
How is fringe width of an interference in Young’s double slit experiment affected if the two slits are brought closer to each other?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: Here, it is asked that what happens to the fringe width of interference in Young’s double slit experiment when the slits are brought closer. For this we have to study the Young’s double slit experiment thoroughly and understand the properties of interference and its patterns.
Complete answer:
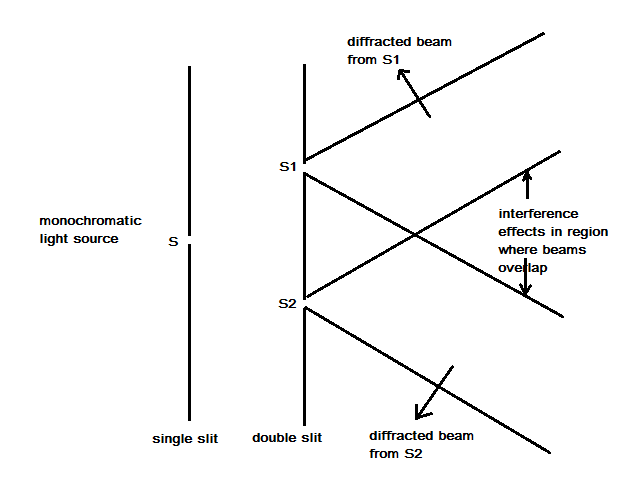
Monochromatic light (single wavelength) from narrow vertical slit S falls on two narrow slits S1 and S2 which are very close together and parallel to S. S1 and S2 act as two coherent sources (both being derived from S). If S, S1 and S2 all are very narrow, diffraction (bending of light at openings whose width is of the order of wavelength of light) causes the emerging beams to spread into the region beyond the slits. Superposition occurs in the shaded area, where the diffracted beams overlap. Alternate bright and dark equally spaced vertical bands (interference fringes) can be observed on a screen placed at some distance from the slits. If either of S1 or S2 is covered, the fringes disappear. Consider figure given below:
Interference: The phenomenon in which two waves superpose to form the resultant wave of the lower, higher or same amplitude. The most commonly known interference is the optical interference or light interference.
Complete answer:
Monochromatic light (single wavelength) from narrow vertical slit S falls on two narrow slits S1 and S2 which are very close together and parallel to S. S1 and S2 act as two coherent sources (both being derived from S). If S, S1 and S2 all are very narrow, diffraction (bending of light at openings whose width is of the order of wavelength of light) causes the emerging beams to spread into the region beyond the slits. Superposition occurs in the shaded area, where the diffracted beams overlap. Alternate bright and dark equally spaced vertical bands (interference fringes) can be observed on a screen placed at some distance from the slits. If either of S1 or S2 is covered, the fringes disappear. Consider figure given below:

Interference: The phenomenon in which two waves superpose to form the resultant wave of the lower, higher or same amplitude. The most commonly known interference is the optical interference or light interference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




