
When a p-n-p transistor is operated in a saturation region, then its _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
A. Base-emitter junction is forward biased and base-collector junction is reverse biased.
B. Both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are reverse biased.
C. Both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
D. Base-emitter junction is reversed biased and base-collector junction is forward biased.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: When a transistor is operated in a saturation region, the emitter and the collector terminals are at higher potential. When the anode terminal of a junction diode is at higher potential than that of the cathode, the junction diode is said to be forward biased.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device, which is formed by fusing two junction diodes. When the anodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called an n-p-n transistor. When the cathodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a p-n-p transistor.
A transistor consists of three parts – a collector, an emitter and a base. The middle part is base.
Consider a p-n-p transistor. In a p-n-p transistor, the outer ends (terminal) of the emitter and the collector are anodes (positive terminals). And the terminal of the base is a cathode.
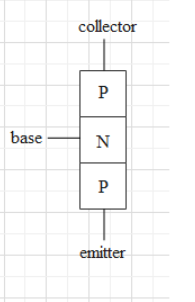
When a transistor is operated in a saturation region, the emitter and the collector terminals are at higher potential. When the anode terminal of a junction diode is at higher potential than that of the cathode, the junction diode is said to be forward biased.
Since in a p-n-p transistor the emitter and collector are the anodes, they are at higher potential. Hence, both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
This means that the correct option is C.
Note:
When the both junctions are forward biased, a high amount current will flow in the transistor. Therefore, the resistance of the circuit is very low.
In case of a n-p-n transition, in the saturation region, both junctions will be reverse biased. Hence, no current will flow and the resistance will be high.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device, which is formed by fusing two junction diodes. When the anodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called an n-p-n transistor. When the cathodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a p-n-p transistor.
A transistor consists of three parts – a collector, an emitter and a base. The middle part is base.
Consider a p-n-p transistor. In a p-n-p transistor, the outer ends (terminal) of the emitter and the collector are anodes (positive terminals). And the terminal of the base is a cathode.

When a transistor is operated in a saturation region, the emitter and the collector terminals are at higher potential. When the anode terminal of a junction diode is at higher potential than that of the cathode, the junction diode is said to be forward biased.
Since in a p-n-p transistor the emitter and collector are the anodes, they are at higher potential. Hence, both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
This means that the correct option is C.
Note:
When the both junctions are forward biased, a high amount current will flow in the transistor. Therefore, the resistance of the circuit is very low.
In case of a n-p-n transition, in the saturation region, both junctions will be reverse biased. Hence, no current will flow and the resistance will be high.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




