
State the SI unit of magnetic dipole moment.
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: Approach the problem from its definition. A magnetic dipole is a magnetic north and south pole separated by a small distance. The magnetic dipole moment of the magnet is given by the multiplication of magnetic strength and distance between the two poles. However, to determine the SI unit of magnetic dipole moment we depend on the electromagnetic definition. Magnetic dipole moment is given by the multiplication of current and the area of the enclosed loop.
Complete step by step answer:
Magnetic Dipole is a concept which helps us to determine the interaction with an external magnetic field. The following diagram shows the magnetic dipole moment constructed by the current loop.
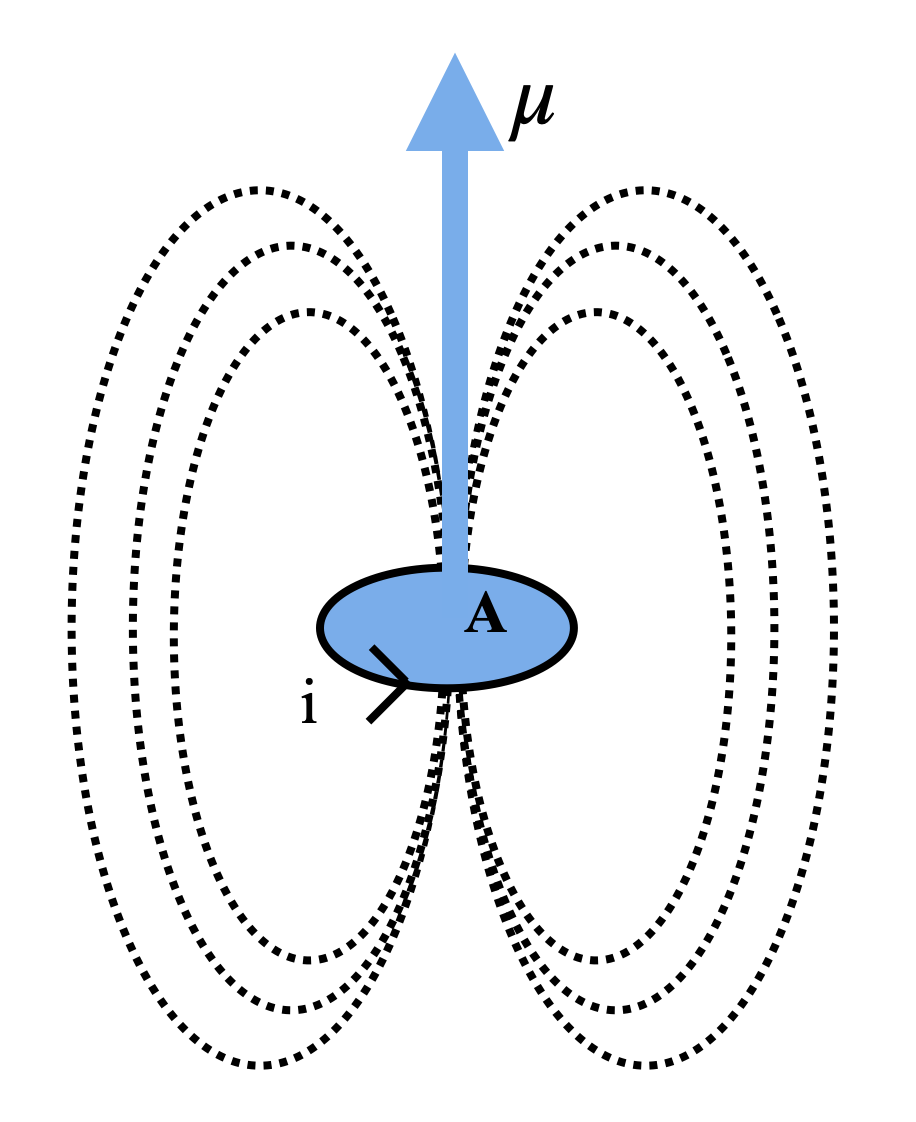
In this picture, we assume that the magnetic field is generated only by the current loop. If we consider current travelling in a circular path, whose area is A, the magnetic dipole moment of the system is given by,
$\mu =iA$…………(1)
In this case, magnetic dipole moment and area are vector quantities. We need to use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the magnetic dipole moment.
For example, as the current is moving in the anticlockwise direction, the right-hand rule gives us the magnetic dipole moment in the upwards direction.Now, that we have understood the definition of magnetic dipole moment, let’s look into the SI units of the quantity.
So, equation (1) shows us the quantity as,
$\mu =iA$
SI unit of current is Ampere (A).
And SI unit of the area is ${{m}^{2}}$
So, simply we can write that the SI unit of the magnetic dipole moment is,
$A{{m}^{2}}$
Note:
Magnetic dipole moment is an important quantity because it determines the way a magnetic dipole would react in the presence of an external magnetic field. For example, the following figure shows the interaction between a magnetic dipole and an external magnetic field.
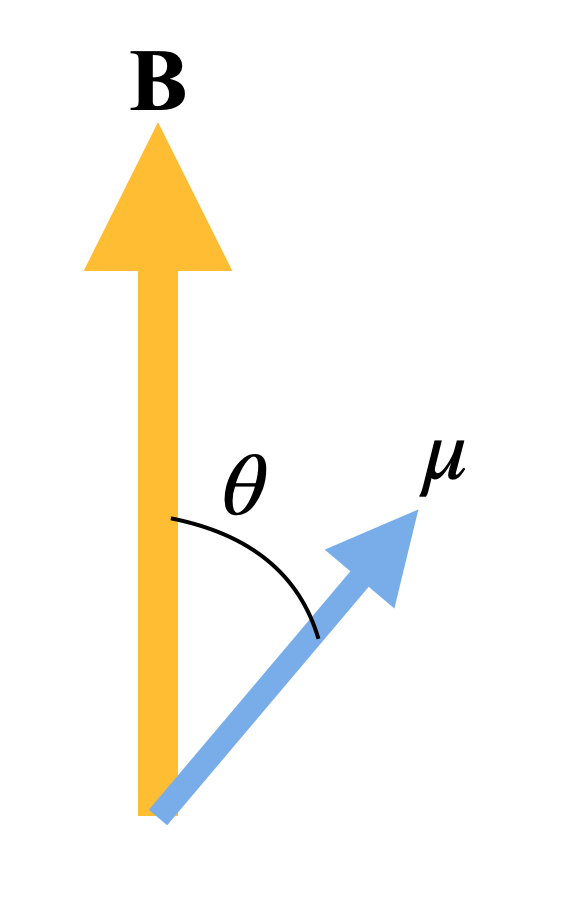
Here,
B is the external magnetic field vector
$\mu $ is the magnetic dipole moment vector
The torque on the magnetic dipole is given by,
$\tau =B\times \mu $
Complete step by step answer:
Magnetic Dipole is a concept which helps us to determine the interaction with an external magnetic field. The following diagram shows the magnetic dipole moment constructed by the current loop.

In this picture, we assume that the magnetic field is generated only by the current loop. If we consider current travelling in a circular path, whose area is A, the magnetic dipole moment of the system is given by,
$\mu =iA$…………(1)
In this case, magnetic dipole moment and area are vector quantities. We need to use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the magnetic dipole moment.
For example, as the current is moving in the anticlockwise direction, the right-hand rule gives us the magnetic dipole moment in the upwards direction.Now, that we have understood the definition of magnetic dipole moment, let’s look into the SI units of the quantity.
So, equation (1) shows us the quantity as,
$\mu =iA$
SI unit of current is Ampere (A).
And SI unit of the area is ${{m}^{2}}$
So, simply we can write that the SI unit of the magnetic dipole moment is,
$A{{m}^{2}}$
Note:
Magnetic dipole moment is an important quantity because it determines the way a magnetic dipole would react in the presence of an external magnetic field. For example, the following figure shows the interaction between a magnetic dipole and an external magnetic field.

Here,
B is the external magnetic field vector
$\mu $ is the magnetic dipole moment vector
The torque on the magnetic dipole is given by,
$\tau =B\times \mu $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




