
To determine refractive index of glass slab using a travelling microscope, minimum number of readings required is:
(A). Two
(B). Four
(C). Three
(D). Five
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The experiment is done to calculate the refractive index of glass slab using real and apparent height. When light travels from one medium to another its path also changes due to which we see apparent or false height of objects through a medium. Follow the precautions to do the experiment accurately.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We can determine the refractive index of a glass slab through an experiment using a travelling microscope and glass slab.
For the experiment we require a travelling microscope, three glass slabs of different thickness but material should be the same and lycopodium powder.
When an object is viewed through a glass slab, it appears to be at an elevated height due to refraction of light. The height at which the object appears to be is known as apparent height, while its original height is known as the real height. Then the refractive index of glass slab is-
$\mu =\dfrac{real\,height}{apparent\,height}$.
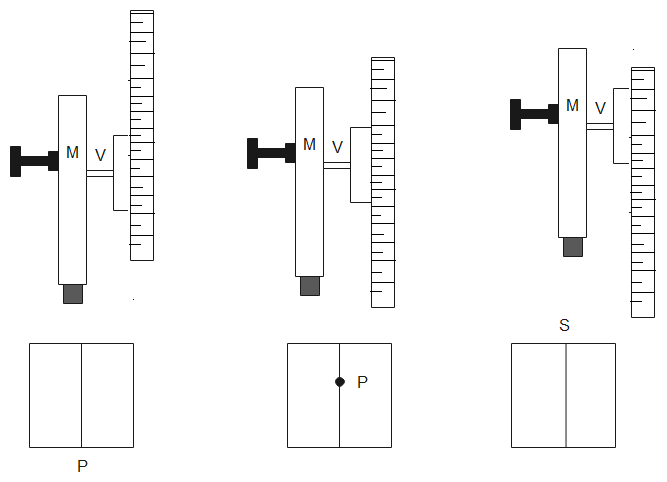
Take a travelling microscope and keep it near a window so as to get maximum light. Determine the vernier constant of the vertical scale. Make sure that the base of the travelling microscope is horizontal. Take a paper and mark a point P on it using black ink. Observe the point from the travelling microscope by focusing on point P and record the reading. Let ${{R}_{1}}$ be the reading of the main scale and vernier scale on the vertical scale.
Take the least thick glass slab and place it on point P. Move the travelling microscope to focus on the image of point P. Mark the reading for image of P and let the readings be ${{R}_{2}}$.
Do the same for the other glass slabs and measure their readings as ${{R}_{3}}$ and ${{R}_{4}}$.
We need to calculate at least three readings to calculate real thickness as well as apparent thickness.
Therefore, we need at least three readings for the experiment.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
We calculate the real height and apparent height by subtracting the readings as- ${{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{2}}$ and ${{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{3}}$. The ratio of the value of smallest division in the main scale to the total number of divisions on the vernier scale is called the vernier constant. Refractive index of a material is the ratio of speed of light in the material to the speed of light in air.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We can determine the refractive index of a glass slab through an experiment using a travelling microscope and glass slab.
For the experiment we require a travelling microscope, three glass slabs of different thickness but material should be the same and lycopodium powder.
When an object is viewed through a glass slab, it appears to be at an elevated height due to refraction of light. The height at which the object appears to be is known as apparent height, while its original height is known as the real height. Then the refractive index of glass slab is-
$\mu =\dfrac{real\,height}{apparent\,height}$.
Take a travelling microscope and keep it near a window so as to get maximum light. Determine the vernier constant of the vertical scale. Make sure that the base of the travelling microscope is horizontal. Take a paper and mark a point P on it using black ink. Observe the point from the travelling microscope by focusing on point P and record the reading. Let ${{R}_{1}}$ be the reading of the main scale and vernier scale on the vertical scale.
Take the least thick glass slab and place it on point P. Move the travelling microscope to focus on the image of point P. Mark the reading for image of P and let the readings be ${{R}_{2}}$.
Do the same for the other glass slabs and measure their readings as ${{R}_{3}}$ and ${{R}_{4}}$.
We need to calculate at least three readings to calculate real thickness as well as apparent thickness.
Therefore, we need at least three readings for the experiment.
Hence, the correct option is (C).

Note:
We calculate the real height and apparent height by subtracting the readings as- ${{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{2}}$ and ${{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{3}}$. The ratio of the value of smallest division in the main scale to the total number of divisions on the vernier scale is called the vernier constant. Refractive index of a material is the ratio of speed of light in the material to the speed of light in air.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




