
What is a zener diode? How is it used as a voltage regulator?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: A zener diode is a diode that works in reverse bias. A very small current flows through it until the breakdown voltage. It is used as a voltage regulator in DC circuits wherein the load is connected in parallel to the zener and the current through the zener is restricted.
Complete answer:
A diode is a semiconductor device which lets current flow through it in one direction but restricts it from flowing in the opposite direction. A zener diode works on a breakdown voltage. It is reverse biased, this means that its p-junction is connected to the negative terminal and its n-junction is connected to its positive terminal.
A very small current flows in the zener diode up until a voltage called breakdown voltage is reached after which a large amount of current flows through the diode.
Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator in DC circuits. A voltage regulator is a device which maintains a constant voltage or decreases and keeps the output voltage constant even when the input voltage varies continuously.
The working diagram of zener diode is
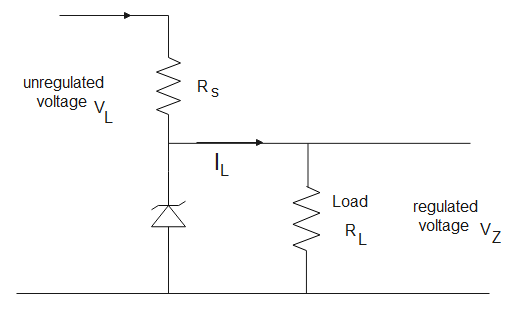
A resistance is connected in series with zener to limit the current that goes into the diode. As the current decreases, the voltage across the zener also decreases. The load is connected in parallel to the zener so the potential drop on the load also decreases. Hence the voltage drop across the load resistance is very less and hence the output voltage is regulated.
Note: Diodes have two junctions; the p-junction is where holes are in majority, in the n-junction, the electrons are in majority. At the breakdown voltage, the barrier between p and n-junction breaks due to which a large current flows across the junctions. The output is obtained across the load resistor.
Complete answer:
A diode is a semiconductor device which lets current flow through it in one direction but restricts it from flowing in the opposite direction. A zener diode works on a breakdown voltage. It is reverse biased, this means that its p-junction is connected to the negative terminal and its n-junction is connected to its positive terminal.
A very small current flows in the zener diode up until a voltage called breakdown voltage is reached after which a large amount of current flows through the diode.
Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator in DC circuits. A voltage regulator is a device which maintains a constant voltage or decreases and keeps the output voltage constant even when the input voltage varies continuously.
The working diagram of zener diode is

A resistance is connected in series with zener to limit the current that goes into the diode. As the current decreases, the voltage across the zener also decreases. The load is connected in parallel to the zener so the potential drop on the load also decreases. Hence the voltage drop across the load resistance is very less and hence the output voltage is regulated.
Note: Diodes have two junctions; the p-junction is where holes are in majority, in the n-junction, the electrons are in majority. At the breakdown voltage, the barrier between p and n-junction breaks due to which a large current flows across the junctions. The output is obtained across the load resistor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




