
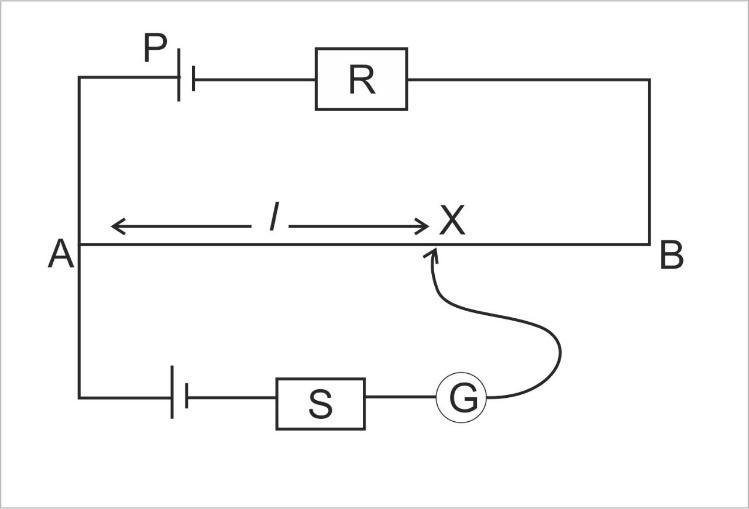
In the potentiometer circuit shown, the null point is at $X$. State with the reason, where the balance point will be shifted when:
i) Resistance $R$ is increased, keeping all other parameters unchanged.
ii) Resistance $S$ is increased, keeping $R$ constant.

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of the null point is used to provide the answer of part (i) and (ii). Apply the condition changed and discuss where the balance point or null point will shift and discuss about the relations between $R$ and $S$ with the resistance of the wire.
Complete step by step answer:
This is a circuit diagram of a potentiometer where resistance is connected as $R$, $S$.The length of the wire is $AB$. The null point is at $X$.
Now we know the resistance $R$ is directly proportional to the resistance of the wire $AB$ and the resistance $S$is inversely proportional to the resistance of the wire.
Hence, $R \propto {R_{AB}}$ and $S \propto \dfrac{1}{{{R_{AB}}}}$
i) In this case resistance $R$is increased and all the other parameters are unchanged. So as the resistance $R$ increases the resistance of the wire $AB$ increases. Hence the current flow in the wire will decrease and the potential drop per unit length of the wire will also decrease, so a greater length of wire is required to find the null point. Thus, the null point will shift towards the point $B$.
ii) In this case resistance $S$ is increased keeping $R$ constant. So the resistance $S$ is inversely proportional to ${R_{AB}}$. Hence, when the resistance $S$ is increased the resistance of the wire $AB$ will decrease so as a result the terminal potential difference of the cell will decrease. Hence the balance point will be at a shorter distance and it will shift towards the point $A$.
Note: As we know that the null point measurement is more accurate than then other measurement techniques because the internal resistance of the battery and the resistance of the potentiometer do not affect the null point during measurement.
Complete step by step answer:
This is a circuit diagram of a potentiometer where resistance is connected as $R$, $S$.The length of the wire is $AB$. The null point is at $X$.
Now we know the resistance $R$ is directly proportional to the resistance of the wire $AB$ and the resistance $S$is inversely proportional to the resistance of the wire.
Hence, $R \propto {R_{AB}}$ and $S \propto \dfrac{1}{{{R_{AB}}}}$
i) In this case resistance $R$is increased and all the other parameters are unchanged. So as the resistance $R$ increases the resistance of the wire $AB$ increases. Hence the current flow in the wire will decrease and the potential drop per unit length of the wire will also decrease, so a greater length of wire is required to find the null point. Thus, the null point will shift towards the point $B$.
ii) In this case resistance $S$ is increased keeping $R$ constant. So the resistance $S$ is inversely proportional to ${R_{AB}}$. Hence, when the resistance $S$ is increased the resistance of the wire $AB$ will decrease so as a result the terminal potential difference of the cell will decrease. Hence the balance point will be at a shorter distance and it will shift towards the point $A$.
Note: As we know that the null point measurement is more accurate than then other measurement techniques because the internal resistance of the battery and the resistance of the potentiometer do not affect the null point during measurement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




