
A Zener diode works on the principle of –
A) Tunnelling of charge carriers across the junction.
B) Doping of charge carriers across the junction.
C) Diffusion of charge carriers across the junction.
D) None of the above.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: We need to completely understand the working mechanism of a Zener diode to solve this problem. The components involved in making a Zener diode, its similarities and differences between normal diodes will also help in solving.
Complete answer:
The p-n junction diodes are semiconductor electronic devices with two terminals. We know that a p-n junction diode can be biased in two different ways depending on our requirement.
The forward biasing involves the application of external voltage in such a way that the potential barrier within the junction is reduced. This enables flow of current through the junction giving characteristic of current increasing with the voltage.
The reverse biasing in the other way will not allow the current flow by diffusion in the junction as the potential barrier increases with the external voltage. The current initially shows to be almost zero.
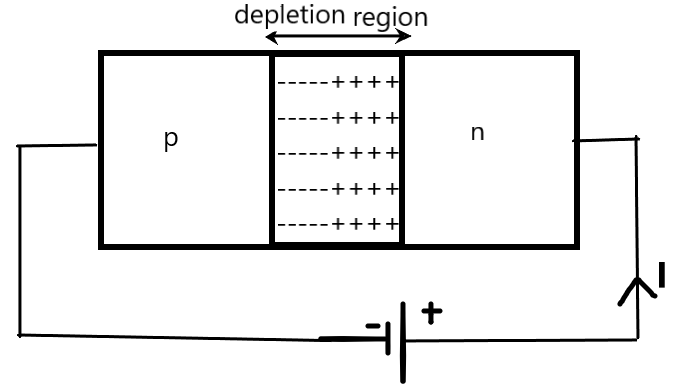
A Zener diode is used as a reverse biasing device, which at the breakdown voltage allows the current flow by the process of tunnelling. The current becomes so high suddenly after the Zener voltage. The tunnelling of the charge carriers across the junction is allowed only by the Zener diodes which are specially designed to tolerate high negative potentials without the diode getting damaged.
This is the required solution.
The correct answer is option A.
Note:
Tunnelling is the process in which the charge carriers in the strong electrical fields move from across the potential barrier even when they possess a comparatively lower potential. It is a quantum mechanical process which is observed everywhere.
Complete answer:
The p-n junction diodes are semiconductor electronic devices with two terminals. We know that a p-n junction diode can be biased in two different ways depending on our requirement.
The forward biasing involves the application of external voltage in such a way that the potential barrier within the junction is reduced. This enables flow of current through the junction giving characteristic of current increasing with the voltage.
The reverse biasing in the other way will not allow the current flow by diffusion in the junction as the potential barrier increases with the external voltage. The current initially shows to be almost zero.

A Zener diode is used as a reverse biasing device, which at the breakdown voltage allows the current flow by the process of tunnelling. The current becomes so high suddenly after the Zener voltage. The tunnelling of the charge carriers across the junction is allowed only by the Zener diodes which are specially designed to tolerate high negative potentials without the diode getting damaged.
This is the required solution.
The correct answer is option A.
Note:
Tunnelling is the process in which the charge carriers in the strong electrical fields move from across the potential barrier even when they possess a comparatively lower potential. It is a quantum mechanical process which is observed everywhere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




