
In a bridge rectifier, the number of diodes required is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: You could firstly recall what actually a rectifier is. Then you could find out what makes the bridge rectifiers different from the other rectifiers. You could now recall the construction and working of the bridge rectifiers and hence you could get the number of diodes required to make a bridge rectifier.
Complete step-by-step solution
Various electric circuits are known to require a rectified DC power supply to power various electronic basic components from the available AC mains supply. That is when the rectifiers come into the picture. They convert the AC power into DC power. The bridge rectifier is known to be the most efficient rectifier circuit among the rectifiers.
Bridge rectifiers are the type of full-wave rectifier that uses four or more diodes in a bridge circuit configuration. Thereby, it can very efficiently convert AC current to DC current.
Therefore, the number of diodes found in a bridge rectifier is 4. Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Let us do a brief discussion on the construction and working of bridge rectifiers.
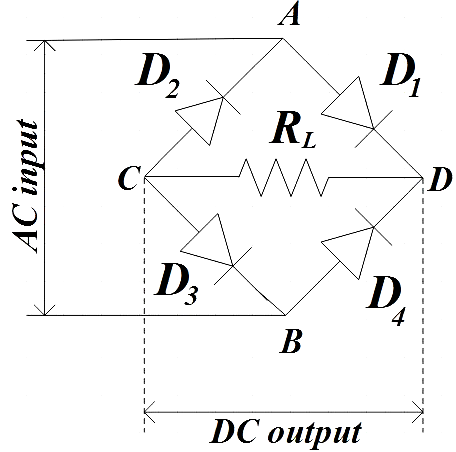
We see that the bridge rectifier consists of 4 diodes in a closed-loop configuration and a load resistance. The major advantage here is that we shouldn’t use the expensive center-tapped transformer.
During the positive half cycle of the AC signal, terminal A is positive and B is negative that causes the diodes ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{3}}$ to be forward biased, ${{D}_{2}}$ and ${{D}_{4}}$ to be reverse biased. For the negative half cycle, the polarity of the terminals is reversed causing ${{D}_{2}}$ and ${{D}_{4}}$ to be forward biased, ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{3}}$ to be reverse biased.
However, the current flow across the load resistor is the same during both the half cycles with signal polarity either completely positive or completely negative.
So for a bridge rectifier, both positive and negative half-cycles allow the current flow through the load resistance.
Note: Though the efficiency of the bridge rectifier is greater than that of a half-wave rectifier, it is the same as that of a center-tapped full-wave rectifier. As it is not required to use an expensive center-tapped transformer, the size and cost of the bridge rectifier are very small. However, the more the number of diodes used, the more will be the power loss that occurs.
Complete step-by-step solution
Various electric circuits are known to require a rectified DC power supply to power various electronic basic components from the available AC mains supply. That is when the rectifiers come into the picture. They convert the AC power into DC power. The bridge rectifier is known to be the most efficient rectifier circuit among the rectifiers.
Bridge rectifiers are the type of full-wave rectifier that uses four or more diodes in a bridge circuit configuration. Thereby, it can very efficiently convert AC current to DC current.
Therefore, the number of diodes found in a bridge rectifier is 4. Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Let us do a brief discussion on the construction and working of bridge rectifiers.

We see that the bridge rectifier consists of 4 diodes in a closed-loop configuration and a load resistance. The major advantage here is that we shouldn’t use the expensive center-tapped transformer.
During the positive half cycle of the AC signal, terminal A is positive and B is negative that causes the diodes ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{3}}$ to be forward biased, ${{D}_{2}}$ and ${{D}_{4}}$ to be reverse biased. For the negative half cycle, the polarity of the terminals is reversed causing ${{D}_{2}}$ and ${{D}_{4}}$ to be forward biased, ${{D}_{1}}$ and ${{D}_{3}}$ to be reverse biased.
However, the current flow across the load resistor is the same during both the half cycles with signal polarity either completely positive or completely negative.
So for a bridge rectifier, both positive and negative half-cycles allow the current flow through the load resistance.
Note: Though the efficiency of the bridge rectifier is greater than that of a half-wave rectifier, it is the same as that of a center-tapped full-wave rectifier. As it is not required to use an expensive center-tapped transformer, the size and cost of the bridge rectifier are very small. However, the more the number of diodes used, the more will be the power loss that occurs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




