What Are the Main Structures and Roles of the Human Brain?
The human brain is the command centre of our body, responsible for thoughts, memory, emotions, and coordination. It enables us to perceive the world, process information, and respond to our environment. In this article, we will explore the structure, functions, and significance of the human brain with an easy, student-friendly approach, perfect for school and competitive exam preparations.
What is the Human Brain?
The human brain is the most complex organ in the human body. It is located within the skull and is part of the central nervous system. The brain controls voluntary and involuntary actions, including thinking, movement, breathing, and heartbeat. Its intricate network of neurons allows humans to learn, remember, communicate, and solve problems. Understanding the brain helps in decoding how we function and stay healthy.
Structure of the Human Brain
The human brain is divided into several regions, each with a unique role. It consists of three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. These structures work together to process and relay information throughout the body. The brain is protected by the skull and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid for cushioning and nutrient transport.
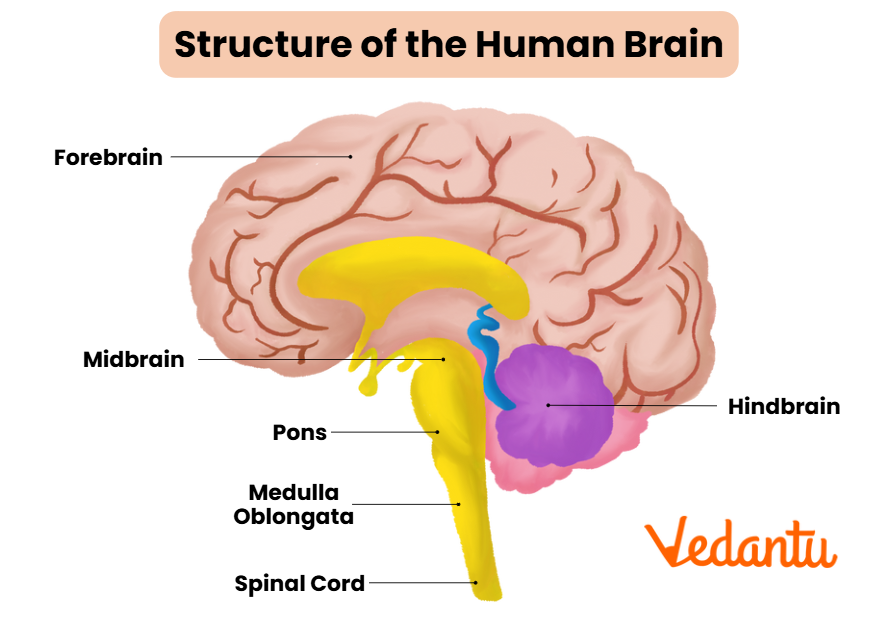
Main Parts of the Human Brain
- Cerebrum: The largest part, divided into right and left hemispheres. It controls reasoning, memory, senses, speech, and voluntary movements. Find more details on parts of the brain.
- Cerebellum: Located below the cerebrum, it manages posture, balance, and fine motor movements.
- Brainstem: Connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls involuntary actions such as breathing, digestion, and heartbeat.
Each region contains millions of nerve cells or neurons that communicate through electrical and chemical signals. The brain also includes specialized structures like the hypothalamus and thalamus, which regulate hormones and sensory processing.
Functions of the Human Brain
The human brain manages a wide variety of vital functions that help us survive and thrive. Understanding these functions is important in learning, medicine, sports, and many real-life situations.
- Sensory Processing: Receives information from eyes, ears, skin, nose, and tongue, then interprets sensations like sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell. Explore sensory perception for in-depth details.
- Motor Control: Sends signals to muscles for movement, from walking and running to facial expressions.
- Cognition and Memory: Enables us to think, reason, learn, store, and recall information.
- Emotion and Behavior: Regulates feelings and responses such as happiness, anger, or fear.
- Regulation of Body Systems: Controls heartbeat, breathing, digestion, and other involuntary functions.
The brain also works closely with the endocrine system to produce hormones that influence growth, metabolism, and stress responses.
How the Human Brain Works
The human brain works by transmitting electrical impulses between billions of neurons. When sensory input is received, the brain analyzes it, decides on an action, and sends signals to relevant body parts. This process happens in fractions of a second and is vital for everything from reflex actions to conscious problem-solving.
- Sense organs detect changes and send signals via sensory nerves.
- The brain processes the information and makes decisions.
- Motor nerves carry out responses, like moving a hand away from a hot object.
The study of the nervous system and brain functions is known as neuroscience or biological science. For a deeper dive into nerves and their roles, visit neurons and nerve impulse.
Significance of the Human Brain
The human brain is essential for everything we do. It differentiates humans from other animals by supporting advanced language, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Good brain health is important for learning, daily activities, sports, and maintaining relationships. Disorders affecting the brain, such as dementia or stroke, can have severe impacts on overall well-being.
- It helps us adapt and react to the environment.
- Plays a major role in innovation, technology, and the arts.
- Maintains balance in body systems by interacting with organs like the heart, lungs, and muscles.
Proper nutrition, exercise, and rest support healthy brain function. For more about nutrients and their importance, see what do various nutrients do for our body.
Human Brain and Medicine
Medical science uses brain research to treat diseases such as epilepsy, brain tumors, and mental health conditions. Medicines, therapy, and surgery help restore brain functions when injuries or diseases occur. Studying the brain is crucial in developing therapies, learning aids, and treatments for people with special needs.
- Neurological exams assess brain health.
- Brain imaging (MRI, CT scan) helps in diagnosis.
- Understanding the human brain guides research in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Learn about tablet medicines and their impact on the nervous system at tablet medicine. Disorders of muscular tissue are also closely related to brain health (Muscular Tissue).
Interesting Facts About the Human Brain
- The adult human brain weighs about 1.4 kg and uses around 20% of the body’s energy.
- The brain contains over 86 billion neurons connected through trillions of synapses.
- Damage to specific brain regions causes distinct symptoms, helping doctors diagnose issues.
- The brain keeps developing and adapting throughout life, a property called neuroplasticity.
- Different types of nutrients and hormones, such as those produced by the endocrine system, are crucial for healthy brain function.
Related Topics and Further Learning
To expand your understanding of the human brain and body, explore related Vedantu topics:
- Difference between Brain and Mind
- Spinal Cord
- Parts of the Brain
- External and Internal Organs
- Central Nervous System
- Control and Coordination
You can also learn how acquired and inherited traits impact brain development here.
Summary
The human brain is the most advanced organ, directing thoughts, movement, and essential life functions. Learning about its structure and function helps us appreciate how we think, feel, and interact with the world. Understanding the brain is key to advances in health, technology, and education, which Vedantu supports for all students.


FAQs on Exploring the Human Brain: Key Parts and Functions
1. What is the human brain and what are its main functions?
The human brain is the central organ of the nervous system responsible for controlling most bodily activities and processing information. Main functions of the human brain include:
- Processing sensory information (sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell)
- Coordinating voluntary movement and balance
- Regulating vital functions like breathing and heart rate
- Enabling memory, learning, reasoning, and emotions
- Controlling speech, language, and problem-solving abilities
2. What are the main parts of the human brain?
The main parts of the human brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. These parts include:
- Cerebrum – largest part; responsible for thinking, memory, senses, and voluntary movement
- Cerebellum – controls balance, coordination, and posture
- Brainstem – regulates involuntary actions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion
3. What is the role of the cerebrum in the human brain?
The cerebrum is responsible for higher order brain functions, such as intellect, memory, and voluntary actions. Key functions include:
- Interpreting sensory data (vision, hearing, touch, etc.)
- Managing reasoning, planning, and decision making
- Controlling voluntary muscle movements
- Regulating emotions and personality
4. How does the brain coordinate and control body activities?
The brain coordinates and controls body activities by processing information and sending signals through the nervous system. This process involves:
- Receiving information from sensory organs
- Interpreting and analysing the data
- Sending appropriate motor commands to muscles and glands
- Regulating both voluntary and involuntary actions
5. What protects the human brain?
The human brain is protected by the skull (cranium), three layers of meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid. Protection measures include:
- Skull: Bony structure that surrounds the brain
- Meninges: Three protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord
- Cerebrospinal fluid: Provides cushioning and shock absorption
6. What are neurons and what is their function in the brain?
Neurons are specialised nerve cells in the human brain responsible for transmitting and processing information. Their functions include:
- Receiving signals from sensory organs
- Relaying messages within the brain and to the rest of the body
- Facilitating communication between different brain regions
- Supporting thinking, learning, and memory formation
7. How is the human brain different from other animals?
The human brain is unique due to its large cerebrum and advanced abilities. Key differences include:
- Well-developed areas for language, abstract thinking, and problem-solving
- Greater intelligence and ability to learn complex skills
- Distinct regions dedicated to social interaction and culture
8. Name any two functions of the cerebellum.
The cerebellum is mainly responsible for:
- Maintaining balance and posture
- Coordinating voluntary muscle movements
9. What is the function of the brainstem?
The brainstem controls many vital involuntary actions necessary for survival. Key roles include:
- Regulating heartbeat and breathing
- Controlling swallowing and digestion
- Managing reflexes (e.g. blinking, coughing)
10. How does the brain help in learning and memory?
The brain enables learning and memory by processing sensory information and forming connections between neurons. Functions involved are:
- Storing experiences for recall
- Connecting new information with existing knowledge
- Enabling problem-solving and skill development
11. What are the protective coverings of the brain called?
The protective coverings of the brain are called meninges. These are three layers –
- Dura mater (outermost layer)
- Arachnoid mater (middle layer)
- Pia mater (innermost layer)
12. Why is the human brain called the command centre of the body?
The human brain is known as the command centre because it controls all bodily functions and coordinates every action. Reasons include:
- Sending and receiving signals throughout the body
- Regulating movements, senses, and internal organs
- Processing thought, emotional response, and decision-making










