
What is the null point in a potentiometer?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: A Potentiometer is basically a resistor which comprises three terminals. Out of these three terminals - one is varying, and the rest two are fixed. It is basically an electric component which is used to measure the unknown voltage by comparing it with the known one, which can be drawn by cell or any of the other supply sources.
Complete step by step solution:
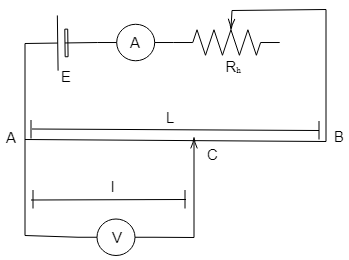
The potentiometer is based on the principle that the potential across a piece of the wire is always directly proportional to length of the given wire, which has a uniform cross-sectional area and a constant current is also flowing through it.
Some important points about the Potentiometer are as follows:
(1) Since a potentiometer works on the comparative method and not on the deflection method, they are very accurate.
(2) The potentiometers measures the null point that doesn't require the power for measurement
(3) Since no current flows through pots when they are in a balanced state, their working is free from the source resistance.
The formula for a potentiometer is given by the expression,
$\dfrac{E}{V} = \dfrac{l}{L}$
Where,
$E$ is the cell voltage,
$V$ is the driving source,
$l$ is the balancing length,
$L$ is the length of the wire
The balancing point, also known as the null point, of the potentiometer is the point on the slide wire when the galvanometer shows zero deflection. The balance point is used to find out the unknown voltage of the cell connected to the cell.
Note:
There are two types of potentiometer, namely, Rotary potentiometer and Linear potentiometer. Rotary potentiometer is the potentiometer that has a wiper that rotates across two terminals for varying the resistance of the potentiometer. Linear potentiometers are the potentiometers in which the wiper slides on a straight resistive strip.
Complete step by step solution:

The potentiometer is based on the principle that the potential across a piece of the wire is always directly proportional to length of the given wire, which has a uniform cross-sectional area and a constant current is also flowing through it.
Some important points about the Potentiometer are as follows:
(1) Since a potentiometer works on the comparative method and not on the deflection method, they are very accurate.
(2) The potentiometers measures the null point that doesn't require the power for measurement
(3) Since no current flows through pots when they are in a balanced state, their working is free from the source resistance.
The formula for a potentiometer is given by the expression,
$\dfrac{E}{V} = \dfrac{l}{L}$
Where,
$E$ is the cell voltage,
$V$ is the driving source,
$l$ is the balancing length,
$L$ is the length of the wire
The balancing point, also known as the null point, of the potentiometer is the point on the slide wire when the galvanometer shows zero deflection. The balance point is used to find out the unknown voltage of the cell connected to the cell.
Note:
There are two types of potentiometer, namely, Rotary potentiometer and Linear potentiometer. Rotary potentiometer is the potentiometer that has a wiper that rotates across two terminals for varying the resistance of the potentiometer. Linear potentiometers are the potentiometers in which the wiper slides on a straight resistive strip.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




