Maths Notes for Chapter 1 Patterns in Mathematics Class 6 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 - Patterns in Mathematics - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts summarised in the Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 Patterns in Mathematics revision notes?
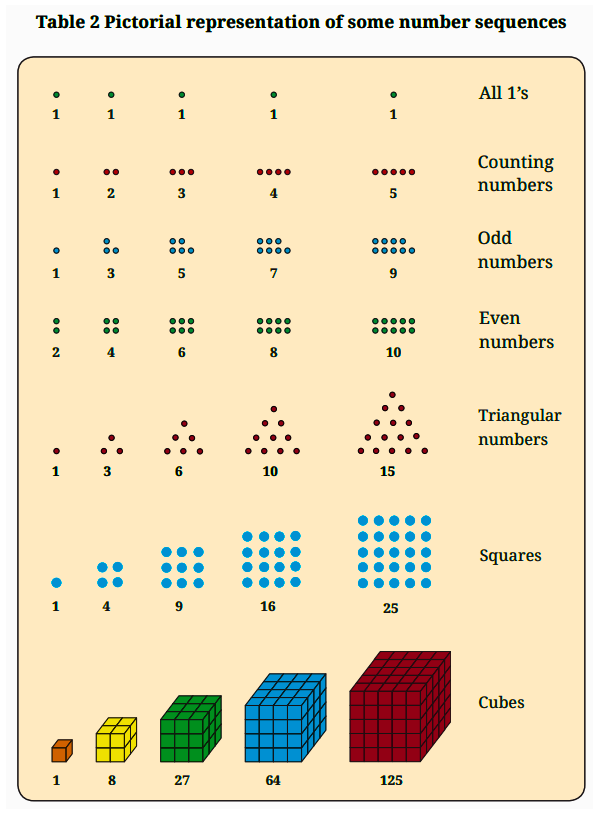
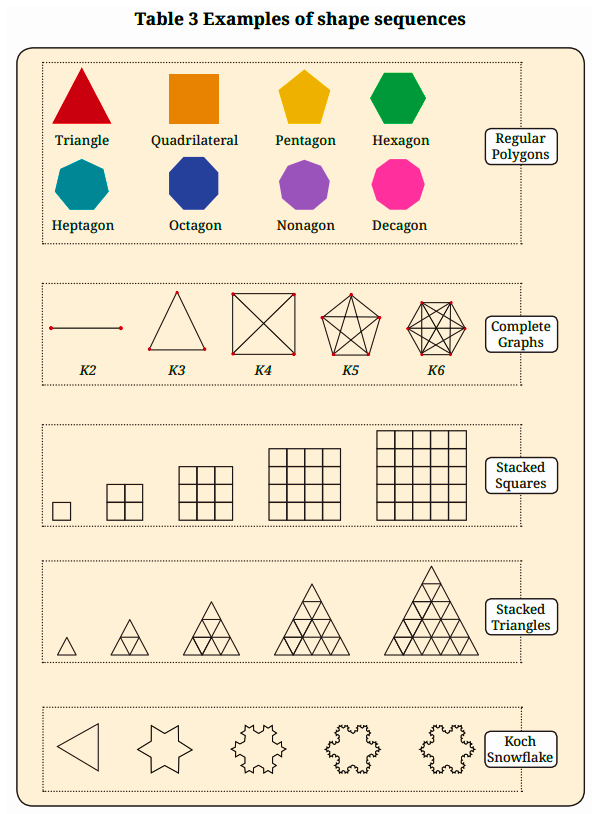
The revision notes for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 summarise number patterns (like counting, odd, even, square, and triangular numbers), visualising sequences pictorially, patterns in shapes (such as polygons), and the relationship between numbers and shapes. These notes help students quickly recall fundamental ideas and spot connections within mathematical patterns as per CBSE 2025–26.
2. How can students use revision notes to prepare efficiently for Class 6 Maths Patterns in Mathematics?
To prepare efficiently, students should:
- Review important sequences and definitions highlighted in the notes.
- Practice identifying and predicting patterns in numbers and shapes as summarised in the revision material.
- Utilise visual representations given in the notes for better understanding.
- Refer to the summary tables or concept maps included in the notes for quick revision before exams.
3. What is the quick revision order recommended for Chapter 1 Patterns in Mathematics?
A suggested quick revision order is:
- Start with basic number sequences (counting, odd, even numbers).
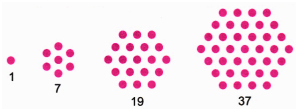
- Move on to visualising patterns using pictures (such as square and triangular numbers).
- Examine relationships between different sequences (e.g., sum of odd numbers forming squares).
- Finish with patterns in shapes and how numbers and shapes are related.
4. How do revision notes help in understanding the connection between number sequences and shape patterns?
Revision notes present both number and shape sequences side by side, showing patterns such as the relationship between the number of sides in regular polygons (triangle: 3, square: 4, pentagon: 5, etc.) and counting numbers. These visual and conceptual links deepen your understanding, enabling you to recognise mathematical structures quickly.
5. What are some sample key terms and definitions included in the summary notes of this chapter?
Common key terms and definitions in the summary notes include:
- Number sequence: An ordered set of numbers following a particular rule.
- Pattern: A repeated arrangement that can be observed in numbers or shapes.
- Triangular number: Numbers that can be arranged in the shape of a triangle.
- Square number: Numbers obtained by multiplying a number by itself.
- Regular polygon: A shape with equal sides and angles (e.g., triangle, square, pentagon).
6. (FUQ) Why is recognising patterns in mathematics important for further studies?
Recognising patterns builds a foundation for higher-level mathematical concepts. It improves problem-solving skills, encourages logical thinking, and aids in topics like algebra, geometry, and number theory. Pattern recognition also helps in predicting trends and applying mathematics to real-life situations, which is essential for success in later classes.
7. (FUQ) How can visual representations in revision notes make learning patterns easier?
Visual representations like dot arrangements or pictorial grids in the revision notes allow students to see abstract number patterns in concrete ways. This method helps learners understand difficult concepts faster, spot sequences easily, and remember the connections between numbers and shapes more effectively.
8. (FUQ) What misconceptions should students avoid when revising Patterns in Mathematics?
Students should avoid assuming that all sequences are formed by simply adding the same number each time. It's crucial to check for other rules, such as multiplication patterns, geometric progressions, or visual clues. Also, not every pattern has to do with numbers; shapes and their arrangements can be patterns too.
9. (FUQ) How do revision notes connect the concepts in Patterns in Mathematics to real-life situations?
Revision notes often include examples of patterns found in nature, technology, and daily life, such as in architecture (repeating designs), games (number patterns), and natural growth (spirals, sequences). By recognising these connections, students gain appreciation for the usefulness of mathematical reasoning beyond textbooks.
10. (FUQ) What is the benefit of using summary notes for last-minute revision before exams?
Summary notes distil the chapter into concise points and key concepts, enabling students to revise quickly and efficiently. They help in retaining important information, spotting links across topics, and boosting confidence before attempting exam questions in Patterns in Mathematics.