
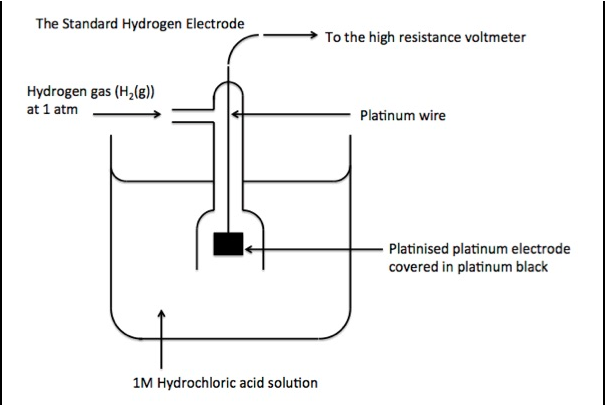
a) Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). Write its half-cell reaction of ${{\text{E}}^{0}}$ value.
b) Calculate $\Delta r{{G}^{0}}$ for the following reaction:
$F{{e}^{+2}}_{\left( aq \right)}+A{{g}^{+}}\to F{{e}^{+3}}_{(aq)}+A{{g}_{\left( s \right)}}$, (Given$E_{\left( cell \right)}^{0}=+0.03V,F=96500C$)
Answer
552.6k+ views
Hint: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode, is a redox electrode which is the basic of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potential. It is basically used as a reference electrode on half-cell potential reactions. The value of the standard electrode potential is zero, which forms the basis to calculate cell potentials using different electrodes or different concentrations.
Complete answer:
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode also known as SHE. The potential of SHE is always 0 at 298K, this is the reason it is used as a reference electrode.
The redox half-cell reaction of the SHE is:
$2{{H}^{+}}_{\left( aq \right)}+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}_{\left( g \right)}$${{E}^{0}}$
Hydrogen Standard electrode potential (${{E}^{0}}$) is declared as zero at any temperature.
Addition Information:
The absolute electrode potential of SHE is measured to be 4.44+-0.02V at room temperature. But for a basic comparison with all other electrode reactions, Hydrogen standard electrode potential (${{E}^{0}}$) is declared to be zero volts at any temperature.
The reasons for choice for platinum for the hydrogen electrode is:
-Inertness of platinum
-The capability of platinum to catalyze the reaction of proton reduction
-Use a surface material that absorbs hydrogen well at its interface. This increases the reaction kinetics
Note:
The value of standard electrode potential is always zero. During the reaction, hydrogen gas is passed through and into the solution and the reaction that takes place is: $2{{H}^{+}}_{\left( aq \right)}+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}_{\left( g \right)}$
b) Calculate $\Delta r{{G}^{0}}$ for the following reaction:
$F{{e}^{+2}}_{\left( aq \right)}+A{{g}^{+}}\to F{{e}^{+3}}_{(aq)}+A{{g}_{\left( s \right)}}$, (Given$E_{(cell)}^{0}=+0.03V,F=96500C$)
Complete answer:
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode also known as SHE. The potential of SHE is always 0 at 298K, this is the reason it is used as a reference electrode.
The redox half-cell reaction of the SHE is:
$2{{H}^{+}}_{\left( aq \right)}+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}_{\left( g \right)}$${{E}^{0}}$
Hydrogen Standard electrode potential (${{E}^{0}}$) is declared as zero at any temperature.

Addition Information:
The absolute electrode potential of SHE is measured to be 4.44+-0.02V at room temperature. But for a basic comparison with all other electrode reactions, Hydrogen standard electrode potential (${{E}^{0}}$) is declared to be zero volts at any temperature.
The reasons for choice for platinum for the hydrogen electrode is:
-Inertness of platinum
-The capability of platinum to catalyze the reaction of proton reduction
-Use a surface material that absorbs hydrogen well at its interface. This increases the reaction kinetics
Note:
The value of standard electrode potential is always zero. During the reaction, hydrogen gas is passed through and into the solution and the reaction that takes place is: $2{{H}^{+}}_{\left( aq \right)}+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}_{\left( g \right)}$
b) Calculate $\Delta r{{G}^{0}}$ for the following reaction:
$F{{e}^{+2}}_{\left( aq \right)}+A{{g}^{+}}\to F{{e}^{+3}}_{(aq)}+A{{g}_{\left( s \right)}}$, (Given$E_{(cell)}^{0}=+0.03V,F=96500C$)
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




