
A glass slab made of material of refractive index $ {{\text{n}}_{1}} $ is kept in the medium of refractive index $ {{\text{n}}_{2}} $ . A light ray is incident on slab, complete the path of the rays of light emerging from the glass slab if:-
(A) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
(B) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{= }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
(C) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: Refraction occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium to another. And due to change in medium, change in velocity of light occurs.
Say, light travels from air into the glass, in which it moves slower, due to which wavelength of light must change too. And the light wave changes its direction. Also note that denser medium has higher refractive index as compared to rarer medium.
Complete step by step solution
Given, refractive index of glass slab $ ={{\text{n}}_{1}} $
Refractive index of medium $ ={{\text{n}}_{2}} $
(A) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
i.e. the refractive index of glass slab is greater than that of medium. In this case, light ray will bend towards the normal as it enters the slab, because the speed of light decreases as it enters the denser medium.
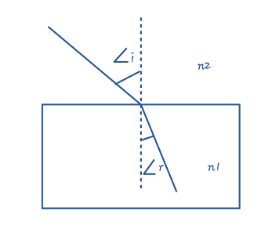
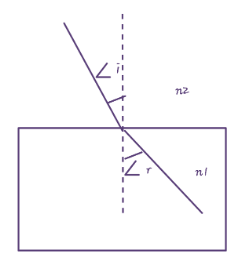
(B) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{= }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
As no change in medium occurs, so no bending or refraction occurs , and light ray travels as it is before entering the slab.
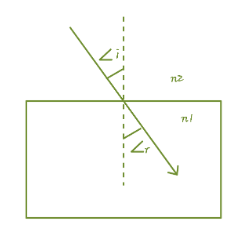
(C) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
Here, light rays will bend away from the normal as this time; it enters into a rarer medium and in this, the speed of light increases.
Note
Refractive index is a value calculated from the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a second medium of greater density. It is mostly applied for identifying a particular substance, confirming its purity, and measuring its concentration. It can be used also in determination of drug concentration in the pharmaceutical industry. Note that,
(1) When $ $ , angle of refraction < angle of incidence.
(2) When $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{= }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $ , angle of refraction = angle of incidence.
(3) When $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $ , angle of refraction > angle of incidence.
Say, light travels from air into the glass, in which it moves slower, due to which wavelength of light must change too. And the light wave changes its direction. Also note that denser medium has higher refractive index as compared to rarer medium.
Complete step by step solution
Given, refractive index of glass slab $ ={{\text{n}}_{1}} $
Refractive index of medium $ ={{\text{n}}_{2}} $
(A) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
i.e. the refractive index of glass slab is greater than that of medium. In this case, light ray will bend towards the normal as it enters the slab, because the speed of light decreases as it enters the denser medium.

(B) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{= }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
As no change in medium occurs, so no bending or refraction occurs , and light ray travels as it is before entering the slab.

(C) $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $
Here, light rays will bend away from the normal as this time; it enters into a rarer medium and in this, the speed of light increases.

Note
Refractive index is a value calculated from the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a second medium of greater density. It is mostly applied for identifying a particular substance, confirming its purity, and measuring its concentration. It can be used also in determination of drug concentration in the pharmaceutical industry. Note that,
(1) When $ $ , angle of refraction < angle of incidence.
(2) When $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{= }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $ , angle of refraction = angle of incidence.
(3) When $ {{\text{n}}_{1}}\text{ }{{\text{n}}_{2}} $ , angle of refraction > angle of incidence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




