuses since it can store and mix reagents during chemical reactions.
Beakers: Glass beakers have a flat bottom, an upper opening, and a spout or no spout, and they come in various sizes. The beakers can be of different sizes and are used for storing, heating, or mixing substances.
Funnel: The funnel is necessary for pouring substances and solutions into conical flasks and narrow-mouthed test tubes. Filters, thistles, and dropping funnels are the most common types.
Conical flask: The conical flask is cylindrical with a flat circular bottom. Since it is mostly used in titrations, it is also called a titration flask.
Measuring cylinder: Measuring cylinders are narrow cylindrical-shaped instruments for measuring liquid volumes. Each marked line on the graduated cylinder symbolises the measured volume of liquid.
China dish: A china dish, also known as the evaporating dish, is made of porcelain. China dishes are thick and come in different sizes. Since they are insulators and can resist higher temperatures, they are used for crystallisation, evaporation, and boiling.
Laboratory apparatus

Laboratory apparatus (Test tubes, beaker, funnel, conical flask, measuring cylinder, China dish)
Glass rod: A glass rod is an object used for mixing. When decanting supernatants, stir rods are used because they form a contact between the supernatants' surface and the side of the glassware, preventing the liquid from running down the side.
Tripod stand: A tripod stand consists of three legs and helps to place beakers, flasks, or china dishes.
Wire gauze: Wire gauze is a net-like, thin metal sheet placed on the tripod stand to hold flasks or beakers while heating.
Bunsen burner: Bunsen burners create a single flame for sterilisation, combustion, and heating.
Wash Bottle: A squeezing bottle with a nozzle for rinsing lab apparatus such as flasks and test tubes. The liquid inside the bottle becomes pressurised and is forced through the nozzle when pressure is applied.
Practical Notebook: Every experiment should be noted down in a practical notebook. Students must maintain regularity in the practical notebook, which should always have
The experiment name and the particular date.
Apparatus required and the principle of the experiment.
The procedure of the experiment, along with observations and results.
Some other apparatuses are required in a chemistry laboratory, such as test tube brushes, test tube holders, spatulas, crucible tongs, clamp stands, watch glasses, pipettes, burettes, water baths, a centrifuge, and a sand bath.
Instructions to Work in Laboratory
Ensure that all the chemistry lab apparatus is thoroughly cleaned before use.
Be careful handling the glass apparatus, and immediately inform your teacher if any part breaks.
Allow water to run for a while by opening the water tap after disposing of all waste liquids in the sink.
Make sure your seat is clean, and if corrosive chemicals are spilled, wash them off with water.
As soon as you have completed your laboratory work, wash your hands with soap.
Observation
Different chemistry laboratory apparatus and their uses with pictures are observed.
Result
With the help of the following experiment, students can easily recognize different laboratory equipment and understand the instructions to be followed before experimenting.
Precautions
In the chemistry laboratory, you should always wear an apron, an eye protector, and a pair of gloves.
As some chemicals are corrosive, do not touch them with your hands.
You should always read the label on any reagent or chemical before using it and never use an unlabeled one.
The flame should not be exposed to inflammable liquids like alcohol or ether.
It is always advisable to add acid to the water and not water to acids.
Heating or adding reagents should never be done with the test tube pointed toward yourself or your neighbours.
Always fan chemicals or vapours gently towards your nose when you smell them.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is the use of wire gauze in a laboratory?
Ans: Wire gauze is a net-like, thin metal sheet placed on the tripod stand to hold flasks or beakers while heating. Since we cannot heat glass apparatus directly in the flame, we use wire gauze to hold them.
2. What is the first aid treatment if you get acid in the eyes?
Ans: If we get acid in the eyes, we should wash the eyes with clean water and then with sodium bicarbonate (1%) solution and again wash with clean water.
3. Why do we need a fume cupboard in a laboratory?
Ans: A fume cupboard is required in a laboratory to conduct experiments releasing harmful gases or vapours.
4. We should not smell chemicals directly. Why?
Ans: Some chemicals may have hazardous effects on our health. Some reagents may irritate the nose, eyes, lungs, and throat. So we should not smell them directly.
Viva Questions
1. Why do we need a wash bottle in a laboratory?
Ans: Wash bottle is required to produce a thin water stream to wash and transfer a precipitate.
2. Which chemical do you apply if you get a minor cut on your hand?
Ans: Methylated spirit is used for the minor cut on the hand.
3. Which equipment is used during filtration?
Ans: A funnel is used during filtration.
4. What is the use of a tripod stand?
Ans: Tripod stand can be used to support a beaker or a china dish while heating on a flame.
5. Which flame is used for the charcoal cavity test?
Ans: Luminous flame is used for the charcoal cavity test.
6. What are the metals used to make wire gauze?
Ans: Iron, copper, nichrome, or steel can be used to make wire gauze.
7. Why do you wear an apron in a chemistry laboratory?
Ans: Aprons protect our clothes from stains or spills. Aprons keep us protected against acids and corrosive chemicals.
8. What do you apply to your skin if you get a burn wound?
Ans: Burnol or mustard oil can be applied on a burn.
9. Which apparatus is used in volumetric analysis to carry out titration
Ans: Conical flask is used in volumetric analysis to carry out the titration.
10. What is the application of a crucible tong?
Ans: A crucible tong is used to hold crucibles, flasks, small beakers, or China dishes that are hot.
Practical-Based Questions
Which apparatus is used for measuring liquid volumes?
A) Conical flask
B) Measuring cylinder
C) Burette
D) Centrifuge
Ans: B) Measuring cylinder
Which of the following chemical is used to wash the eyes if you get alkali in the eyes?
A) Boric acid
B) Nitric acid
C) Sodium hydroxide
D) Hydrochloric acid
Ans: A) Boric acid
Which of the following apparatus is used to stir a liquid mixture?
A) Spatula
B) Glass rod
C) Test tube
D) Pipette
Ans: B) Glass rod
China dish is made of ____.
A) Glass
B) Silver
C) Aluminum
D) Porcelain
Ans: D) Porcelain
Which part of a burner is used to regulate the air supply?
A) Glass inlet tube
B) Burner tube
C) Air regulator
D) Base
Ans: C) Air regulator
Which first aid treatment should be given if someone swallows caustic alkali??
A) Drink a lot of water
B) Drink lemon juice
C) Drink orange juice
D) All the above
Ans: D) All the above
Which instrument is used to separate different fluids based on their densities?
A) Colorimeter
B) Centrifuge
C) Spectrometer
D) None of the following
Ans: B) Centrifuge
Which apparatus is used to remove the poisonous gases from the laboratory?
A) Exhaust fans
B) Fume cupboard
C) Side Shelves
D) Table fans
Ans: A) Exhaust fans
Bunsen burners create a single flame that is used for
A) Sterilization
B) Combustion
C) Heating
D) All the above
Ans: D) All the above
Generally, a spatula is made up of which material?
A) Plastic
B) Copper
C) Stainless steel
D) Aluminum
Ans: C) Stainless steel
Conclusion
The student must know where to get the necessary apparatus and where to place the chemicals before starting an experiment. All the chemistry lab equipment serves different purposes. The conical flask is a cylindrical flask with a flat circular bottom. Since it is mostly used in titrations, it is also called a titration flask. Wire gauze is a net-like, thin metal sheet placed on the tripod stand to hold flasks or beakers while heating. In the chemistry laboratory, you should always wear an apron, an eye protector, and a pair of gloves.
FAQs on Class 12 Chemistry Introduction To Basic Laboratory Equipment Experiment
1. What types of questions are considered important from the 'Introduction to Basic Laboratory Equipment' topic for the Class 12 CBSE exams?
For the Class 12 Chemistry board exam, important questions from this topic typically focus on:
- Identifying common lab apparatus from diagrams.
- Stating the specific function and principle of equipment like burettes, pipettes, and volumetric flasks.
- Drawing neat, labelled diagrams of apparatus used in titrations.
- Explaining the significance of key safety protocols in the laboratory.
2. Which diagrams of laboratory equipment are frequently asked in the Class 12 Chemistry practical exams for 2025-26?
Students should focus on practising neat, labelled diagrams for the following essential apparatus:
- Burette and Pipette: Emphasise the calibration marks and stopcock/bulb.
- Volumetric Flask: Clearly show the single graduation mark on the neck.
- Conical Flask and Beaker: Differentiate their shapes and uses.
- Setup for Titration: An assembly showing the burette, pipette, conical flask, and stand.
3. What are the crucial safety rules that I must mention if asked in an exam or viva?
Examiners expect you to know and state these critical safety measures:
- Always wear a lab coat and safety goggles to prevent injury from chemical splashes.
- Never handle chemicals with bare hands; use gloves or a spatula.
- Do not taste or directly smell any chemicals; gently waft vapours towards your nose if needed.
- Ensure you know the location and use of the fire extinguisher and first-aid kit.
4. How can I score full marks on a question about the difference between a beaker and a conical flask?
To get full marks, don't just describe their shapes. Explain their functions in context. State that a beaker is used for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, but not for accurate measurement. Mention that a conical flask is ideal for titrations because its narrow neck minimises splashing and allows for swirling the solution without loss of contents.
5. Why is it so important to differentiate between a pipette and a measuring cylinder in an experiment?
This distinction is crucial because it relates directly to experimental accuracy, a key concept in chemistry. A pipette is designed to deliver a highly accurate and precise fixed volume of liquid (e.g., 20.0 mL). A measuring cylinder provides only an approximate volume. Using a measuring cylinder for a titration would introduce significant errors, and explaining this demonstrates a deeper understanding of quantitative analysis.
6. What is a common mistake students make when answering questions about lab apparatus, and how can I avoid it?
A common mistake is giving a vague or incomplete use for an apparatus. For example, instead of just saying a volumetric flask is for 'making solutions,' a better answer for full marks would be: 'A volumetric flask is used to prepare a standard solution of a known concentration with a high degree of accuracy, as indicated by the single graduation mark on its neck.' Always be specific and link the apparatus to its precise function.
7. Are questions about lab equipment ever linked to numerical problems in the theory paper?
Yes, they can be. A question on molarity or stoichiometry might have a follow-up part asking you to name the primary apparatus required to perform the experiment accurately. For instance, after calculating the mass of oxalic acid needed to make a 0.1 M solution, you might be asked which pieces of equipment (like a volumetric flask and a weighing balance) are essential for its preparation.
























