
Define displacement current.
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: Ampere's law in its original form is applicable only for electric fields that do not vary with time. When the charge within an enclosed surface is changing it becomes necessary to add another current in the ampere law called the displacement current.
Formula used:
${I_d} = {\varepsilon _o}\dfrac{{dE}}{{dt}}$ ${I_d}$ represents the displacement current,${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space $E$ is the electric field intensity.
Complete step by step answer:
Displacement current is defined in terms of the rate of change of electric displacement field D. It is an electric current due to time varying electric field. Its unit is the same as that of current density.
Displacement current is used in the Maxwell equation. The electric displacement field is defined as $D = {\varepsilon _0}E + P$ here ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space $E$ is the electric field intensity $P$ is the polarization of the medium. Differentiating this with respect to time we get the displacement current density.
${J_D} = {\varepsilon _0}\dfrac{{dE}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{dP}}{{dt}}$. The first term is referred to as displacement current. The second term is known as the polarization current density which comes due to the change in polarization of the individual molecules of the dielectric material. Under the influence of the electric field when the charges move from their initial position polarization occurs as now exact cancellation is not happening.
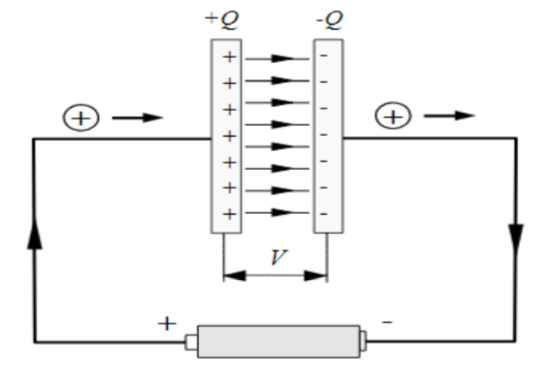
Note: When a capacitor with no medium is charged equal and opposite charges appear on both the plates of the capacitor. Even though no actual charge is flowing in between the capacitors, there exists a magnetic field. One of the explanations is that the displacement current flows in vacuum and so produces magnetic filled in between the plates.
Formula used:
${I_d} = {\varepsilon _o}\dfrac{{dE}}{{dt}}$ ${I_d}$ represents the displacement current,${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space $E$ is the electric field intensity.
Complete step by step answer:
Displacement current is defined in terms of the rate of change of electric displacement field D. It is an electric current due to time varying electric field. Its unit is the same as that of current density.
Displacement current is used in the Maxwell equation. The electric displacement field is defined as $D = {\varepsilon _0}E + P$ here ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space $E$ is the electric field intensity $P$ is the polarization of the medium. Differentiating this with respect to time we get the displacement current density.
${J_D} = {\varepsilon _0}\dfrac{{dE}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{dP}}{{dt}}$. The first term is referred to as displacement current. The second term is known as the polarization current density which comes due to the change in polarization of the individual molecules of the dielectric material. Under the influence of the electric field when the charges move from their initial position polarization occurs as now exact cancellation is not happening.

Note: When a capacitor with no medium is charged equal and opposite charges appear on both the plates of the capacitor. Even though no actual charge is flowing in between the capacitors, there exists a magnetic field. One of the explanations is that the displacement current flows in vacuum and so produces magnetic filled in between the plates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




