
The elastic limit of an elevator cable is $2\times 10^{9} \dfrac{N}{m^2 }$ . The maximum upward acceleration that an elevator of mass $2\times 10^3 $kg can have when supported by a cable whose cross-sectional area is $10^{-4}$ provided the stress in the cable would not exceed half of the elastic limit would be:
A.) 10 $ms^{-2}$
B.) 50 $ms^{-2}$
C.) 40 $ms^{-2}$
D.) Not possible to move up
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Make a free body diagram of the elevator and calculate the net force acting on the elevator. Calculate the maximum stress possible and hence the maximum force possible and apply the condition to the expression for the net force acting on the elevator to get max possible acceleration.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given elastic limit of the elevator cable is $2\times 10^{9} N/m^2$
the area of cross-section of elevator cable is $10^{-4}m^2$
The mass of the elevator is $2\times 10^3$ kg
The free body diagram of the elevator can be drawn as
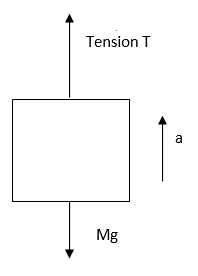
We are given the stress in the cable should not exceed half of the elastic limit of the cable so we get
We know the stress is given by $stress= \alpha = \dfrac{Tension}{Area} = \dfrac{T}{A} = \dfrac{m(g+a)}{a}$
We get from the given condition :
$\begin{align}
& \alpha =\dfrac{m(g+a)}{A}\le \dfrac{{{\alpha }_{max}}}{2}=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{9}}}{2} \\
& g+a\le \dfrac{2\times 9}{2}\dfrac{{{10}^{-4}}}{2\times {{10}^{3}}}=50 \\
& a\le 50-10=40\dfrac{m}{{{s}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, using the free body diagram and calculating the net force acting on the elevator and the tension in the cable we got the maximum acceleration possible for the elevator as $40 \dfrac{m}{s^2}$.
Additional Information:
The net force acting on the elevator is equal to mass times the upward acceleration of the elevator as it is moving upward. Now we have seen that the net force in the upward direction is nothing but the T – mg where T is the tension in the rope. Hence we have equated this to the ma. So we get the equation T-mg = ma which gives us T = m(g+a) which we used in the problem.
Note: The possible mistake one can do in this kind of problem is that while taking the forces acting on the elevator. One should be able to differentiate between the forces acting on the body and the forces applied by the body on the cable.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given elastic limit of the elevator cable is $2\times 10^{9} N/m^2$
the area of cross-section of elevator cable is $10^{-4}m^2$
The mass of the elevator is $2\times 10^3$ kg
The free body diagram of the elevator can be drawn as

We are given the stress in the cable should not exceed half of the elastic limit of the cable so we get
We know the stress is given by $stress= \alpha = \dfrac{Tension}{Area} = \dfrac{T}{A} = \dfrac{m(g+a)}{a}$
We get from the given condition :
$\begin{align}
& \alpha =\dfrac{m(g+a)}{A}\le \dfrac{{{\alpha }_{max}}}{2}=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{9}}}{2} \\
& g+a\le \dfrac{2\times 9}{2}\dfrac{{{10}^{-4}}}{2\times {{10}^{3}}}=50 \\
& a\le 50-10=40\dfrac{m}{{{s}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, using the free body diagram and calculating the net force acting on the elevator and the tension in the cable we got the maximum acceleration possible for the elevator as $40 \dfrac{m}{s^2}$.
Additional Information:
The net force acting on the elevator is equal to mass times the upward acceleration of the elevator as it is moving upward. Now we have seen that the net force in the upward direction is nothing but the T – mg where T is the tension in the rope. Hence we have equated this to the ma. So we get the equation T-mg = ma which gives us T = m(g+a) which we used in the problem.
Note: The possible mistake one can do in this kind of problem is that while taking the forces acting on the elevator. One should be able to differentiate between the forces acting on the body and the forces applied by the body on the cable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




