
Number of diodes consisting of bridge rectifier, rectifier using center tap transformer and half-wave rectifier are respectively.
A. 4, 3, 2
B. 4, 2, 1
C. 2, 2, 1
D. 2, 4, 1
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Before we understand the system of connection of diodes, we need to understand the property of diode that makes it suitable in rectifiers, which is –
The diode behaves like a normal conductor when forward biased but offers high resistance in reverse bias.
Complete step by step solution:
Rectification is the process of converting alternating current at the input to pulsating direct current in the output. It ensures that the direction of current is converted from bidirectional at the input to unidirectional at the output end.
The rectification is achieved by usage of diodes.
The diode is a junction of p-type and n-type semiconductor. The middle part of the diode consists of a small thin region that contains a combination of positive and negative charges, known as the depletion region.
When the p-type part of the diode is connected to a positive terminal, the diode is said to be in forward bias. When the p-type of the diode is connected to a negative terminal, the diode is said to be in reverse bias.
The diode in forward bias behaves like a normal resistor with linear variation of current with voltage, while the diode in reverse bias offers huge resistance to the current flowing through the circuit.
Hence, by using diodes in a specified combination in a circuit, the alternating current can be restricted to only one direction.
There are 3 major forms of rectification using diodes: i) Half-wave rectification
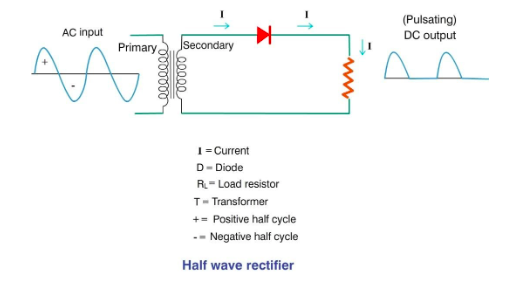
In half-wave rectification, only one diode is used. When the polarity of the input is positive, the diode is forward biased and it conducts. When the polarity is reversed, the diode cuts off the current thereby, allowing only the positive half-cycles at the output.
ii) Full wave rectifier using centre-tap transformer:
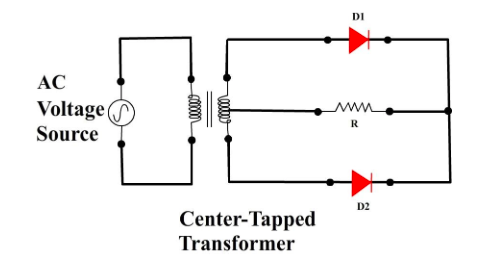
In this circuit, there are 2 diodes used. Here, both the half-cycles of the input are passed at the load, which is tapped at the centre of the transformer and its ends, connected to the diodes. In one half-cycle, the first diode is forward biased and the other is reverse biased, and hence, the first diode conducts. In the second half-cycle, the biases reverse and the second diode conducts, being in forward bias.
iii) Full wave rectifier using bridge rectifier
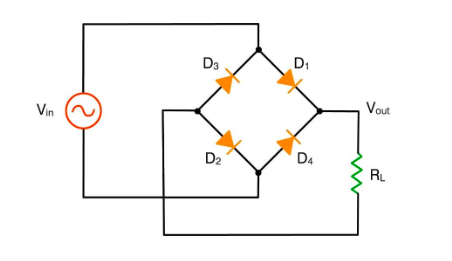
This circuit is based on the Wheatstone’s network. It consists of 4 diodes as connected above. Here, 2 opposite sets of diodes are active in each half-cycle of the input, thereby ensuring that the complete input voltage is converted to pulsating output with unidirectionality.
Hence, In the bridge rectifier, there are 4 diodes used. In the centre tap transformer rectifier, there are 2 diodes used. In a half-wave rectifier, only 1 diode is used.
Hence, the correct option is Option B.
Note: The rectification produces pulsating direct current which is varying. To obtain the steady direct current input, along with rectification, an additional circuit called filter consisting of capacitors and inductors, is required.
Complete step by step solution:
Rectification is the process of converting alternating current at the input to pulsating direct current in the output. It ensures that the direction of current is converted from bidirectional at the input to unidirectional at the output end.
The rectification is achieved by usage of diodes.
The diode is a junction of p-type and n-type semiconductor. The middle part of the diode consists of a small thin region that contains a combination of positive and negative charges, known as the depletion region.
When the p-type part of the diode is connected to a positive terminal, the diode is said to be in forward bias. When the p-type of the diode is connected to a negative terminal, the diode is said to be in reverse bias.
The diode in forward bias behaves like a normal resistor with linear variation of current with voltage, while the diode in reverse bias offers huge resistance to the current flowing through the circuit.
Hence, by using diodes in a specified combination in a circuit, the alternating current can be restricted to only one direction.
There are 3 major forms of rectification using diodes: i) Half-wave rectification

In half-wave rectification, only one diode is used. When the polarity of the input is positive, the diode is forward biased and it conducts. When the polarity is reversed, the diode cuts off the current thereby, allowing only the positive half-cycles at the output.
ii) Full wave rectifier using centre-tap transformer:

In this circuit, there are 2 diodes used. Here, both the half-cycles of the input are passed at the load, which is tapped at the centre of the transformer and its ends, connected to the diodes. In one half-cycle, the first diode is forward biased and the other is reverse biased, and hence, the first diode conducts. In the second half-cycle, the biases reverse and the second diode conducts, being in forward bias.
iii) Full wave rectifier using bridge rectifier

This circuit is based on the Wheatstone’s network. It consists of 4 diodes as connected above. Here, 2 opposite sets of diodes are active in each half-cycle of the input, thereby ensuring that the complete input voltage is converted to pulsating output with unidirectionality.
Hence, In the bridge rectifier, there are 4 diodes used. In the centre tap transformer rectifier, there are 2 diodes used. In a half-wave rectifier, only 1 diode is used.
Hence, the correct option is Option B.
Note: The rectification produces pulsating direct current which is varying. To obtain the steady direct current input, along with rectification, an additional circuit called filter consisting of capacitors and inductors, is required.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




