
An n-p-n transistor is connected in common emitter configuration in which collector supply is \[8V\] and the voltage drop across the load resistance of $800\Omega $ connected in the collector circuit is \[0.8V\]. If current amplification factor is, $25$, determine collector-emitter voltage and base current. If the internal resistance of the resistor is $200\Omega $. Calculate the voltage gain and power gain.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: The transistor in which one p-type material is placed between two n-type materials is known as NPN transistor. The NPN transistor amplifies the weak signal entered into the base and produces strong amplified signals at the collector end. In NPN transistors, the direction of movement of an electron is from the emitter to collector region due to which the current constitutes in the transistor.
Step by step answer:NPN Transistors are three-terminal, three-layer devices that can function as either amplifiers or electronic switches.
Such type of transistor is mostly used in the circuit because their majority charge carriers are electrons which have high mobility as compared to holes.
An n-p-n transistor amplifier circuit with common emitter mode is:
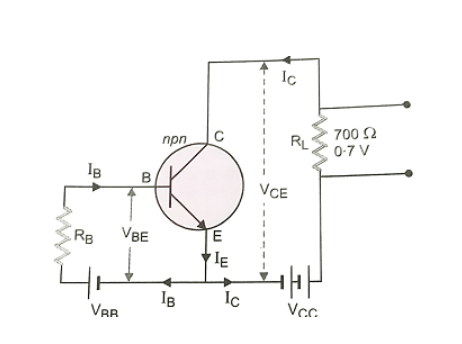
Here,
\[
{V_{CC}} = 9V,\\
{R_L} = 700\Omega
\]
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential along the path of a current flowing in an electrical circuit. Voltage drop across \[{R_L} = {V_0} = 0.7V\]
Collector-emitter voltage,
\[{V_{CE}} = {V_{CC}} - {V_O} = 9 - 0.7 = 8.3V\]
Collector current ${I_C}$= $\dfrac{{voltage{\rm{ }}\;drop{\rm{ }}\;across{R_L}}}\;{{{R_L}}}$
Collector current ${I_C}$= $\dfrac{{0.7}}{{700}} = {10^{ - 3}}ampere$
Current gain $\alpha = \dfrac{{{I_c}}}{{{I_E}}}$
$\Rightarrow {I_E} = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{\alpha }$
$\Rightarrow {I_E} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{\dfrac{{25}}{{26}}}} = \dfrac{{26 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{25}}$
$\Rightarrow{I_E} = \dfrac{{26}}{{25}} \times {10^{ - 3}}$
Base current, ${I_C} = {I_E} - {I_B}$
$\Rightarrow{I_C} = \dfrac{{26}}{{25}} \times {10^{ - 3}} - {10^{ - 3}}$
$\Rightarrow{I_C} = \dfrac{1}{{25}} \times {10^{ - 3}}$
$\therefore{I_C} = 0.04mA$
\[\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_B}}} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 3}}A}}{{\left( {1/25} \right) \times {{10}^{ - 3}}A}} = 25\]
Here, the resistance of input circuit \[{R_i} = 100\Omega \]
Input voltage= \[Vi = Ri \times IB = 100 \times (0.04 \times {10^{ - 3}})\]
\[Vi = 4 \times {10^{ - 3}}V\]
Voltage gain,
\[{A_V} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}} = \dfrac{{0.7}}{{4 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}} = 175\]
Gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal.
The power gain of an electrical network is the ratio of an output power to an input power.
Hence, Power gain AP=current gain x voltage gain \[\beta \times Av = 25 \times 175 = 4375\]
Note: The NPN transistor has two diodes connected back to back. The diode on the left side is called an emitter-base diode, and the diodes on the left side are called collector-base diodes.
Step by step answer:NPN Transistors are three-terminal, three-layer devices that can function as either amplifiers or electronic switches.
Such type of transistor is mostly used in the circuit because their majority charge carriers are electrons which have high mobility as compared to holes.
An n-p-n transistor amplifier circuit with common emitter mode is:

Here,
\[
{V_{CC}} = 9V,\\
{R_L} = 700\Omega
\]
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential along the path of a current flowing in an electrical circuit. Voltage drop across \[{R_L} = {V_0} = 0.7V\]
Collector-emitter voltage,
\[{V_{CE}} = {V_{CC}} - {V_O} = 9 - 0.7 = 8.3V\]
Collector current ${I_C}$= $\dfrac{{voltage{\rm{ }}\;drop{\rm{ }}\;across{R_L}}}\;{{{R_L}}}$
Collector current ${I_C}$= $\dfrac{{0.7}}{{700}} = {10^{ - 3}}ampere$
Current gain $\alpha = \dfrac{{{I_c}}}{{{I_E}}}$
$\Rightarrow {I_E} = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{\alpha }$
$\Rightarrow {I_E} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{\dfrac{{25}}{{26}}}} = \dfrac{{26 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{25}}$
$\Rightarrow{I_E} = \dfrac{{26}}{{25}} \times {10^{ - 3}}$
Base current, ${I_C} = {I_E} - {I_B}$
$\Rightarrow{I_C} = \dfrac{{26}}{{25}} \times {10^{ - 3}} - {10^{ - 3}}$
$\Rightarrow{I_C} = \dfrac{1}{{25}} \times {10^{ - 3}}$
$\therefore{I_C} = 0.04mA$
\[\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_B}}} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 3}}A}}{{\left( {1/25} \right) \times {{10}^{ - 3}}A}} = 25\]
Here, the resistance of input circuit \[{R_i} = 100\Omega \]
Input voltage= \[Vi = Ri \times IB = 100 \times (0.04 \times {10^{ - 3}})\]
\[Vi = 4 \times {10^{ - 3}}V\]
Voltage gain,
\[{A_V} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{{V_i}}} = \dfrac{{0.7}}{{4 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}} = 175\]
Gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal.
The power gain of an electrical network is the ratio of an output power to an input power.
Hence, Power gain AP=current gain x voltage gain \[\beta \times Av = 25 \times 175 = 4375\]
Note: The NPN transistor has two diodes connected back to back. The diode on the left side is called an emitter-base diode, and the diodes on the left side are called collector-base diodes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




