
The diagram shows electricity cables being put up on a warm day. The cables are left loose between the poles, as shown in the diagram. Why are the cables left loose?
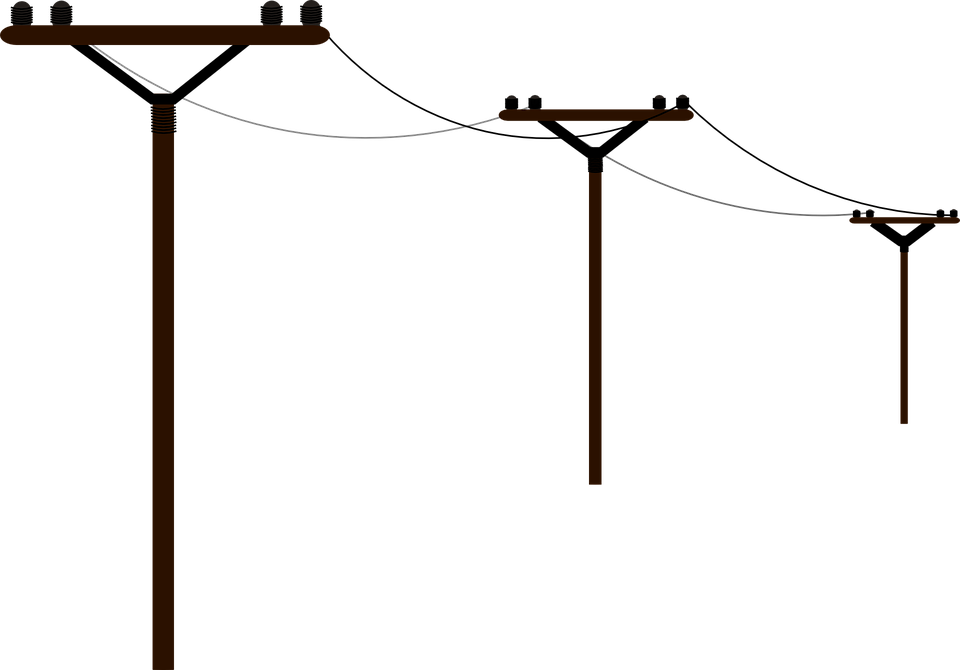
(A) They will contract on cold day
(B) They will contract on very warm day
(C) They will expand on cold days
(D) They will expand on very warm days

Answer
501.9k+ views
Hint :A utility pole is a column or post that supports overhead electricity lines and other public services including electrical cable, fibre optic cable, and associated equipment like transformers and street lights. Depending on the use, it might be called a transmission pole, telephone pole, telecommunication pole, power pole, hydro pole, telegraph pole, or telegraph post.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The quantity of heat lost from the conductors might be affected by a drop in temperature. This results in a reduction in conductor temperature and, as a result, a shortening or contraction of power lines. If there was insufficient leeway left after installation, these cables might snap as a result of the shortening. Poles/towers snapping and falling may be disastrous, resulting in flames and fatalities. Ice build-up on electricity lines during the winter renders them too heavy to be supported by poles or towers, increasing the risk of collapse. Sagging is influenced by wind, in addition to temperature and ice build-up. Wind has been reported to cool wires, allowing them to transmit more electricity than they would otherwise. When the wind is blowing at a straight angle to the power line, the quantity of electricity transmitted increases by 10–40 percent. This might cause the lines to overheat, resulting in even more drooping. Extreme wind conditions with uncontrolled sagging, on the other hand, might increase the likelihood of the lines colliding with each other or the adjacent structure.
Hence option A is correct.
Note :
Cables are excellent heat conductors. The cable contracts in the winter owing to a drop in ambient temperature. As a result, the wire is frequently kept slack so that it does not break owing to cable stress on cold days. There are a variety of methods for dealing with sagging electricity lines. While extending the lines longer than the actual distance between the two poles or towers can help to prevent snapping, leaving too much room for drooping can cause the lines to droop.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The quantity of heat lost from the conductors might be affected by a drop in temperature. This results in a reduction in conductor temperature and, as a result, a shortening or contraction of power lines. If there was insufficient leeway left after installation, these cables might snap as a result of the shortening. Poles/towers snapping and falling may be disastrous, resulting in flames and fatalities. Ice build-up on electricity lines during the winter renders them too heavy to be supported by poles or towers, increasing the risk of collapse. Sagging is influenced by wind, in addition to temperature and ice build-up. Wind has been reported to cool wires, allowing them to transmit more electricity than they would otherwise. When the wind is blowing at a straight angle to the power line, the quantity of electricity transmitted increases by 10–40 percent. This might cause the lines to overheat, resulting in even more drooping. Extreme wind conditions with uncontrolled sagging, on the other hand, might increase the likelihood of the lines colliding with each other or the adjacent structure.
Hence option A is correct.
Note :
Cables are excellent heat conductors. The cable contracts in the winter owing to a drop in ambient temperature. As a result, the wire is frequently kept slack so that it does not break owing to cable stress on cold days. There are a variety of methods for dealing with sagging electricity lines. While extending the lines longer than the actual distance between the two poles or towers can help to prevent snapping, leaving too much room for drooping can cause the lines to droop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




