
Magnetic dipole moment is a vector quantity directed from:
A. South to north pole
B. North to south pole
C. East to west direction
D. West to east direction
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Consider a bar magnet. Imagine putting it in an external magnetic field. It will point in the direction of the magnetic field.
Complete answer:
Any object or any material that exhibits the properties of magnetism can be called a magnet.
A magnetic dipole can be defined as the magnetic north pole and the magnetic south pole separated by a small distance.
Magnetic moments can be defined as the quantity that can give the strength or orientation of a magnet. This magnetic dipole moment can also be described as the component of magnetic moment. The dipole magnetic moment of a bar magnet can also be described as the product of pole strength and the magnetic length.
Unit of magnetic moment is Ampere-meter squared $\left( A{{m}^{2}} \right)$. Its dimension is $\left[ {{L}^{2}}A \right]$.
If dipole moment is a vector quantity for a bar magnet the direction of the dipole moment is from south pole to north pole.
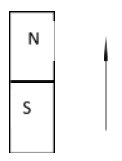 $\mu $(direction of magnetic dipole moment)
$\mu $(direction of magnetic dipole moment)
Hence the correct solution is option (A)
Additional Information: If we place a magnet or magnetic material in an external magnetic field it will experience a torque. The magnetic dipole moment of the object can be described in terms of the torque experienced by the object in the external magnetic field.
$\tau =\mu \times B$
The magnitude will be $\tau =\mu B\sin \theta $
Where $\tau $is the torque experienced by the magnet, $\mu $ is the magnetic dipole moment and B is the external magnetic field.
If we consider a current carrying coil it will also behave like a magnet. Magnetic dipole moment of the current carrying coil is,
$\mu =NiA$
Where N is the number of turns of the coil, i is the current and A is the area of the coil.
Here direction of the magnetic moment is determined by right hand thumb rule.
Note: Considering the bar magnet as a current loop the direction of the dipole moment will be from south pole to north pole of the magnet. Hence, the other options are invalid.
Magnetic dipole moments have dimensions of current times area or energy divided by magnetic flux density. The unit for dipole moment in metre–kilogram– second–ampere is ampere-square metre
Complete answer:
Any object or any material that exhibits the properties of magnetism can be called a magnet.
A magnetic dipole can be defined as the magnetic north pole and the magnetic south pole separated by a small distance.
Magnetic moments can be defined as the quantity that can give the strength or orientation of a magnet. This magnetic dipole moment can also be described as the component of magnetic moment. The dipole magnetic moment of a bar magnet can also be described as the product of pole strength and the magnetic length.
Unit of magnetic moment is Ampere-meter squared $\left( A{{m}^{2}} \right)$. Its dimension is $\left[ {{L}^{2}}A \right]$.
If dipole moment is a vector quantity for a bar magnet the direction of the dipole moment is from south pole to north pole.

Hence the correct solution is option (A)
Additional Information: If we place a magnet or magnetic material in an external magnetic field it will experience a torque. The magnetic dipole moment of the object can be described in terms of the torque experienced by the object in the external magnetic field.
$\tau =\mu \times B$
The magnitude will be $\tau =\mu B\sin \theta $
Where $\tau $is the torque experienced by the magnet, $\mu $ is the magnetic dipole moment and B is the external magnetic field.
If we consider a current carrying coil it will also behave like a magnet. Magnetic dipole moment of the current carrying coil is,
$\mu =NiA$
Where N is the number of turns of the coil, i is the current and A is the area of the coil.
Here direction of the magnetic moment is determined by right hand thumb rule.
Note: Considering the bar magnet as a current loop the direction of the dipole moment will be from south pole to north pole of the magnet. Hence, the other options are invalid.
Magnetic dipole moments have dimensions of current times area or energy divided by magnetic flux density. The unit for dipole moment in metre–kilogram– second–ampere is ampere-square metre
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




