
Draw the symbol of Rheostat, Voltmeter and Electric bulb.
Answer
495k+ views
Hint:In a schematic design of an electrical or electronic circuit, an electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent different electrical and electronic equipment or functions, such as cables, batteries, resistors, and transistors. These symbols are now generally standardised globally, however historic traditions may differ from country to country or engineering discipline to engineering field.
Complete step by step solution:
Rheostat: A rheostat is an electrical device that is used in a variety of applications where current or resistance in an electric circuit must be adjusted. Sir Charles, an English scientist, named this gadget "Rheostat" by combining the Greek terms "rheos" and "status" (which means "current controlling device"). Rheostats have two terminals, one for the wiper and the other for one end of the resistance track. The rheostat is a variable resistor that can alter its resistance to change the amount of current flowing through a circuit.
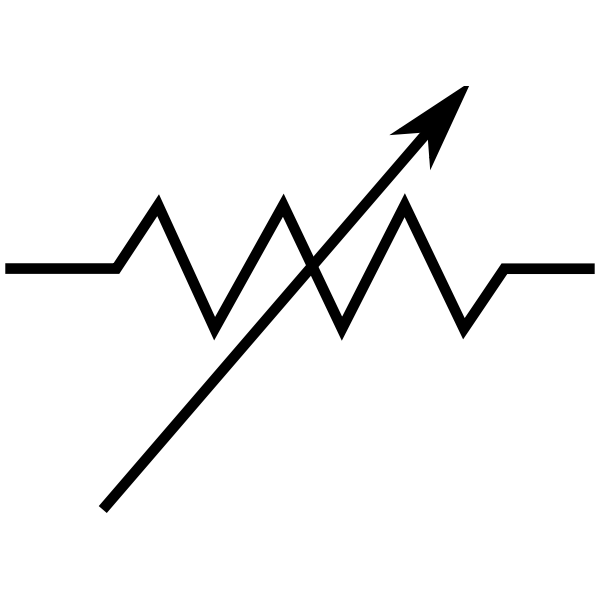
Voltmeter: A voltmeter is a device that measures the difference in electric potential between two locations in an electric circuit. It is linked in a parallel manner. It has a high resistance and so draws very little current from the circuit. Analog voltmeters use a galvanometer and a series resistor to move a pointer around a scale in proportion to the voltage detected. Amplifier-based metres can detect voltages as low as a few microvolts. An analog-to-digital converter is used in digital voltmeters to show voltage numerically.
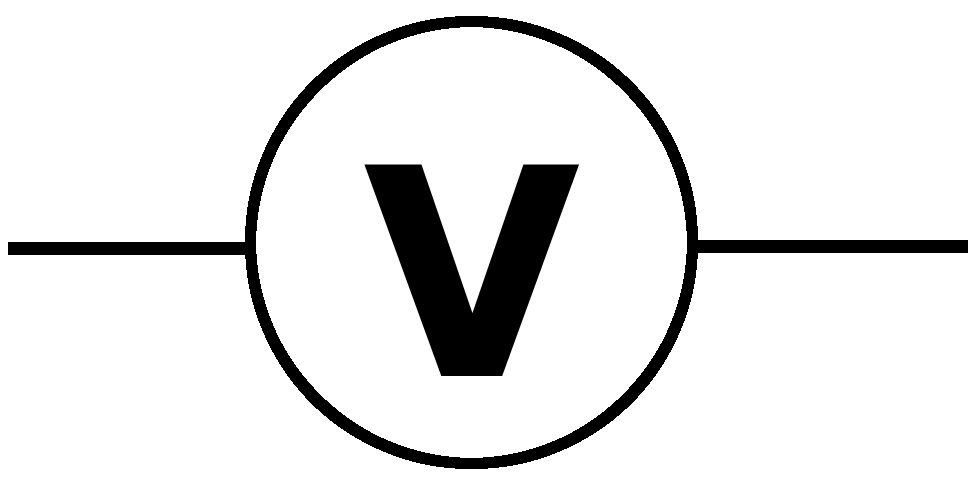
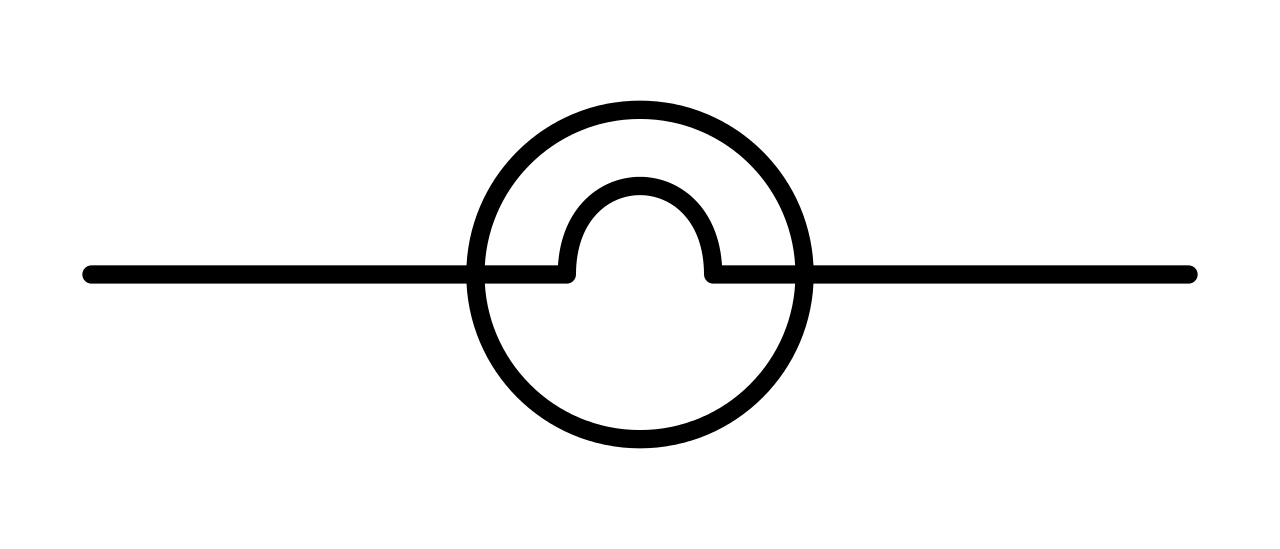
Electric bulb: An incandescent light bulb, lamp, or globe is an electric light that has a wire filament that has been heated till it glows. To protect the filament from oxidation, it is contained in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas. Terminals or wires placed in the glass provide current to the filament. A bulb socket provides both mechanical and electrical support. Incandescent bulbs come in a variety of diameters, light outputs, and voltage ratings, ranging from 1.5 to 300 volts.
Note:
Individual electronic components such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes are connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow to form an electronic circuit. At least one active component is required to be referred to as electronic rather than electrical. Signals can be amplified, computations can be done, and data can be transferred from one location to another thanks to the combination of components and cables.
Complete step by step solution:
Rheostat: A rheostat is an electrical device that is used in a variety of applications where current or resistance in an electric circuit must be adjusted. Sir Charles, an English scientist, named this gadget "Rheostat" by combining the Greek terms "rheos" and "status" (which means "current controlling device"). Rheostats have two terminals, one for the wiper and the other for one end of the resistance track. The rheostat is a variable resistor that can alter its resistance to change the amount of current flowing through a circuit.

Voltmeter: A voltmeter is a device that measures the difference in electric potential between two locations in an electric circuit. It is linked in a parallel manner. It has a high resistance and so draws very little current from the circuit. Analog voltmeters use a galvanometer and a series resistor to move a pointer around a scale in proportion to the voltage detected. Amplifier-based metres can detect voltages as low as a few microvolts. An analog-to-digital converter is used in digital voltmeters to show voltage numerically.

Electric bulb: An incandescent light bulb, lamp, or globe is an electric light that has a wire filament that has been heated till it glows. To protect the filament from oxidation, it is contained in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas. Terminals or wires placed in the glass provide current to the filament. A bulb socket provides both mechanical and electrical support. Incandescent bulbs come in a variety of diameters, light outputs, and voltage ratings, ranging from 1.5 to 300 volts.

Note:
Individual electronic components such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes are connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow to form an electronic circuit. At least one active component is required to be referred to as electronic rather than electrical. Signals can be amplified, computations can be done, and data can be transferred from one location to another thanks to the combination of components and cables.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




