
Calculate the critical angle for glass air interface if a ray of light incident on a glass surface is deviated through 15˚ when angle incident is 45˚.


Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: (i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of given color and for the given pair of media. This constant is also called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first.
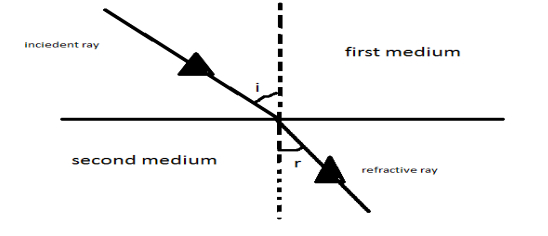
Formula used: When the ray of light enters the second medium through the fist medium.
\[\mu = \dfrac{{sin\left( i \right)}}{{sin\left( r \right)}}\]
Where, µ is the refractive index of glass.
‘$i$’ is the angle of incidence and ‘$r$’ is the angle of refraction.
Step by step solution:-
(a).
Given that,
Incident angle, deviated rays .
Let critical angle be \[{i_c}\].
Now,
\[sin{\text{ }}{i_c} = \mu \]
Where, \[\mu \] is the refractive index of glass.
Now, again \[i = r \& \] \[\dfrac{{sin{\text{ }}r}}{{sin{\text{ }}i}} = \mu \]
\[\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \mu = \sqrt 2 \]
\[\Rightarrow \mu = 1.4\]
Now, the critical angle is
\[sin{i_c} = \dfrac{1}{\mu }\]
\[\Rightarrow sin{i_c} = \dfrac{1}{{1.4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow sin{i_c} = 0.71\]
\[\Rightarrow {i_c} = si{n^{ - 1}}\left( {0.71} \right)\]
Hence, the critical angle is ${45^ \circ }$.
Note :- Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of given color and for the given pair of media. This constant is also called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first.

Formula used: When the ray of light enters the second medium through the fist medium.
\[\mu = \dfrac{{sin\left( i \right)}}{{sin\left( r \right)}}\]
Where, µ is the refractive index of glass.
‘$i$’ is the angle of incidence and ‘$r$’ is the angle of refraction.
Step by step solution:-
(a).
Given that,
Incident angle, deviated rays .
Let critical angle be \[{i_c}\].
Now,
\[sin{\text{ }}{i_c} = \mu \]
Where, \[\mu \] is the refractive index of glass.
Now, again \[i = r \& \] \[\dfrac{{sin{\text{ }}r}}{{sin{\text{ }}i}} = \mu \]
\[\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \mu = \sqrt 2 \]
\[\Rightarrow \mu = 1.4\]
Now, the critical angle is
\[sin{i_c} = \dfrac{1}{\mu }\]
\[\Rightarrow sin{i_c} = \dfrac{1}{{1.4}}\]
\[\Rightarrow sin{i_c} = 0.71\]
\[\Rightarrow {i_c} = si{n^{ - 1}}\left( {0.71} \right)\]
Hence, the critical angle is ${45^ \circ }$.
Note :- Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




