
Define uniform circular motion.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint:Uniform circular motion means that the particle or an object or a body which moves or travels in the circular path, with the uniform acceleration. Uniform acceleration is the acceleration of the object or body or a particle is constant. There is no increase or decrease of the acceleration.
Complete step by step solution:
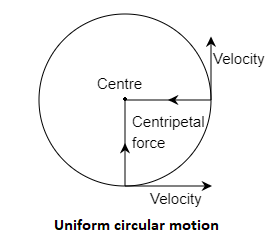
The movement of the body or object or a particle, that is following a circular path is called a circular motion. Now, the motion of a body or object or a particle moving with constant speed along a circular path is called Uniform Circular Motion. Here, the speed is constant but the velocity changes. If the particle is moving in the circular path, then it has some acceleration due to centripetal force acting towards the centre which is making it move in the circular path. Hence, the acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity of the particle at every instant, so the velocity of the direction keeps changing but not the magnitude. So, the motion is called uniform acceleration motion.
Some examples of the uniform circular motion are, motion of the electron around the nucleus of the molecule. The motion of the blades of the windmill, the motion of the blades of the fan until the speed is changed manually, the motion of the satellite around the earth and the motion of the satellite around the moon. These are the real time examples of the uniform circular motion.
Note: The tangential speed at every point on the circumference is found to be constant in a uniform circular motion, and the tangential velocity vector is tangent at every point over the circumference. Tangential velocity is the vector formed to the tangential speed; therefore, the magnitude remains constant and equal to the tangential speed of the uniform circular motion.
Complete step by step solution:
The movement of the body or object or a particle, that is following a circular path is called a circular motion. Now, the motion of a body or object or a particle moving with constant speed along a circular path is called Uniform Circular Motion. Here, the speed is constant but the velocity changes. If the particle is moving in the circular path, then it has some acceleration due to centripetal force acting towards the centre which is making it move in the circular path. Hence, the acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity of the particle at every instant, so the velocity of the direction keeps changing but not the magnitude. So, the motion is called uniform acceleration motion.

Some examples of the uniform circular motion are, motion of the electron around the nucleus of the molecule. The motion of the blades of the windmill, the motion of the blades of the fan until the speed is changed manually, the motion of the satellite around the earth and the motion of the satellite around the moon. These are the real time examples of the uniform circular motion.
Note: The tangential speed at every point on the circumference is found to be constant in a uniform circular motion, and the tangential velocity vector is tangent at every point over the circumference. Tangential velocity is the vector formed to the tangential speed; therefore, the magnitude remains constant and equal to the tangential speed of the uniform circular motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




