




How Does Soap Work Differently in Soft and Hard Water? - Key Concepts for Class 10 Chemistry Exam Preparation
Chemistry Experiment - Study the Comparative Cleaning Capacity of a Sample of Soap in Soft and Hard Water
Hygiene is very important in the case of humans. The removal of impurities such as soil, oil droplets, food wastes, etc. made easier with the help of soaps. Soap is a potassium or sodium salt of long-chain carboxylic acid and when they dissolve in water it can remove the dirty particles present on a particular surface. Soaps are the first-ever detergent used for removing dirt currently soaps in different varieties are available. The ability of soap to remove dirt closely depends on the type of water used for removing the dirt. There are two types of water, hard and soft water. The action of soap is also different.
Table of Content
Aim
Cleaning capacity of soap in hard and soft water
Emulsification effect of soap in hard and soft water when a drop of cooking oil is added
Result
Aim
To study the comparative cleaning capacity of a sample of soap in soft and hard water.
Materials Required
Soap solution
Distilled water
A sample of soap
Dropper
A measuring cylinder (50 mL)
Test tube stands three beakers (100 mL): three glass rods
A measuring scale
Underground water
Three test tubes (20 mL)
Hard water
A physical balance and weight box
Three glass rod
Three beakers (100mL)
Theory
The hardness of water is its soap releasing capacity.
The presence of a high concentration of minerals such as calcium and magnesium ions (sulphates, chlorides, and hydrogen carbonates) makes water hard.
The addition of soap to hard water results in the formation of scum and is due to the reaction of salts present in the hard water with soap.
Scum is an insoluble substance and is found to float on the surface of the water.
The soap used in the case of removing impurities will become ineffective by the formation of insoluble magnesium or calcium salts of fatty acids present in the soap.
The reaction of soap and the ions present in the hard water result in the formation of calcium stearate, which is given below.
Ca(HCO3)2+2 Na+-stearate(aq) Ca(stearate)2(s)+2NaHCO3(aq)
The reaction of soap with calcium sulphates also results in the formation of calcium stearate, and the reaction is,
CaSO4(aq)+2Na+-stearate(aq) Ca(stearate)2(s)+Na2SO4(aq)
The reaction of soaps with the ions present in hard water, such as calcium and magnesium, are similar.
The cleaning capacity of soaps is found to be reduced due to the formation of these insoluble substances.
Cleaning Capacity of Soap in Hard and Soft Water
Procedure
A 20mL test tube is taken and marked with the letter X.
To the test tube marked with X, about 10mL of soft water or groundwater is added.
Then another 20mL test tube marked with Y is taken.
To the test tube marked with Y, about 10mL of hard water is added.
To the two test tubes with the content, a few drops of the soap solution are added.
At an equal amount of time, both the test tubes are shaken well strongly.
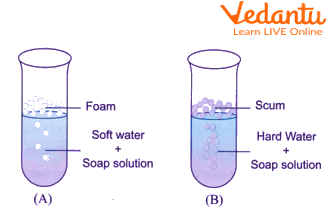
The cleaning capacity of soap in hard and soft water
Then they are placed in a test tube stand.
The changes happening are observed and recorded.
Observation
Emulsification effect of soap in hard and soft water when a drop of cooking oil is added.
Procedure
A 20mL test tube is taken and marked with the letter P.
To the test tube marked with P about 10mL of soft water or groundwater is added.
Then about one drop of cooking oil is added.
Then another 20mL test tube marked with Q is taken.
To the test tube marked with Q, about 10mL of hard water is added.
To the two test tubes with the content, a few drops of the soap solution are added.
At an equal amount of time, both test tubes are shaken well strongly.
Then they are placed in a test tube stand.
The changes happening are observed and recorded.
Observation
Result
From the above experiment, we can conclude that:-
Formation of foam occurs in the addition of soap solution to the test tube marked with an X.
The addition of a solution of soap to the test tube marked with Y results in the formation of a white precipitate.
The addition of soap solution to the test tube marked with P results in emulsification.
The addition of soap solution to the test tube marked with Q will not emulsify.
Precautions
A sufficient amount of soap solution must be prepared in the beginning, then the same solution can be used in the entire experiment.
Care must be taken to add an equal amount of soap solution in both test tubes.
The mixing pattern and time of mixing must be equal for both test tubes.
The test tubes taken must be of equal concentration.
The same cooking oil must be added to both test tubes.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What do you mean by soft water?
Ans. Soft water is a type of water that doesn't contain any type of ions or minerals.
2. What will happen when soap is added to soft water?
Ans. The formation of lather occurs when soap is reacted with soft water.
3. What do you mean by hard water?
Ans. Hard water is a type of water that contains a high concentration of salts and minerals.
4. What is the oil used in the emulsification experiment, and what is the quantity added?
Ans. The oil used is cooling oil and only one drop is used in the experiment.
Viva Questions
1. What is the chemical formula of soap?
Ans. The chemical formula of soap is C17H35COONa.
2. Soap solution is an example of a _________?
Ans. A solution of soap in water is a soap solution. Soap solution is an example of a colloid, as it contains a dispersed phase and medium in it.
3. What is a colloid?
Ans. A colloid is a type of mixture that contains particles of size in the range of 1-1000 nm. A solution of soap in water is a colloid.
4. What is the foaming capacity of soap?
Ans. The foaming capacity of soap is different for different soaps. The foaming capacity of soaps explains the amount of foam produced by soap and the time taken to varnish it.
5. What is a soap test?
Ans. A soap test is a test conducted to check the pH of soap manufactured in the industry.
6. Is soap solution an example of an emulsion?
Ans. No soap is not an example of emulsion. It is considered as an emulsifying agent.
7. What is the range of pH needed after the soap test?
Ans. A pH in the range of 9-10 is needed.
8. What is a soap solution?
Ans. The dissolution of any type of soap in boiling water is a soap solution. Soap solution is an example of a solution that has an alkaline pH value of 9-10.
9. What is the best soap for hard water?
Ans. Soap for hard water is different from the soap used in the case of soft water. It contains some other additives too. Castile is an example of soap for hard water and contains some amount of coconut oil too.
10. Can soft water cause health problems?
Ans. Soft water doesn't cause any severe health issues, but it contains a slightly higher amount of sodium ions.
Practical Questions
What are the two parts of soaps?
Ionic parts only
One ionic and one non-ionic
Two non-ionic parts
None of the above
Ans. Soap has two parts, one ionic and the other non-ionic.
What is the behaviour of hard water on a soap?
The cleaning capacity of soap is increased.
No effect on the behaviour of soap.
The cleaning capacity of soap is decreased.
None of the above
Ans. The cleaning capacity of soap is found to be decreased with hard water.
What is the behaviour of soft water on a soap?
The cleaning capacity of soap is increased.
No effect on the behaviour of soap.
The cleaning capacity of soap is decreased.
None of the above
Ans. The cleaning capacity of soap is found to be increased with soft water.
Why does soap lather better in soft water than in hard water?
The presence of minerals is responsible for this.
Absence of reactive minerals.
No such effect is present.
None of the above.
Ans. The absence of reactive minerals is responsible for the fast lather formation.
Why do we need to use more soap when using hard water?
Due to the scum formation.
The solubility of soap is high in hard water.
Both
None of the above.
Ans. The formation of scum is responsible for this.
Why does soft water make more bubbles?
Due to scum formation
Absence of scum formation.
No such phenomenon happens.
None of the above.
Ans. The absence of scum formation will result in more bubbles in soft water.
What is the soap releasing capacity?
The hardness of water is its soap releasing capacity.
The softness of water is its soap releasing capacity.
Both are correct.
Both are wrong.
Ans. The hardness of water is its soap releasing capacity.
The cleaning action of soap is due to the
Due to its polar nature.
Due to its non-polar nature.
Partly polar and partly non-polar nature.
None of the above.
Ans. The partly polar and partly non-polar nature is responsible for the cleaning action of soap.
In the chemistry project on foaming capacity of soaps, soap is used in the form of?
Soap solution.
In the bar form.
Powder form
Paste form.
Ans. In the chemistry project on foaming capacity of soaps, soap is used in the form of a soap solution.
Which salt is used in the soap industry?
KCl
NaCl
NaBr
KBr
Ans. The salt used in the soap industry is NaCl, sodium chloride.
Conclusion
From the above experiment, we can conclude that the lather formation or the cleaning action of soap is more when the water used is soft. The hard water was found to produce only a white precipitate with the soap solution. And also from the emulsification experiment with the help of cooking oil, the emulsification is found to occur only with the test tube that contains soft water. Soft water is found to produce faster lather formation and emulsification is due to the absence of mineral ions while hard water does not is due to the presence of mineral ions in hard water.
FAQs on Understand Soap’s Cleaning Efficiency in Soft and Hard Water – Class 10 Chemistry 2025-26
1. What are the most important board exam questions on the comparative cleaning capacity of soap in soft and hard water for Class 10 Chemistry?
Key board exam questions include:
- Explain, with a chemical equation, why soap forms less lather in hard water compared to soft water.
- Describe the steps of the experiment to compare soap's cleaning action in both types of water.
- State the observations when emulsification is tested using soap, cooking oil, and soft/hard water.
- Why does soap form scum in hard water and not in soft water?
- What is the importance of equal quantities and concentrations in both test tubes during the experiment?
2. How should answers for 5-mark questions on this chapter be structured in CBSE 2025-26 board exams?
For a 5-mark question, structure your answer as follows:
- Define soft and hard water with examples.
- State the aim and principles of the experiment.
- Describe the procedure step by step.
- Mention key chemical reactions (e.g., formation of calcium/magnesium stearate).
- Record observations comparing foam and scum formation.
- Conclude with why soap is less effective in hard water, including scientific reasoning.
3. Why is scum formed when soap is used with hard water, and how does it impact exam performance?
Scum forms because calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water react with soap to form insoluble compounds (like calcium stearate). This scum decreases the soap's cleaning capacity because it prevents the formation of lather, a critical point often asked for conceptual clarity in board exams.
4. What common mistakes should students avoid in answering comparative cleaning capacity questions in Chemistry exams?
- Do not confuse scum with lather. Scum is a precipitate; lather is foam.
- Always write correct balanced chemical equations for reactions with hard water.
- Describe both the experimental setup and reasoning, not just results.
- Avoid general statements—specify differences due to mineral content.
- Support answers with observations from the experiment, using exam-focused scientific language.
5. Which conceptual questions from this chapter are likely to be expected for high-order thinking skills (HOTS) in board exams?
Likely HOTS questions include:
- Why does soap act as an effective emulsifying agent only in soft water?
- How would you modify soap composition to improve its cleaning action in hard water?
- Explain with examples how the nature of water affects industrial and domestic cleaning processes.
- Predict and explain what will happen if distilled water is replaced by seawater in the experiment.
6. How do you justify your conclusion in a board answer about which water type allows soap to clean better?
You should state that soft water allows soap to clean better because the absence of calcium and magnesium ions prevents scum formation, so more lather is produced and cleaning power is higher. Reference specific experimental results where foam was observed only in soft water. This directly supports your conclusion and aligns with exam expectations for evidence-based answers.
7. What is the marking scheme for answers related to the cleaning capacity of soap in hard and soft water in CBSE Class 10 Chemistry?
The marking scheme generally includes:
- 1 mark for correctly defining hard and soft water
- 1 mark for stating the experiment's aim and principle
- 1 mark for describing correct procedure and setup
- 1 mark for balanced chemical reactions and observations
- 1 mark for analysis and scientific conclusion, ensuring each part is linked to board exam keywords for 2025-26
8. What are common misconceptions students have about soap’s effectiveness in hard and soft water for board exams?
Common misconceptions include:
- Thinking that more soap always means more cleaning, regardless of water type.
- Believing scum is the same as lather.
- Not realizing that mineral content (calcium/magnesium) directly causes reduced cleaning capacity in hard water.
- Assuming rainwater is always effective for cleaning with soap without considering dissolved gases or impurities.
9. Why is equal timing and quantity crucial in comparative experiments for Chemistry board exams?
Consistency in timing and quantity is crucial to ensure a fair comparison between soft and hard water. This removes variables that could otherwise affect the observation of foam or scum, making results accurate—a key point often stressed in CBSE marking criteria.
10. How do industrial applications use the knowledge of soap’s cleaning capacity in different types of water?
Industries recognize that hard water reduces soap efficiency, leading to increased costs and inefficiency. Thus, they may use synthetic detergents designed to work with hard water or install water softening systems. Understanding these differences is essential in manufacturing, textile processing, and cleaning industries, highlighting practical application expected in exam questions.































